Latency arbitrage exploits minimal delays in trade execution to capitalize on price discrepancies in financial markets, often relying on high-frequency trading technology. Index arbitrage involves simultaneously buying and selling a stock index and its futures or ETFs to profit from price differences, ensuring portfolio alignment with market indices. Discover more about these sophisticated arbitrage strategies and their impact on market efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between latency arbitrage and index arbitrage is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and minimizing risks in financial markets. Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in data transmission to gain price advantages, while index arbitrage involves capitalizing on price discrepancies between index futures and their underlying assets. Differentiating these arbitrage types enhances decision-making, improves execution speed, and ensures compliance with market regulations. Knowledge of their mechanisms directly impacts profitability and systematic risk management in high-frequency and institutional trading.
Comparison Table
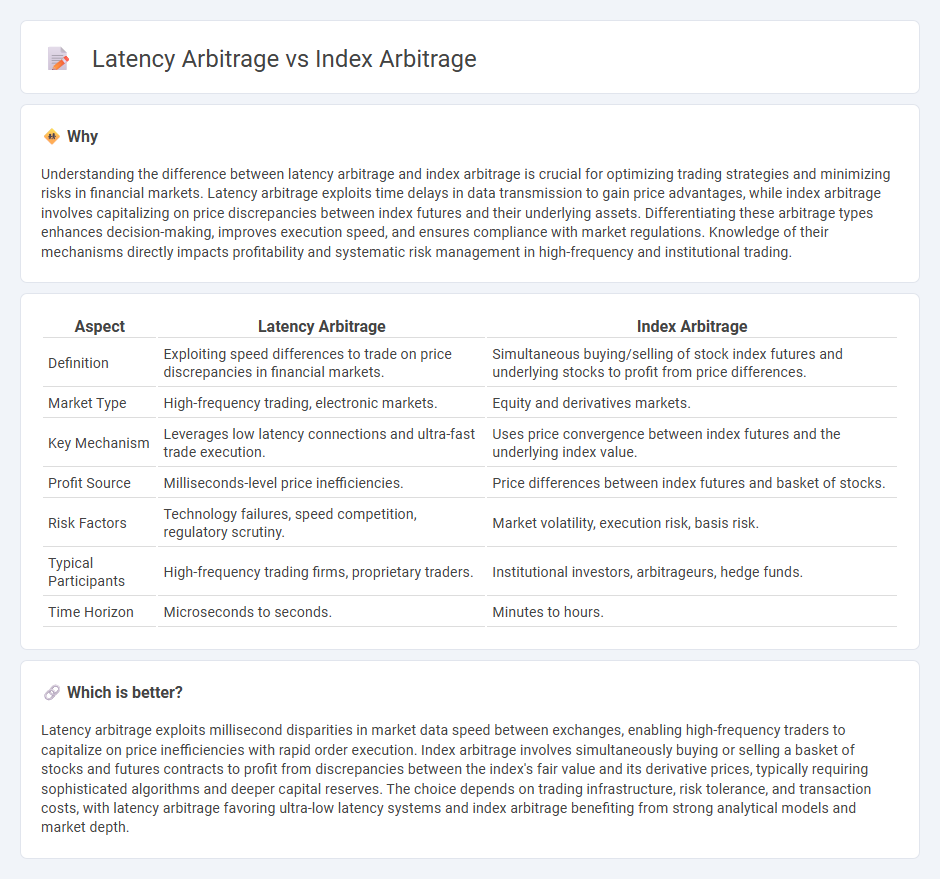
| Aspect | Latency Arbitrage | Index Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting speed differences to trade on price discrepancies in financial markets. | Simultaneous buying/selling of stock index futures and underlying stocks to profit from price differences. |
| Market Type | High-frequency trading, electronic markets. | Equity and derivatives markets. |
| Key Mechanism | Leverages low latency connections and ultra-fast trade execution. | Uses price convergence between index futures and the underlying index value. |
| Profit Source | Milliseconds-level price inefficiencies. | Price differences between index futures and basket of stocks. |
| Risk Factors | Technology failures, speed competition, regulatory scrutiny. | Market volatility, execution risk, basis risk. |
| Typical Participants | High-frequency trading firms, proprietary traders. | Institutional investors, arbitrageurs, hedge funds. |
| Time Horizon | Microseconds to seconds. | Minutes to hours. |
Which is better?
Latency arbitrage exploits millisecond disparities in market data speed between exchanges, enabling high-frequency traders to capitalize on price inefficiencies with rapid order execution. Index arbitrage involves simultaneously buying or selling a basket of stocks and futures contracts to profit from discrepancies between the index's fair value and its derivative prices, typically requiring sophisticated algorithms and deeper capital reserves. The choice depends on trading infrastructure, risk tolerance, and transaction costs, with latency arbitrage favoring ultra-low latency systems and index arbitrage benefiting from strong analytical models and market depth.
Connection
Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data transmission to execute trades before others, gaining price advantages. Index arbitrage involves exploiting price differences between an index and its constituent stocks to achieve riskless profits. Both strategies depend on speed and information asymmetry, where latency arbitrage enhances the effectiveness of index arbitrage by enabling quicker reactions to price discrepancies in index components.
Key Terms
Price Convergence (Index Arbitrage)
Index arbitrage exploits price convergence between a stock index futures contract and its underlying basket of stocks, ensuring alignment between the futures price and the net asset value of the indexed portfolio. Traders implement strategies that capitalize on discrepancies by simultaneously buying undervalued assets and selling overvalued futures, thereby profiting as prices converge to fair value. Explore deeper insights into index arbitrage dynamics and techniques to enhance trading efficiency.
Speed/Execution (Latency Arbitrage)
Latency arbitrage exploits minimal time delays in trade execution by rapidly capitalizing on price discrepancies before others can react, relying heavily on ultra-low latency technology and proximity to exchange servers. Index arbitrage involves simultaneous buying and selling of index futures and underlying stocks to profit from price differences, but speed is less critical compared to latency arbitrage's microsecond-level execution demands. Explore more about how cutting-edge speed and execution technologies distinguish latency arbitrage strategies from traditional index arbitrage methods.
Market Inefficiency
Index arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between stock index futures and their underlying cash markets, capitalizing on market inefficiencies caused by delayed price adjustments. Latency arbitrage leverages speed advantages to trade on stale prices across different venues, profiting from temporary lags in market data transmission. Explore deeper insights on how these strategies reveal and exploit market inefficiencies.
Source and External Links
Index Arbitrage - Quantra by QuantInsti - This webpage explains index arbitrage as a strategy that exploits price discrepancies between a stock index and its futures contract, aiming to profit from their convergence.
Index Arbitrage - Wikipedia - This article details index arbitrage as a method to profit from price differences between index futures and the underlying stocks, often involving ETFs and futures contracts.
What is Stock Index Arbitrage? Definition and Examples - Groww - This page describes index arbitrage as a trading method that exploits disparities between an index and its futures contract, focusing on the concept of fair value and its implications for trading strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com