Quantamental investing combines quantitative analysis and fundamental research to identify undervalued stocks with strong growth potential, leveraging algorithms alongside human expertise. Quantitative investing relies purely on mathematical models and statistical techniques to drive investment decisions. Explore the distinct advantages and applications of each strategy to refine your investment approach.
Why it is important
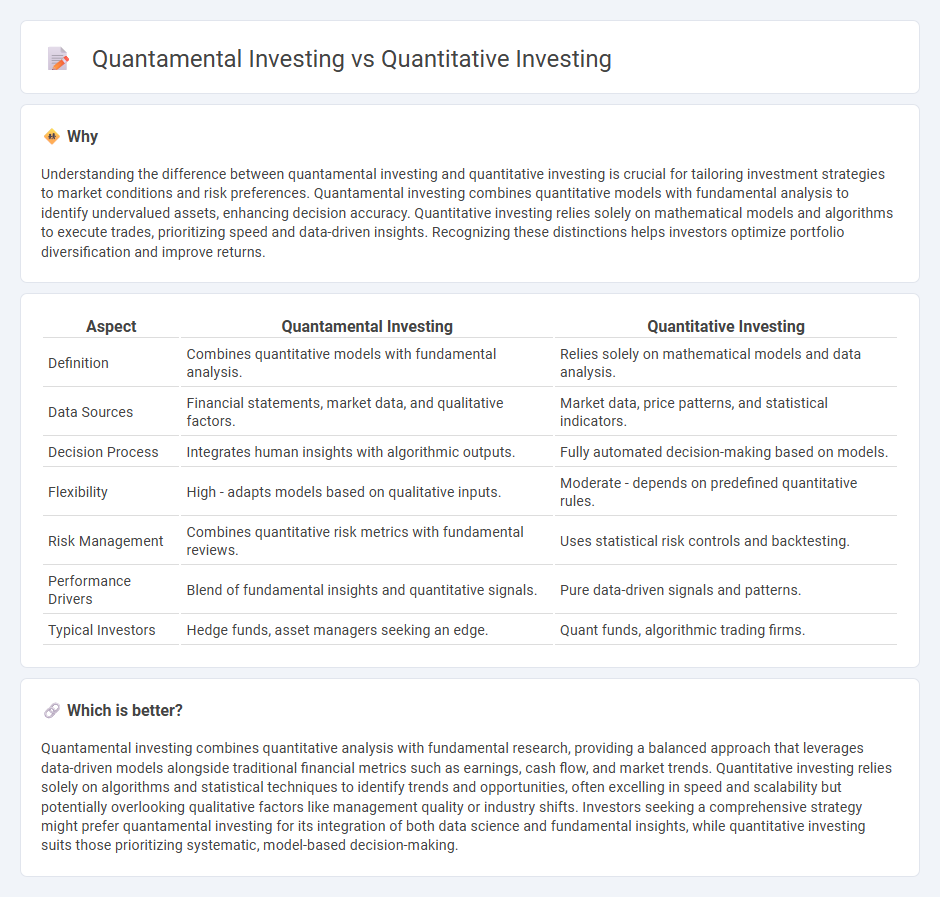
Understanding the difference between quantamental investing and quantitative investing is crucial for tailoring investment strategies to market conditions and risk preferences. Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis to identify undervalued assets, enhancing decision accuracy. Quantitative investing relies solely on mathematical models and algorithms to execute trades, prioritizing speed and data-driven insights. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors optimize portfolio diversification and improve returns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantamental Investing | Quantitative Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis. | Relies solely on mathematical models and data analysis. |
| Data Sources | Financial statements, market data, and qualitative factors. | Market data, price patterns, and statistical indicators. |
| Decision Process | Integrates human insights with algorithmic outputs. | Fully automated decision-making based on models. |
| Flexibility | High - adapts models based on qualitative inputs. | Moderate - depends on predefined quantitative rules. |
| Risk Management | Combines quantitative risk metrics with fundamental reviews. | Uses statistical risk controls and backtesting. |
| Performance Drivers | Blend of fundamental insights and quantitative signals. | Pure data-driven signals and patterns. |
| Typical Investors | Hedge funds, asset managers seeking an edge. | Quant funds, algorithmic trading firms. |
Which is better?
Quantamental investing combines quantitative analysis with fundamental research, providing a balanced approach that leverages data-driven models alongside traditional financial metrics such as earnings, cash flow, and market trends. Quantitative investing relies solely on algorithms and statistical techniques to identify trends and opportunities, often excelling in speed and scalability but potentially overlooking qualitative factors like management quality or industry shifts. Investors seeking a comprehensive strategy might prefer quantamental investing for its integration of both data science and fundamental insights, while quantitative investing suits those prioritizing systematic, model-based decision-making.
Connection
Quantamental investing integrates quantitative models with fundamental analysis to identify investment opportunities, blending data-driven algorithms with traditional financial metrics. Quantitative investing relies heavily on statistical techniques and computational models to analyze large datasets, uncovering patterns and trends that guide decision-making. Both approaches leverage data analytics to enhance portfolio performance, but quantamental investing uniquely combines human judgment with algorithmic insights for a comprehensive investment strategy.
Key Terms
**Quantitative Investing:**
Quantitative investing relies on mathematical models, algorithms, and statistical techniques to analyze large datasets and identify investment opportunities with minimal human intervention. This data-driven approach prioritizes objective decision-making, risk management, and systematic execution to achieve consistent returns. Explore the nuances of quantitative investing to enhance your portfolio strategy with advanced analytics and automation.
Algorithmic Models
Quantitative investing relies heavily on algorithmic models that process vast datasets to identify patterns and execute trades based on statistical analysis and mathematical computations. Quantamental investing combines these quantitative techniques with fundamental analysis, integrating qualitative insights into the algorithmic models to enhance decision-making and risk assessment. Explore how blending algorithmic models with fundamental data can optimize investment strategies.
Backtesting
Quantitative investing relies heavily on rigorous backtesting techniques to validate algorithmic trading models using historical market data, ensuring strategies are statistically sound before deployment. Quantamental investing combines quantitative backtesting with fundamental analysis, integrating financial health metrics and qualitative factors to enhance predictive accuracy and risk management. Explore how backtesting methodologies differ across these approaches to optimize your investment strategy.
Source and External Links
Quantitative investing definition - Risk.net - Quantitative investing uses mathematical models, data analysis, and computer systems to systematically identify and execute profitable trades, often incorporating techniques like machine learning and factor investing.
Quantitative analysis (finance) - Wikipedia - Quantitative analysis in finance applies mathematical and statistical methods to investment management, with professionals ("quants") specializing in areas like derivatives pricing, risk management, and algorithmic trading.
Quantitative vs. Fundamental Equity Investing - Quantitative investing is a repeatable, data-driven approach that rigorously tests and systematically applies investment insights, leveraging computing power to process large datasets and minimize behavioral biases.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com