Catastrophe bonds provide insurers with alternative risk transfer by allowing them to raise capital from investors to cover losses from extreme events, while reinsurance involves transferring portions of risk to another insurance company to mitigate potential claims. These financial instruments differ in liquidity, cost, and market accessibility, impacting how firms manage disaster-related exposures. Explore the unique features and benefits of catastrophe bonds versus reinsurance to optimize your risk management strategy.
Why it is important
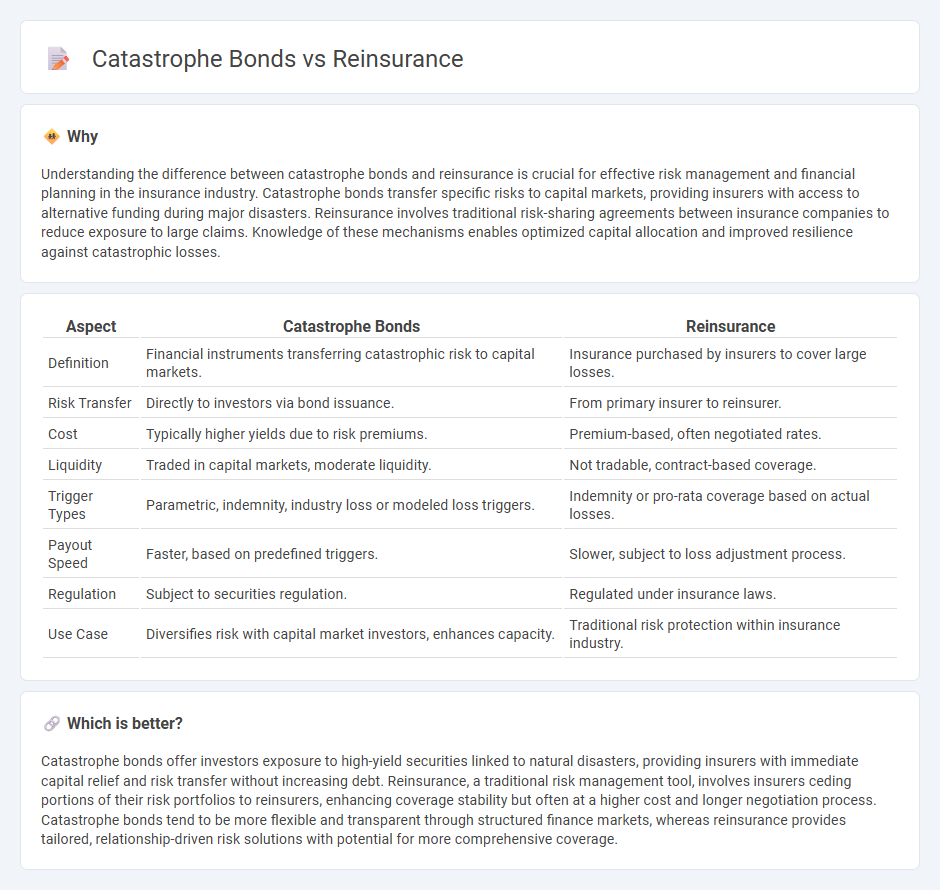
Understanding the difference between catastrophe bonds and reinsurance is crucial for effective risk management and financial planning in the insurance industry. Catastrophe bonds transfer specific risks to capital markets, providing insurers with access to alternative funding during major disasters. Reinsurance involves traditional risk-sharing agreements between insurance companies to reduce exposure to large claims. Knowledge of these mechanisms enables optimized capital allocation and improved resilience against catastrophic losses.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Catastrophe Bonds | Reinsurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial instruments transferring catastrophic risk to capital markets. | Insurance purchased by insurers to cover large losses. |
| Risk Transfer | Directly to investors via bond issuance. | From primary insurer to reinsurer. |
| Cost | Typically higher yields due to risk premiums. | Premium-based, often negotiated rates. |
| Liquidity | Traded in capital markets, moderate liquidity. | Not tradable, contract-based coverage. |
| Trigger Types | Parametric, indemnity, industry loss or modeled loss triggers. | Indemnity or pro-rata coverage based on actual losses. |
| Payout Speed | Faster, based on predefined triggers. | Slower, subject to loss adjustment process. |
| Regulation | Subject to securities regulation. | Regulated under insurance laws. |
| Use Case | Diversifies risk with capital market investors, enhances capacity. | Traditional risk protection within insurance industry. |
Which is better?
Catastrophe bonds offer investors exposure to high-yield securities linked to natural disasters, providing insurers with immediate capital relief and risk transfer without increasing debt. Reinsurance, a traditional risk management tool, involves insurers ceding portions of their risk portfolios to reinsurers, enhancing coverage stability but often at a higher cost and longer negotiation process. Catastrophe bonds tend to be more flexible and transparent through structured finance markets, whereas reinsurance provides tailored, relationship-driven risk solutions with potential for more comprehensive coverage.
Connection
Catastrophe bonds serve as a financial instrument that transfers catastrophic risk from insurers and reinsurers to capital market investors, providing an alternative to traditional reinsurance. Reinsurance companies utilize catastrophe bonds to diversify their risk exposure and enhance capital efficiency during high-severity disaster events. This connection allows risk to be spread more broadly, reducing the financial strain on reinsurers while offering investors the potential for high yields linked to catastrophe-related losses.
Key Terms
Risk Transfer
Reinsurance provides traditional risk transfer by allowing insurers to cede portions of their risk portfolios to reinsurers, thereby stabilizing loss experience and protecting against large claims. Catastrophe bonds transfer risk to capital markets by offering investors returns in exchange for absorbing specified catastrophic event losses, effectively diversifying risk beyond insurance entities. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how each solution optimizes risk transfer strategies in different market conditions.
Securitization
Reinsurance provides traditional risk transfer by insurers ceding portions of risk to reinsurers, while catastrophe bonds utilize securitization to transfer catastrophic event risks to capital markets via structured financial instruments. Catastrophe bonds offer investors a fixed return unless a predefined catastrophe event occurs, triggering loss payments to the issuer and providing insurers with alternative capital sources. Explore the evolving dynamics and benefits of securitized risk transfer methods to deepen understanding of reinsurance versus catastrophe bonds.
Indemnity Trigger
Reinsurance contracts with indemnity triggers provide coverage based on the actual losses an insurer incurs, ensuring precise alignment of payouts with financial impact. Catastrophe bonds, contrastingly, often use parametric or modeled loss triggers, paying out when predefined event metrics occur, not necessarily on the insurer's actual losses. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how indemnity triggers influence risk transfer efficiency and capital market solutions.
Source and External Links
REINSURANCE - A risk management tool where insurers transfer some or all insurance risk to another insurer to spread risk, manage capital, and protect against large or unusual insurance claims.
What is Reinsurance? - Reinsurance is insurance for insurance companies, helping limit liability, increase capacity, share risks, and stabilize insurers' business especially with large or catastrophic losses.
Background on: Reinsurance | III - Reinsurance involves insurers ceding part of their risk to reinsurers who share premiums and losses, and the market has evolved to include alternative risk mechanisms like catastrophe bonds.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com