Green bonds are debt securities specifically issued to finance projects that have clear environmental benefits, such as renewable energy or pollution reduction. Climate bonds represent a subset of green bonds focused exclusively on mitigating or adapting to climate change impacts through initiatives like carbon reduction or climate resilience. Discover the distinctions and investment opportunities within these sustainable finance instruments.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between green bonds and climate bonds is crucial for investors aiming to align their portfolios with specific environmental goals, as green bonds finance projects with broader environmental benefits while climate bonds focus exclusively on climate change mitigation and adaptation. This distinction helps in assessing the impact, risk, and regulatory compliance associated with each bond type. Accurate classification enhances transparency and supports informed decision-making in sustainable finance. Understanding these nuances aids in maximizing positive environmental outcomes while meeting fiduciary responsibilities.
Comparison Table
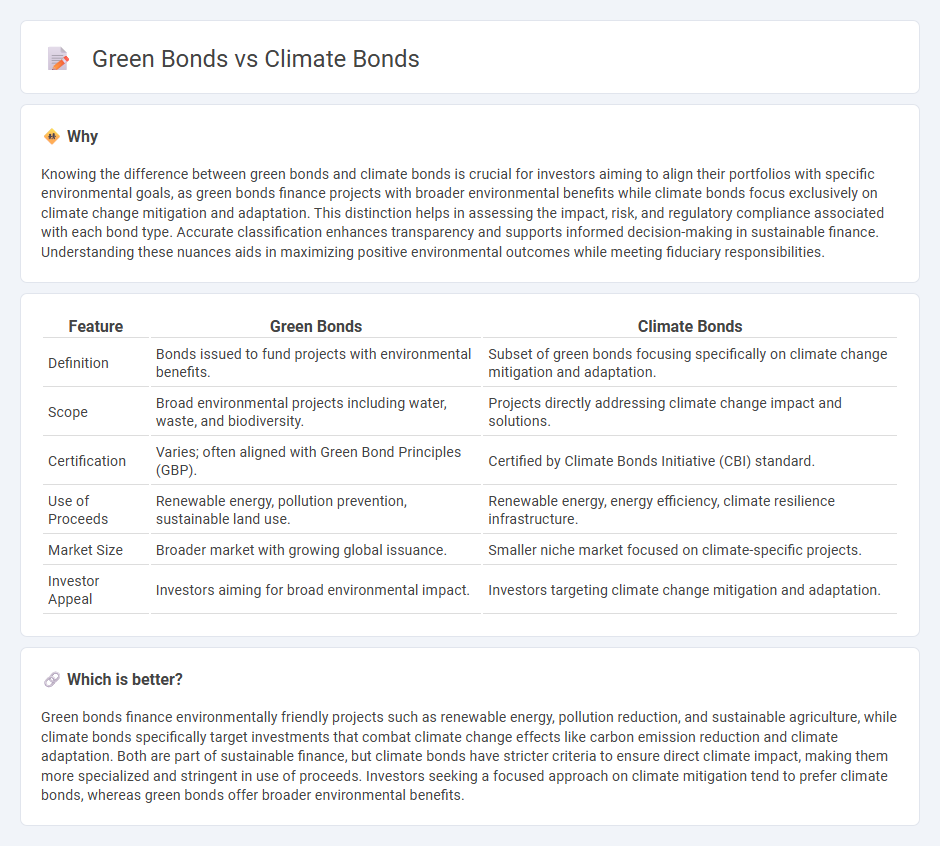
| Feature | Green Bonds | Climate Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bonds issued to fund projects with environmental benefits. | Subset of green bonds focusing specifically on climate change mitigation and adaptation. |
| Scope | Broad environmental projects including water, waste, and biodiversity. | Projects directly addressing climate change impact and solutions. |
| Certification | Varies; often aligned with Green Bond Principles (GBP). | Certified by Climate Bonds Initiative (CBI) standard. |
| Use of Proceeds | Renewable energy, pollution prevention, sustainable land use. | Renewable energy, energy efficiency, climate resilience infrastructure. |
| Market Size | Broader market with growing global issuance. | Smaller niche market focused on climate-specific projects. |
| Investor Appeal | Investors aiming for broad environmental impact. | Investors targeting climate change mitigation and adaptation. |
Which is better?
Green bonds finance environmentally friendly projects such as renewable energy, pollution reduction, and sustainable agriculture, while climate bonds specifically target investments that combat climate change effects like carbon emission reduction and climate adaptation. Both are part of sustainable finance, but climate bonds have stricter criteria to ensure direct climate impact, making them more specialized and stringent in use of proceeds. Investors seeking a focused approach on climate mitigation tend to prefer climate bonds, whereas green bonds offer broader environmental benefits.
Connection
Green bonds and climate bonds both serve as financial instruments designed to fund projects with positive environmental impacts, targeting sustainability and carbon reduction goals. These bonds attract investors focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, facilitating capital flow toward renewable energy, clean transportation, and climate resilience initiatives. Their alignment enhances market confidence in financing solutions that address global climate change challenges effectively.
Key Terms
Use of Proceeds
Climate bonds are specifically tied to projects that directly address climate change mitigation and adaptation, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and climate resilience initiatives. Green bonds have a broader scope, financing projects that deliver environmental benefits, including sustainable agriculture, clean transportation, and biodiversity conservation. Explore the distinct frameworks and criteria that define the use of proceeds in climate bonds versus green bonds to make informed investment decisions.
Certification Standards
Climate bonds and green bonds both adhere to certification standards ensuring environmental impact, with climate bonds specifically certified under the Climate Bonds Standard focusing on projects that address climate change mitigation and adaptation. Green bonds follow broader green bond principles established by the International Capital Market Association (ICMA), encompassing diverse environmental projects beyond just climate issues. Explore detailed certification criteria and benefits to understand which bond best aligns with your sustainability goals.
Project Eligibility
Climate bonds prioritize projects directly addressing climate change mitigation and adaptation, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and low-carbon transportation. Green bonds fund a broader range of environmentally friendly projects, including water management, pollution prevention, and sustainable agriculture. Explore detailed criteria and examples to better understand project eligibility in climate and green bonds.
Source and External Links
Green Bonds - The World Bank - The World Bank Green Bonds raise funds from investors to support projects that mitigate climate change or help people adapt, focusing on developing countries and global cooperation since 2008.
What are Green Bonds and How Can They Fight Climate Crisis - Green bonds finance projects with positive environmental impact, originating in 2007, with the World Bank issuing the first official green bond in 2008 to support climate-focused investments and set market standards.
Climate Bonds | Homepage - Climate Bonds is an international organization that mobilizes global capital for climate action, setting science-based standards for green bonds whose market reached USD670.9 billion issuance in 2024 and over USD6 trillion in aligned sustainable debt outstanding.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com