Zero day options, expiring within 24 hours, offer high-risk, high-reward trading opportunities due to their extreme time sensitivity and volatility. Barrier options activate or extinguish when the underlying asset hits a specific price level, providing tailored strategies for risk management and speculative purposes. Explore deeper insights into how these derivatives function and their strategic applications in modern finance.
Why it is important
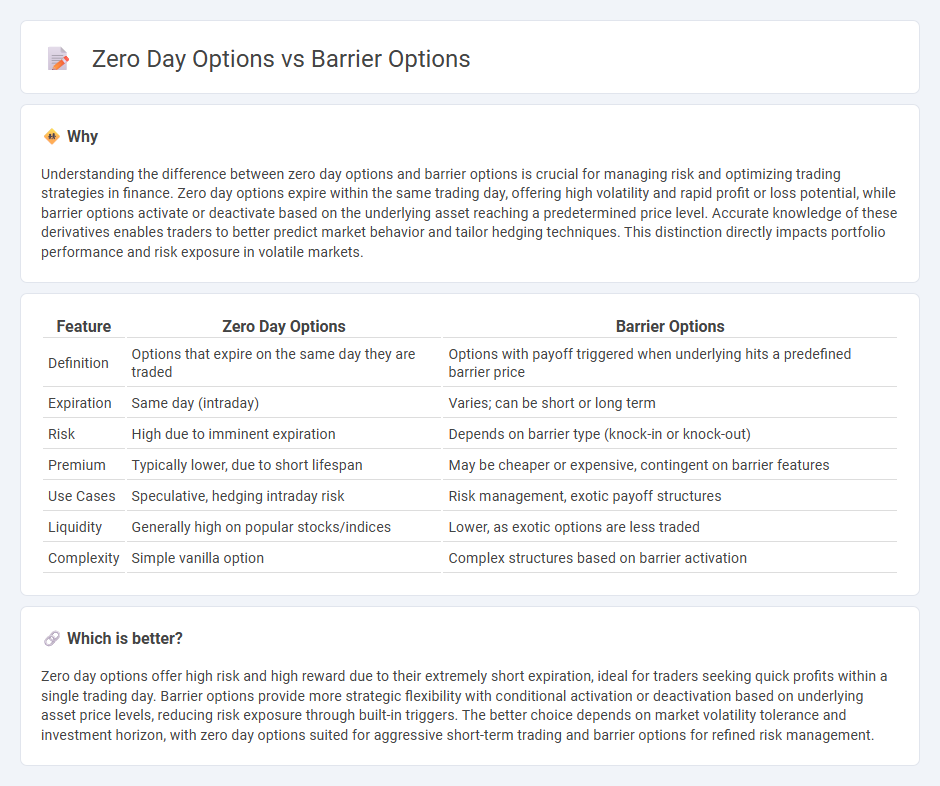
Understanding the difference between zero day options and barrier options is crucial for managing risk and optimizing trading strategies in finance. Zero day options expire within the same trading day, offering high volatility and rapid profit or loss potential, while barrier options activate or deactivate based on the underlying asset reaching a predetermined price level. Accurate knowledge of these derivatives enables traders to better predict market behavior and tailor hedging techniques. This distinction directly impacts portfolio performance and risk exposure in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Day Options | Barrier Options |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Options that expire on the same day they are traded | Options with payoff triggered when underlying hits a predefined barrier price |
| Expiration | Same day (intraday) | Varies; can be short or long term |
| Risk | High due to imminent expiration | Depends on barrier type (knock-in or knock-out) |
| Premium | Typically lower, due to short lifespan | May be cheaper or expensive, contingent on barrier features |
| Use Cases | Speculative, hedging intraday risk | Risk management, exotic payoff structures |
| Liquidity | Generally high on popular stocks/indices | Lower, as exotic options are less traded |
| Complexity | Simple vanilla option | Complex structures based on barrier activation |
Which is better?
Zero day options offer high risk and high reward due to their extremely short expiration, ideal for traders seeking quick profits within a single trading day. Barrier options provide more strategic flexibility with conditional activation or deactivation based on underlying asset price levels, reducing risk exposure through built-in triggers. The better choice depends on market volatility tolerance and investment horizon, with zero day options suited for aggressive short-term trading and barrier options for refined risk management.
Connection
Zero day options and barrier options are connected through their reliance on precise market timing and price thresholds to influence payoff structures in financial trading. Both derivative instruments enable traders to implement highly specific risk management and speculative strategies by exploiting short time horizons or conditional triggers. Their combined use enhances portfolio flexibility by allowing tailored exposure to market movements within constrained time frames or upon activation of predetermined barrier levels.
Key Terms
Knock-in / Knock-out
Barrier options include knock-in and knock-out features that activate or deactivate the option when the underlying asset reaches a pre-set barrier level, adding conditional triggers to their payoff structure. Zero day options, typically expiring on the same day they are traded, rarely feature complex barriers but emphasize rapid time decay and short-term volatility plays. Explore how these different option types can optimize trading strategies under varying market conditions.
Expiry (Maturity)
Barrier options are exotic derivatives that activate or expire based on the underlying asset hitting a predetermined price level before or at expiration, while their maturity varies from short to long term. Zero day options, typically standard options expiring the same day they are traded, offer ultra-short-term exposure with high gamma and time decay sensitivity. Explore further to understand which expiration strategy aligns with your trading goals and risk tolerance.
Intraday Volatility
Barrier options are path-dependent derivatives that activate or extinguish based on the underlying asset's price reaching a predetermined barrier level, making them highly sensitive to intraday volatility fluctuations. Zero day options, expiring within the same trading day, capitalize on short-term volatility spikes and rapid price movements, offering traders opportunities for quick gains but increased risk. Explore detailed strategies and risk management techniques to optimize trading with barrier and zero day options in volatile intraday markets.
Source and External Links
Barrier option - Wikipedia - Barrier options are path-dependent exotic options that become active ("in" options) or extinguished ("out" options) only if the underlying asset breaches a predetermined barrier level during the option's lifetime, with various types such as knock-in and knock-out, and different payoff structures depending on whether the barrier is hit or not.
Optimal Static-Dynamic Hedges for Barrier Options - Barrier options, which have payoffs contingent on the asset price hitting a barrier, are cheaper alternatives to vanilla options but exhibit more complex pricing and hedging challenges due to their path-dependent nature, with common forms including knock-in and knock-out, and require sophisticated hedging strategies combining static and dynamic approaches.
FX Barrier Option Pricing - Imperial College London - Barrier options in foreign exchange markets serve important roles in risk management and speculative trading, coming in single and double barrier forms, with variants such as European and American styles, and involving features like rebates and window barriers that add complexity to their valuation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com