Basis trading exploits price differences between a futures contract and its underlying asset to generate risk-free profits, focusing on the convergence of these prices at contract maturity. Volatility arbitrage, on the other hand, capitalizes on discrepancies between forecasted volatility and market-implied volatility through options strategies. Explore the nuances and strategies behind these trading techniques to enhance your financial acumen.
Why it is important
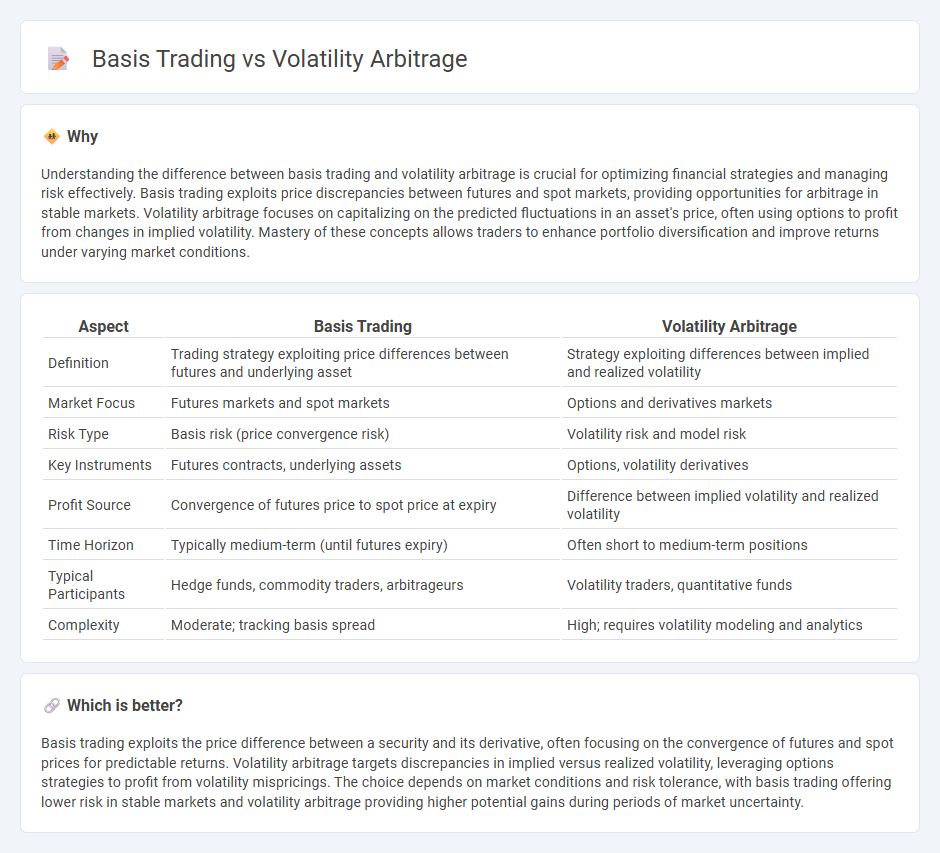
Understanding the difference between basis trading and volatility arbitrage is crucial for optimizing financial strategies and managing risk effectively. Basis trading exploits price discrepancies between futures and spot markets, providing opportunities for arbitrage in stable markets. Volatility arbitrage focuses on capitalizing on the predicted fluctuations in an asset's price, often using options to profit from changes in implied volatility. Mastery of these concepts allows traders to enhance portfolio diversification and improve returns under varying market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Basis Trading | Volatility Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading strategy exploiting price differences between futures and underlying asset | Strategy exploiting differences between implied and realized volatility |
| Market Focus | Futures markets and spot markets | Options and derivatives markets |
| Risk Type | Basis risk (price convergence risk) | Volatility risk and model risk |
| Key Instruments | Futures contracts, underlying assets | Options, volatility derivatives |
| Profit Source | Convergence of futures price to spot price at expiry | Difference between implied volatility and realized volatility |
| Time Horizon | Typically medium-term (until futures expiry) | Often short to medium-term positions |
| Typical Participants | Hedge funds, commodity traders, arbitrageurs | Volatility traders, quantitative funds |
| Complexity | Moderate; tracking basis spread | High; requires volatility modeling and analytics |
Which is better?
Basis trading exploits the price difference between a security and its derivative, often focusing on the convergence of futures and spot prices for predictable returns. Volatility arbitrage targets discrepancies in implied versus realized volatility, leveraging options strategies to profit from volatility mispricings. The choice depends on market conditions and risk tolerance, with basis trading offering lower risk in stable markets and volatility arbitrage providing higher potential gains during periods of market uncertainty.
Connection
Basis trading exploits price discrepancies between a futures contract and its underlying asset, while volatility arbitrage capitalizes on differences between forecasted and implied volatility in options pricing. Both strategies rely on identifying and exploiting market inefficiencies related to asset price behavior and volatility dynamics. Their connection lies in leveraging mispricings in derivative markets to generate risk-adjusted returns.
Key Terms
Implied Volatility
Volatility arbitrage exploits discrepancies between implied volatility and realized volatility to generate profits by trading options and hedging underlying assets. Basis trading focuses on the price difference between the futures contract and the spot price, leveraging changes in implied volatility to identify mispricings. Discover more about how implied volatility drivers impact both volatility arbitrage and basis trading strategies.
Spot-Futures Spread
Volatility arbitrage exploits discrepancies between implied and realized volatility, while basis trading centers on the spot-futures spread, capitalizing on price differences between the spot market and futures contracts. The spot-futures spread reflects factors like interest rates, storage costs, and dividend yields, offering opportunities for arbitrage when mispriced relative to expected cost of carry. Explore detailed strategies and risk profiles of volatility arbitrage and basis trading to enhance your trading acumen.
Delta Neutral
Volatility arbitrage focuses on exploiting discrepancies between implied and realized volatility while maintaining a delta-neutral position to hedge directional risk. Basis trading involves profiting from the price difference between futures and underlying assets, also employing delta-neutral strategies to minimize exposure to market movements. Explore the nuances and strategies of delta-neutral trading to optimize your investment approach.
Source and External Links
Volatility arbitrage - Wikipedia - Volatility arbitrage is a trading strategy that involves taking advantage of the difference between implied volatility of options and the forecasted future realized volatility of their underlying asset by maintaining a delta-neutral portfolio of options and underlying assets.
Volatility Arbitrage - Overview, How it Works, and Concerns - This strategy generates profits from discrepancies between implied volatility in option prices and the forecasted volatility of the underlying, implemented through delta-neutral portfolios requiring frequent rebalancing to maintain neutrality.
Volatility arbitrage indices - S&P Global - Volatility arbitrage strategies focus on exploiting differences in volatility measures, often through variance swaps and delta-neutral portfolios combining options and underlying assets to profit from volatility rather than price movements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com