Quantitative tightening involves the Federal Reserve reducing liquidity by selling government securities or allowing them to mature, which decreases the money supply and aims to control inflation. Balance sheet reduction is a specific method within quantitative tightening focused on shrinking the central bank's assets by decreasing holdings of Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed securities. Explore how these financial strategies impact interest rates, credit availability, and economic growth to understand their role in monetary policy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quantitative tightening and balance sheet reduction is crucial for interpreting central bank policies and their impact on interest rates, inflation, and financial markets. Quantitative tightening refers to the process of increasing interest rates to control money supply, while balance sheet reduction involves selling off or allowing assets to mature to shrink the central bank's financial holdings. This distinction helps investors and policymakers gauge the pace and methods of monetary policy normalization. Accurate knowledge of these concepts enables better forecasting of economic conditions and asset valuations.
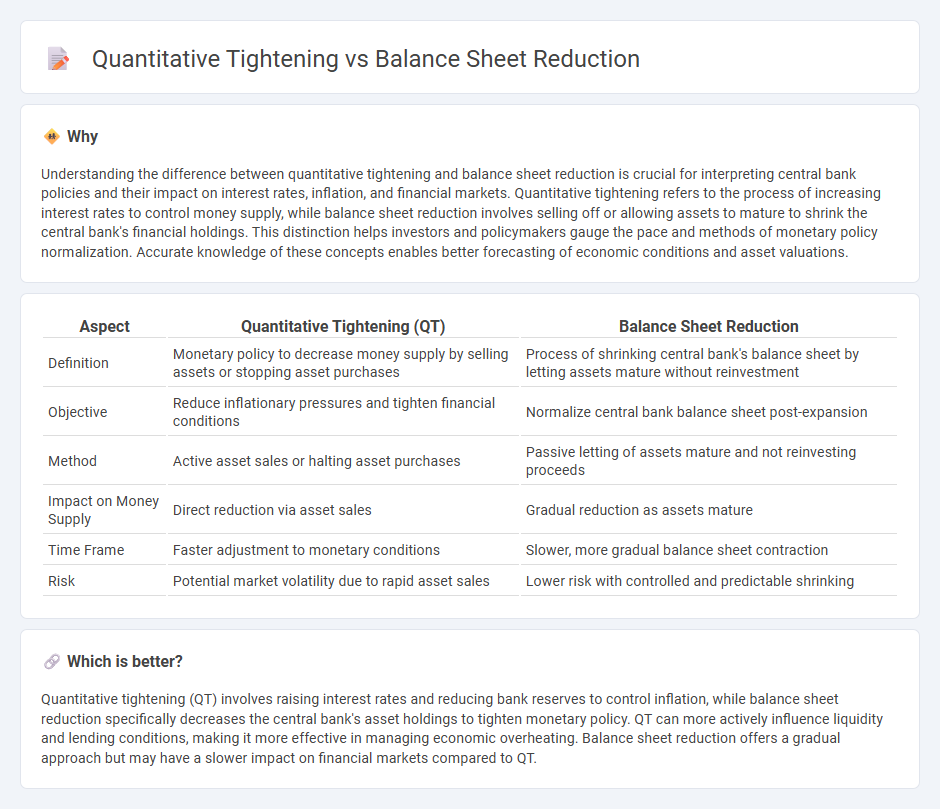
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Tightening (QT) | Balance Sheet Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monetary policy to decrease money supply by selling assets or stopping asset purchases | Process of shrinking central bank's balance sheet by letting assets mature without reinvestment |
| Objective | Reduce inflationary pressures and tighten financial conditions | Normalize central bank balance sheet post-expansion |
| Method | Active asset sales or halting asset purchases | Passive letting of assets mature and not reinvesting proceeds |
| Impact on Money Supply | Direct reduction via asset sales | Gradual reduction as assets mature |
| Time Frame | Faster adjustment to monetary conditions | Slower, more gradual balance sheet contraction |
| Risk | Potential market volatility due to rapid asset sales | Lower risk with controlled and predictable shrinking |
Which is better?
Quantitative tightening (QT) involves raising interest rates and reducing bank reserves to control inflation, while balance sheet reduction specifically decreases the central bank's asset holdings to tighten monetary policy. QT can more actively influence liquidity and lending conditions, making it more effective in managing economic overheating. Balance sheet reduction offers a gradual approach but may have a slower impact on financial markets compared to QT.
Connection
Quantitative tightening involves the Federal Reserve reducing its balance sheet by allowing government bonds and mortgage-backed securities to mature without reinvestment. This process decreases the central bank's assets, tightening monetary policy and reducing liquidity in the financial system. Balance sheet reduction is a critical mechanism through which quantitative tightening constrains credit availability and influences interest rates.
Key Terms
Central Bank Reserves
Balance sheet reduction involves the gradual selling or maturing of assets held by a central bank to decrease its balance sheet size and reduce excess reserves in the banking system. Quantitative tightening (QT) refers to the broader monetary policy strategy aimed at tightening liquidity conditions by shrinking central bank reserves and increasing interest rates. Explore more about how these mechanisms affect liquidity, inflation, and economic growth.
Securities Portfolio
Balance sheet reduction refers to the Federal Reserve's process of gradually decreasing its holdings of securities, primarily Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed securities, to normalize monetary policy following asset purchases. Quantitative tightening encompasses a broader strategy that includes balance sheet reduction alongside other measures like raising interest rates to reduce liquidity in the financial system. Explore more about how these policies impact securities portfolios and overall economic conditions.
Liquidity
Balance sheet reduction involves the Federal Reserve actively allowing its assets to mature without reinvestment, directly decreasing reserves and bank liquidity. Quantitative tightening broadly encompasses policies aimed at reducing money supply and tightening financial conditions, impacting liquidity by restricting credit availability. Explore detailed analyses to understand their nuanced effects on market liquidity.
Source and External Links
What is "Shrinking the Balance Sheet"? - Balance sheet reduction is a central bank strategy to tighten money supply by shrinking assets through asset sales, no reinvestment of maturing bonds, early debt repayment, and raising interest rates, which can affect inflation, interest rates, and employment.
Balance sheets: the not-so-visible normalisation of monetary policy - The reduction of central bank balance sheets is typically done passively by not renewing maturing assets, helping to decrease the central bank's market footprint and normalize monetary policy without causing market turmoil.
What are the implications of the Fed slowing down its balance sheet ... - The Federal Reserve reduces its balance sheet mainly by letting Treasuries and mortgage-backed securities mature without reinvestment, with recent policies slowing this reduction pace to moderate the effects on financial markets and liquidity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com