Dark pool trading enables large institutional investors to execute sizable trades anonymously, minimizing market impact and price volatility, whereas auction market trading occurs on public exchanges where buy and sell orders are matched transparently through a bidding process. Dark pools offer privacy but often lack real-time price discovery, while auction markets provide greater liquidity and price transparency through competitive bidding among participants. Explore how these contrasting trading environments affect market dynamics and investment strategies.
Why it is important
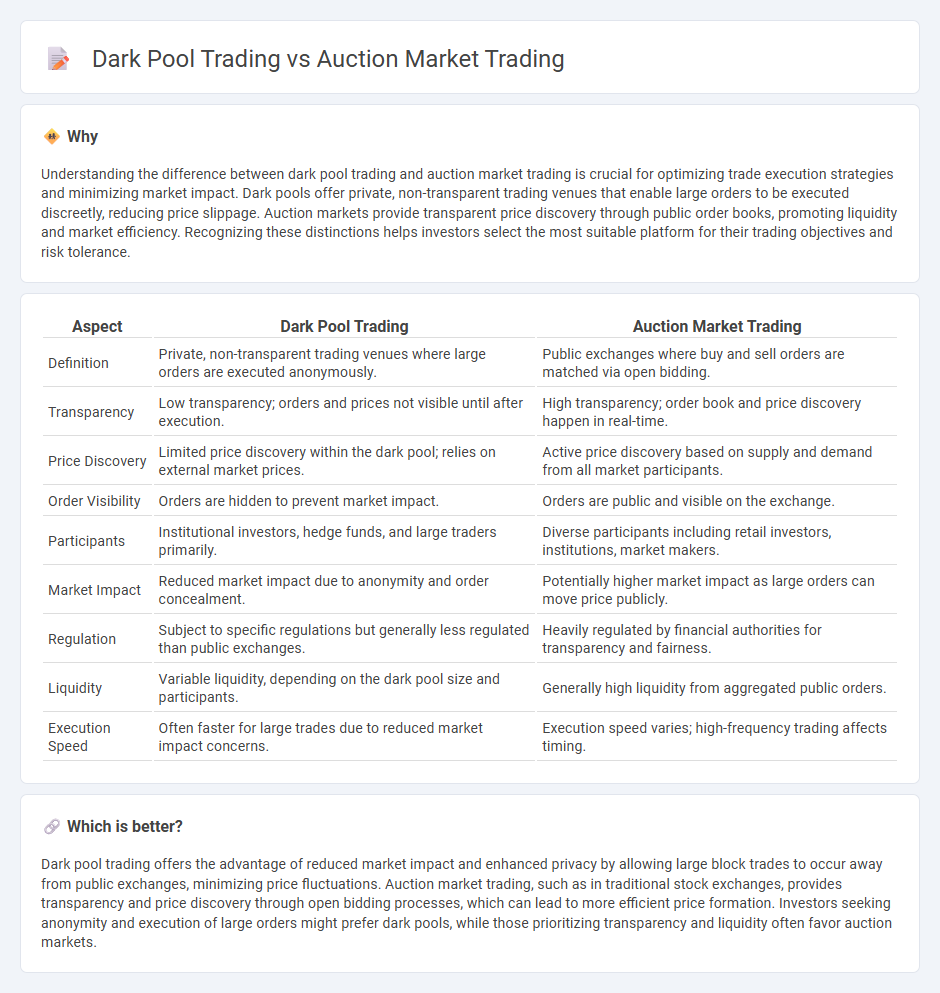
Understanding the difference between dark pool trading and auction market trading is crucial for optimizing trade execution strategies and minimizing market impact. Dark pools offer private, non-transparent trading venues that enable large orders to be executed discreetly, reducing price slippage. Auction markets provide transparent price discovery through public order books, promoting liquidity and market efficiency. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors select the most suitable platform for their trading objectives and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pool Trading | Auction Market Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private, non-transparent trading venues where large orders are executed anonymously. | Public exchanges where buy and sell orders are matched via open bidding. |
| Transparency | Low transparency; orders and prices not visible until after execution. | High transparency; order book and price discovery happen in real-time. |
| Price Discovery | Limited price discovery within the dark pool; relies on external market prices. | Active price discovery based on supply and demand from all market participants. |
| Order Visibility | Orders are hidden to prevent market impact. | Orders are public and visible on the exchange. |
| Participants | Institutional investors, hedge funds, and large traders primarily. | Diverse participants including retail investors, institutions, market makers. |
| Market Impact | Reduced market impact due to anonymity and order concealment. | Potentially higher market impact as large orders can move price publicly. |
| Regulation | Subject to specific regulations but generally less regulated than public exchanges. | Heavily regulated by financial authorities for transparency and fairness. |
| Liquidity | Variable liquidity, depending on the dark pool size and participants. | Generally high liquidity from aggregated public orders. |
| Execution Speed | Often faster for large trades due to reduced market impact concerns. | Execution speed varies; high-frequency trading affects timing. |
Which is better?
Dark pool trading offers the advantage of reduced market impact and enhanced privacy by allowing large block trades to occur away from public exchanges, minimizing price fluctuations. Auction market trading, such as in traditional stock exchanges, provides transparency and price discovery through open bidding processes, which can lead to more efficient price formation. Investors seeking anonymity and execution of large orders might prefer dark pools, while those prioritizing transparency and liquidity often favor auction markets.
Connection
Dark pool trading and auction market trading are connected through their roles in price discovery and liquidity provision in financial markets. Dark pools facilitate large block trades away from public exchanges, minimizing market impact and information leakage, while auction markets aggregate buy and sell orders transparently at a central price point. The interplay between dark pools' off-exchange liquidity and auction markets' public price formation helps balance market efficiency and investor anonymity.
Key Terms
Price Transparency
Auction market trading offers high price transparency, displaying real-time bid and ask prices publicly on an exchange, which facilitates fair price discovery. Dark pool trading lacks this level of transparency because it occurs in private venues where large trades are executed without revealing prices to the broader market until after completion, minimizing market impact but increasing opacity. Explore deeper insights on how price transparency affects trading strategies in different market environments.
Order Matching
Auction market trading matches buy and sell orders through a transparent competitive process, revealing order books to ensure price discovery and liquidity. Dark pool trading shields large orders from public view, allowing participants to trade anonymously and minimize market impact without exposing order details. Discover the intricacies of how order matching shapes market dynamics in both trading venues.
Liquidity
Auction market trading provides high liquidity through transparent order books where buyers and sellers actively compete, resulting in efficient price discovery. Dark pool trading offers liquidity by enabling large block trades to occur privately, minimizing market impact and price slippage. Explore more about how these trading venues optimize liquidity for different investor strategies.
Source and External Links
Auction markets: What is it, types, Importance, Example, FAQ | POEMS - An auction market is where buyers and sellers compete by submitting bids and offers, which are matched according to price, with highest bids paired with lowest asks, allowing price discovery through market interaction rather than dealer-set prices.
What is an Auction in Trading? | Definition and Examples - TIOmarkets - Auctions in trading facilitate buying and selling via bids, commonly used during stock market openings and closings or IPOs to determine prices through aggregated demand, ensuring fair price discovery and market stability.
Auction Market Theory: Forces Behind Market Movements - Auction Market Theory explains market price movements as a continuous auction process where buyer and seller interactions establish prices based on supply and demand dynamics, resembling Wyckoff Theory principles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com