Crowdlending and microfinance both provide alternative financing options supporting small businesses and entrepreneurs, with crowdlending connecting borrowers directly to individual lenders through online platforms, while microfinance focuses on offering small loans to underserved populations often facilitated by nonprofit organizations. Crowdlending typically involves a broader range of investors seeking returns, whereas microfinance emphasizes social impact and financial inclusion. Explore the distinct benefits and mechanisms of crowdlending versus microfinance to better understand their roles in expanding financial access.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between crowdlending and microfinance is crucial for selecting the appropriate funding method tailored to specific business or social impact goals. Crowdlending involves individuals lending money directly to businesses or projects through online platforms, often seeking financial returns within set terms. Microfinance typically focuses on providing small loans to low-income or underserved individuals to promote financial inclusion and entrepreneurship. Knowing these distinctions helps optimize capital acquisition strategies while aligning with risk tolerance and social objectives.
Comparison Table
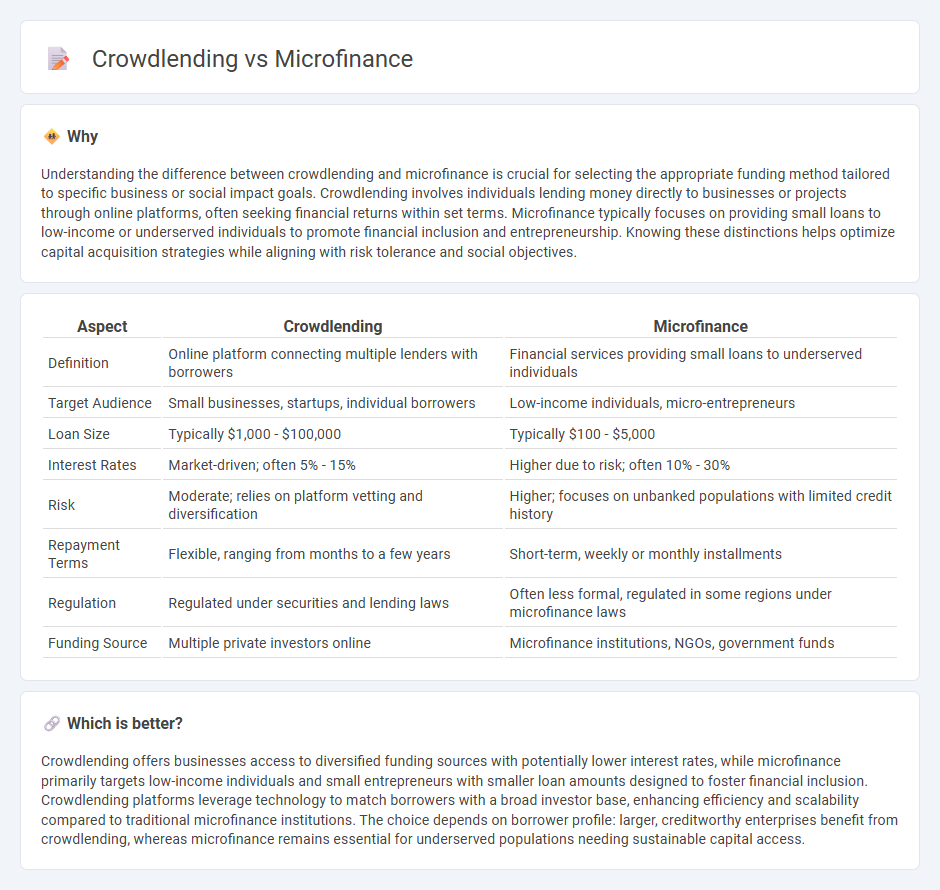
| Aspect | Crowdlending | Microfinance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Online platform connecting multiple lenders with borrowers | Financial services providing small loans to underserved individuals |
| Target Audience | Small businesses, startups, individual borrowers | Low-income individuals, micro-entrepreneurs |
| Loan Size | Typically $1,000 - $100,000 | Typically $100 - $5,000 |
| Interest Rates | Market-driven; often 5% - 15% | Higher due to risk; often 10% - 30% |
| Risk | Moderate; relies on platform vetting and diversification | Higher; focuses on unbanked populations with limited credit history |
| Repayment Terms | Flexible, ranging from months to a few years | Short-term, weekly or monthly installments |
| Regulation | Regulated under securities and lending laws | Often less formal, regulated in some regions under microfinance laws |
| Funding Source | Multiple private investors online | Microfinance institutions, NGOs, government funds |
Which is better?
Crowdlending offers businesses access to diversified funding sources with potentially lower interest rates, while microfinance primarily targets low-income individuals and small entrepreneurs with smaller loan amounts designed to foster financial inclusion. Crowdlending platforms leverage technology to match borrowers with a broad investor base, enhancing efficiency and scalability compared to traditional microfinance institutions. The choice depends on borrower profile: larger, creditworthy enterprises benefit from crowdlending, whereas microfinance remains essential for underserved populations needing sustainable capital access.
Connection
Crowdlending and microfinance both facilitate access to capital for individuals and small businesses often underserved by traditional banks. Crowdlending platforms connect multiple individual lenders directly to borrowers, enabling microfinance-type loans through decentralized funding sources. This synergy increases financial inclusion by leveraging peer-to-peer networks to provide affordable credit and support economic development in emerging markets.
Key Terms
**Interest Rate**
Microfinance interest rates typically range from 15% to 30% annually, reflecting higher operational costs and risk management for lenders targeting low-income borrowers. Crowdlending platforms often offer more competitive rates between 5% and 15%, leveraging peer-to-peer funding to reduce overhead and attract diverse investors. Explore further to understand how these interest rate differences impact borrower accessibility and lender returns.
**Risk Assessment**
Microfinance institutions conduct thorough risk assessments by analyzing borrowers' credit history, income stability, and local economic conditions to minimize default rates, while crowdlending platforms use algorithm-driven credit scoring coupled with investor risk profiles to diversify and mitigate potential losses. The granular insight in microfinance often results in personalized lending terms, whereas crowdlending balances risk through loan portfolio diversification across multiple borrowers. Explore how these contrasting risk assessment strategies impact investor confidence and loan performance.
**Funding Source**
Microfinance funding sources primarily include specialized institutions like microfinance banks and nonprofit organizations that provide small loans to underserved populations. Crowdlending relies on a digital platform connecting individual investors directly with borrowers, pooling funds from a large audience through online campaigns. Explore more to understand the nuances of how these funding mechanisms impact borrower access and lender risk.
Source and External Links
Microfinance 101: All you need to know - Microfinance delivers financial services such as loans, savings, insurance, and fund transfers to individuals and small businesses without access to traditional banking, addressing systemic inequalities and poverty worldwide.
Microfinancing Basics - My Own Business Institute - Microfinance involves small loans and increasingly savings and insurance aimed at entrepreneurs who lack access to mainstream financial services, helping them start and grow businesses.
Microfinance - Wikipedia - Microfinance targets financially excluded individuals, especially women, providing them with credit, savings, and microinsurance to support income-generating activities with a strong focus on female clients due to lower default rates.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com