Alternative data encompasses diverse non-traditional datasets such as satellite imagery, social media trends, and transactional records, providing unique insights beyond conventional financial metrics. Web-scraped data specifically refers to information systematically extracted from websites, including pricing, product reviews, and consumer behavior patterns crucial for market analysis. Explore deeper to understand how leveraging these data sources can transform investment strategies and risk assessment.
Why it is important
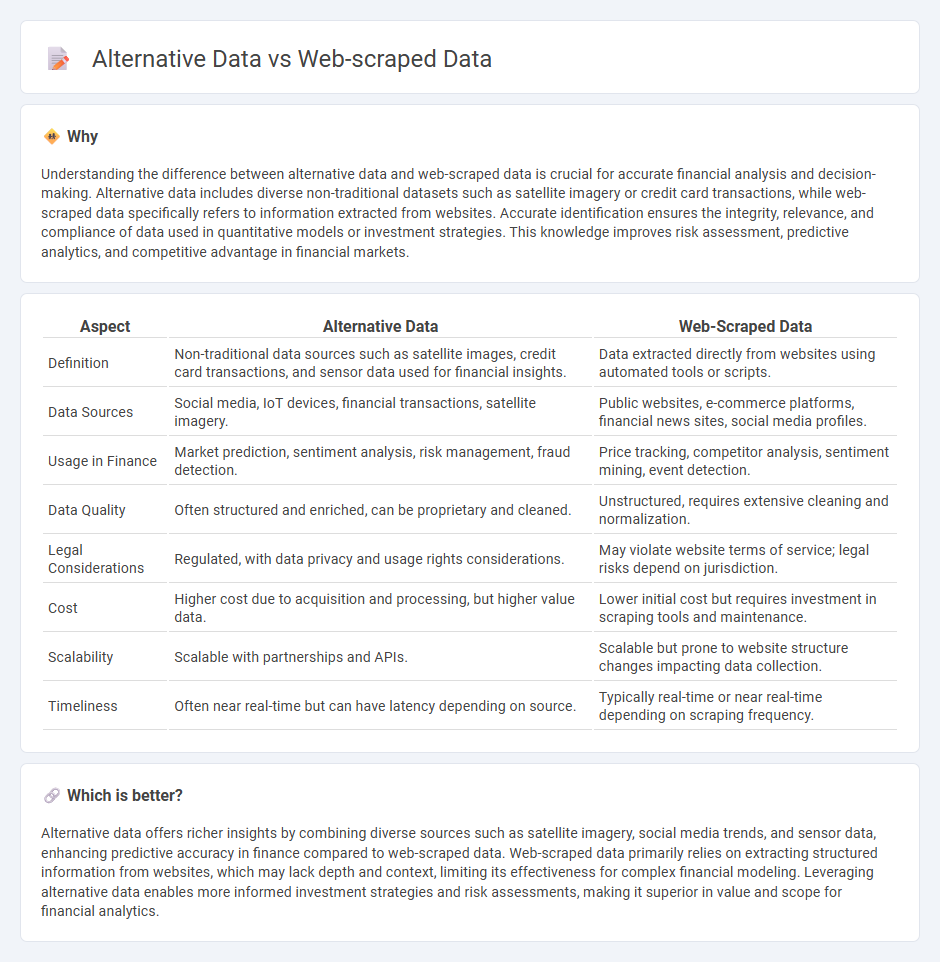
Understanding the difference between alternative data and web-scraped data is crucial for accurate financial analysis and decision-making. Alternative data includes diverse non-traditional datasets such as satellite imagery or credit card transactions, while web-scraped data specifically refers to information extracted from websites. Accurate identification ensures the integrity, relevance, and compliance of data used in quantitative models or investment strategies. This knowledge improves risk assessment, predictive analytics, and competitive advantage in financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alternative Data | Web-Scraped Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-traditional data sources such as satellite images, credit card transactions, and sensor data used for financial insights. | Data extracted directly from websites using automated tools or scripts. |
| Data Sources | Social media, IoT devices, financial transactions, satellite imagery. | Public websites, e-commerce platforms, financial news sites, social media profiles. |
| Usage in Finance | Market prediction, sentiment analysis, risk management, fraud detection. | Price tracking, competitor analysis, sentiment mining, event detection. |
| Data Quality | Often structured and enriched, can be proprietary and cleaned. | Unstructured, requires extensive cleaning and normalization. |
| Legal Considerations | Regulated, with data privacy and usage rights considerations. | May violate website terms of service; legal risks depend on jurisdiction. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to acquisition and processing, but higher value data. | Lower initial cost but requires investment in scraping tools and maintenance. |
| Scalability | Scalable with partnerships and APIs. | Scalable but prone to website structure changes impacting data collection. |
| Timeliness | Often near real-time but can have latency depending on source. | Typically real-time or near real-time depending on scraping frequency. |
Which is better?
Alternative data offers richer insights by combining diverse sources such as satellite imagery, social media trends, and sensor data, enhancing predictive accuracy in finance compared to web-scraped data. Web-scraped data primarily relies on extracting structured information from websites, which may lack depth and context, limiting its effectiveness for complex financial modeling. Leveraging alternative data enables more informed investment strategies and risk assessments, making it superior in value and scope for financial analytics.
Connection
Alternative data, including web-scraped data, provides unique financial insights by extracting non-traditional information such as social media trends, satellite imagery, and consumer behavior from online sources. Web scraping techniques enable the collection of large-scale, real-time data sets that enhance predictive modeling and risk assessment in finance. Integrating these diverse data streams improves investment strategies, portfolio management, and market analysis beyond conventional financial metrics.
Key Terms
Data Source
Web-scraped data is collected directly from publicly accessible websites, providing real-time insights and vast volumes of unstructured information such as product prices, reviews, or social media activity. Alternative data, on the other hand, encompasses diverse sources beyond traditional datasets, including satellite imagery, sensor data, and transactional records, offering unique perspectives not available through web scraping alone. Explore the distinctions and benefits of each data source to enhance your data-driven strategies.
Unstructured Data
Web-scraped data, a type of unstructured data extracted from websites, offers extensive textual and multimedia information that requires advanced processing techniques like natural language processing and image recognition for meaningful analysis. Alternative data encompasses a broader category including sensor data, social media feeds, and satellite imagery, often unstructured but valuable for unique insights beyond traditional datasets. Explore the nuances between web-scraped and alternative unstructured data to leverage their full potential in data-driven decision-making.
Signal Generation
Web-scraped data offers real-time, granular insights extracted from online sources, enabling enhanced signal generation for predictive analytics. Alternative data encompasses diverse non-traditional datasets such as satellite imagery, social media activity, and transaction records, enriching signal strength beyond conventional financial indicators. Explore how combining web-scraped data with alternative data fuels more robust signal generation strategies.
Source and External Links
Web scraping - Web scraping is the process of automatically extracting or mining data from websites, often using techniques like HTML parsing, HTTP programming, and text pattern matching to convert web content into structured data formats.
What is Web Scraping and How to Use It? - Web scraping is an automated method to collect large amounts of usually unstructured data from websites and convert it into structured data, using tools like crawlers and scrapers especially when APIs are not available.
What is Web Scraping and What is it Used For? - Web scraping involves extracting website data by loading HTML and optionally rendering JavaScript, then selecting and exporting specific information into useful formats, enabling efficient access to large data sets such as prices or contact info.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com