Private credit offers businesses flexible financing options with faster approval and tailored terms, often filling gaps left by traditional bank loans. Bank loans typically provide standardized lending products with regulated interest rates and stringent qualification criteria, making them suitable for established companies with strong credit histories. Explore the differences between private credit and bank loans to determine the best financial strategy for your business.
Why it is important
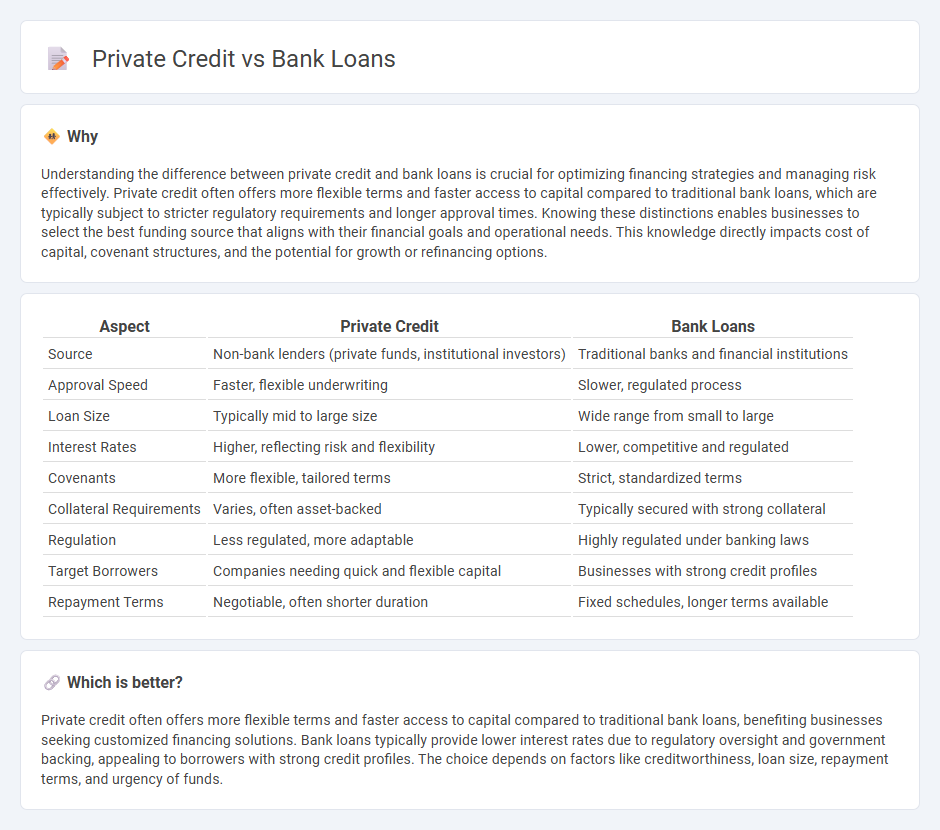
Understanding the difference between private credit and bank loans is crucial for optimizing financing strategies and managing risk effectively. Private credit often offers more flexible terms and faster access to capital compared to traditional bank loans, which are typically subject to stricter regulatory requirements and longer approval times. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses to select the best funding source that aligns with their financial goals and operational needs. This knowledge directly impacts cost of capital, covenant structures, and the potential for growth or refinancing options.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Private Credit | Bank Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Non-bank lenders (private funds, institutional investors) | Traditional banks and financial institutions |
| Approval Speed | Faster, flexible underwriting | Slower, regulated process |
| Loan Size | Typically mid to large size | Wide range from small to large |
| Interest Rates | Higher, reflecting risk and flexibility | Lower, competitive and regulated |
| Covenants | More flexible, tailored terms | Strict, standardized terms |
| Collateral Requirements | Varies, often asset-backed | Typically secured with strong collateral |
| Regulation | Less regulated, more adaptable | Highly regulated under banking laws |
| Target Borrowers | Companies needing quick and flexible capital | Businesses with strong credit profiles |
| Repayment Terms | Negotiable, often shorter duration | Fixed schedules, longer terms available |
Which is better?
Private credit often offers more flexible terms and faster access to capital compared to traditional bank loans, benefiting businesses seeking customized financing solutions. Bank loans typically provide lower interest rates due to regulatory oversight and government backing, appealing to borrowers with strong credit profiles. The choice depends on factors like creditworthiness, loan size, repayment terms, and urgency of funds.
Connection
Private credit and bank loans are interconnected as both serve as vital sources of financing for businesses, with private credit often filling gaps left by traditional bank lending. Private credit typically involves non-bank lenders offering flexible loan structures to middle-market companies that may not meet stringent bank loan criteria. This dynamic creates a complementary relationship where private credit expands access to capital beyond conventional banking channels, supporting diverse financing needs and market segments.
Key Terms
Collateral
Bank loans typically require substantial collateral, including real estate, equipment, or inventory, to secure the loan and mitigate lender risk. Private credit often offers more flexible collateral requirements, sometimes accepting softer assets or offering unsecured options tailored to borrower needs. Explore the nuances of collateral structures to understand which financing option aligns with your business strategy.
Interest Rate
Bank loans typically offer lower interest rates compared to private credit due to regulated lending practices and access to cheaper capital sources. Private credit tends to have higher rates reflecting increased risk and less regulatory oversight, appealing to borrowers who may not qualify for traditional bank financing. Explore how interest rate differences between bank loans and private credit impact borrowing costs and financing strategies.
Covenants
Bank loans typically feature stricter covenants, including financial ratios and operational restrictions, to minimize lender risk and ensure borrower compliance. Private credit agreements often offer more flexible covenant structures, catering to borrowers seeking tailored financing with fewer operational constraints. Explore the nuances of covenant differences to find the optimal financing solution.
Source and External Links
Personal loans: See options and apply online | Wells Fargo - Wells Fargo offers unsecured personal loans from $3,000 to $100,000 with terms ranging from 12 to 84 months, featuring fixed monthly payments and interest rates based on your credit profile, plus fast, same-day funding is possible after approval.
Personal Loans, Unsecured, Fixed Rate | TD Bank Fit Loan - TD Bank provides unsecured personal loans between $2,000 and $50,000 with fixed interest rates, terms up to 60 months, no fees, no prepayment penalties, and funds available within one business day after approval.
Loans | U.S. Small Business Administration - The SBA offers government-backed loans to small businesses for various purposes including operating capital and fixed assets, by partnering with lenders to reduce risk and expand access to financing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com