Decentralized Finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries, promoting transparency and accessibility. Centralized Finance (CeFi), on the other hand, relies on traditional financial institutions to manage assets and transactions, often providing regulatory oversight and established security measures. Explore the evolving landscape of finance to understand the benefits and challenges of both DeFi and CeFi.
Why it is important
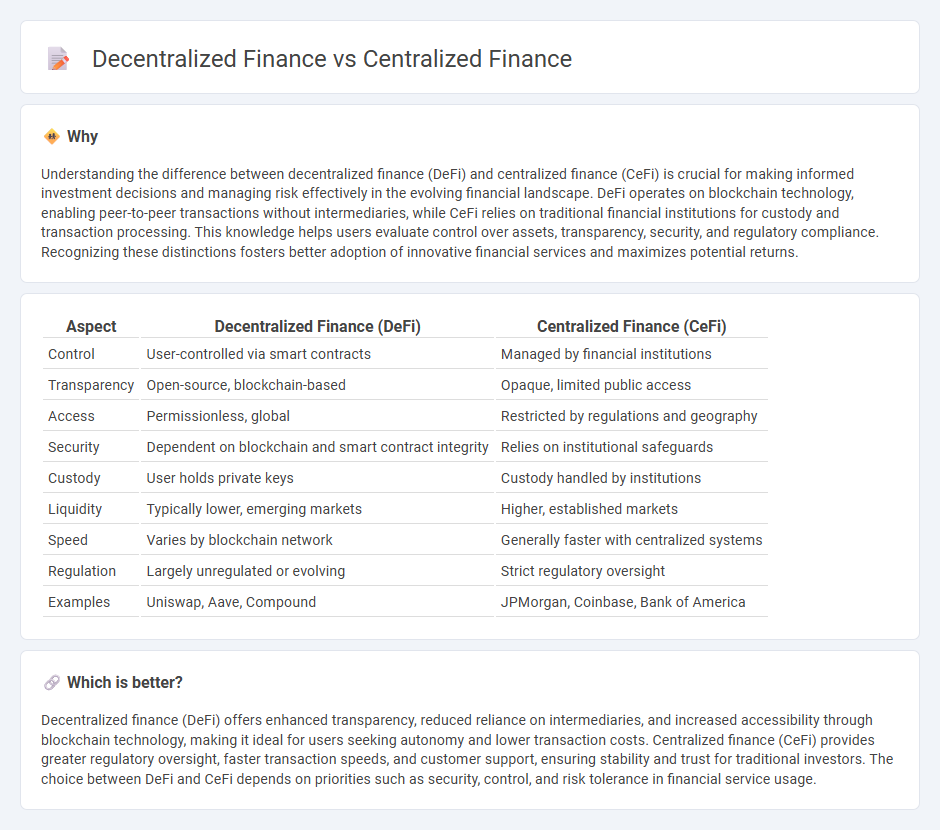
Understanding the difference between decentralized finance (DeFi) and centralized finance (CeFi) is crucial for making informed investment decisions and managing risk effectively in the evolving financial landscape. DeFi operates on blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, while CeFi relies on traditional financial institutions for custody and transaction processing. This knowledge helps users evaluate control over assets, transparency, security, and regulatory compliance. Recognizing these distinctions fosters better adoption of innovative financial services and maximizes potential returns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Centralized Finance (CeFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | User-controlled via smart contracts | Managed by financial institutions |
| Transparency | Open-source, blockchain-based | Opaque, limited public access |
| Access | Permissionless, global | Restricted by regulations and geography |
| Security | Dependent on blockchain and smart contract integrity | Relies on institutional safeguards |
| Custody | User holds private keys | Custody handled by institutions |
| Liquidity | Typically lower, emerging markets | Higher, established markets |
| Speed | Varies by blockchain network | Generally faster with centralized systems |
| Regulation | Largely unregulated or evolving | Strict regulatory oversight |
| Examples | Uniswap, Aave, Compound | JPMorgan, Coinbase, Bank of America |
Which is better?
Decentralized finance (DeFi) offers enhanced transparency, reduced reliance on intermediaries, and increased accessibility through blockchain technology, making it ideal for users seeking autonomy and lower transaction costs. Centralized finance (CeFi) provides greater regulatory oversight, faster transaction speeds, and customer support, ensuring stability and trust for traditional investors. The choice between DeFi and CeFi depends on priorities such as security, control, and risk tolerance in financial service usage.
Connection
Decentralized finance (DeFi) and centralized finance (CeFi) intersect through interoperability protocols that enable asset transfers and liquidity sharing between blockchain networks and traditional financial institutions. CeFi platforms often act as on-ramps, providing fiat-to-crypto services that facilitate user access to DeFi applications, while DeFi introduces transparency and programmable smart contracts that influence CeFi operations. The ongoing integration of these systems drives financial innovation by combining CeFi's regulatory compliance and customer trust with DeFi's decentralized access and automation.
Key Terms
Intermediaries
Centralized finance relies heavily on intermediaries such as banks, brokers, and payment processors to facilitate transactions, maintain security, and ensure regulatory compliance. In contrast, decentralized finance eliminates intermediaries by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts, enabling peer-to-peer interactions and increased transparency. Explore the key differences and implications of intermediaries in centralized versus decentralized finance to understand their impact on the future of financial services.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts serve as automated, self-executing agreements integral to both centralized finance (CeFi) and decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems, but their application differs significantly. In CeFi, smart contracts are controlled by a central authority that manages the rules and execution, whereas in DeFi, they operate autonomously on blockchain networks, enhancing transparency and reducing intermediaries. Explore how these contrasting implementations impact security, efficiency, and user trust by learning more about smart contract roles in CeFi and DeFi.
Custody
Centralized finance (CeFi) relies on third-party institutions to hold and manage users' funds, ensuring security but introducing risks of custodial mismanagement or breaches. Decentralized finance (DeFi) empowers users with self-custody through smart contracts and blockchain technology, eliminating intermediaries and granting full control over assets. Explore how custody models impact security, control, and user experience in both CeFi and DeFi ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Centralized Finance (CeFi) - Ledger - Centralized Finance (CeFi) refers to cryptocurrency financial services like trading, lending, borrowing, and yield opportunities managed by third-party centralized institutions that control user accounts, custody assets, and comply with regulations.
CeFi vs. DeFi: What's the Difference? - TechTarget - CeFi involves handling crypto transactions and trading through central exchanges that hold custody of users' assets, require identity verification (KYC), charge fees, and offer services such as margin trading and loans.
MANTRA's Guide to Centralised Finance (CeFi) - CeFi combines the ease and security of traditional finance with crypto yield benefits, allowing users to borrow, buy, sell crypto, and earn interest via centralized platforms like Coinbase, Binance, Celsius, or BlockFi.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com