Carbon credits provide a market-based mechanism allowing companies to offset their greenhouse gas emissions by investing in environmental projects, while ESG investing focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance criteria into financial decisions to promote sustainable business practices. Both approaches aim to address climate impact but differ in strategy and risk exposure. Explore how these financial tools shape sustainable investing trends and opportunities.
Why it is important
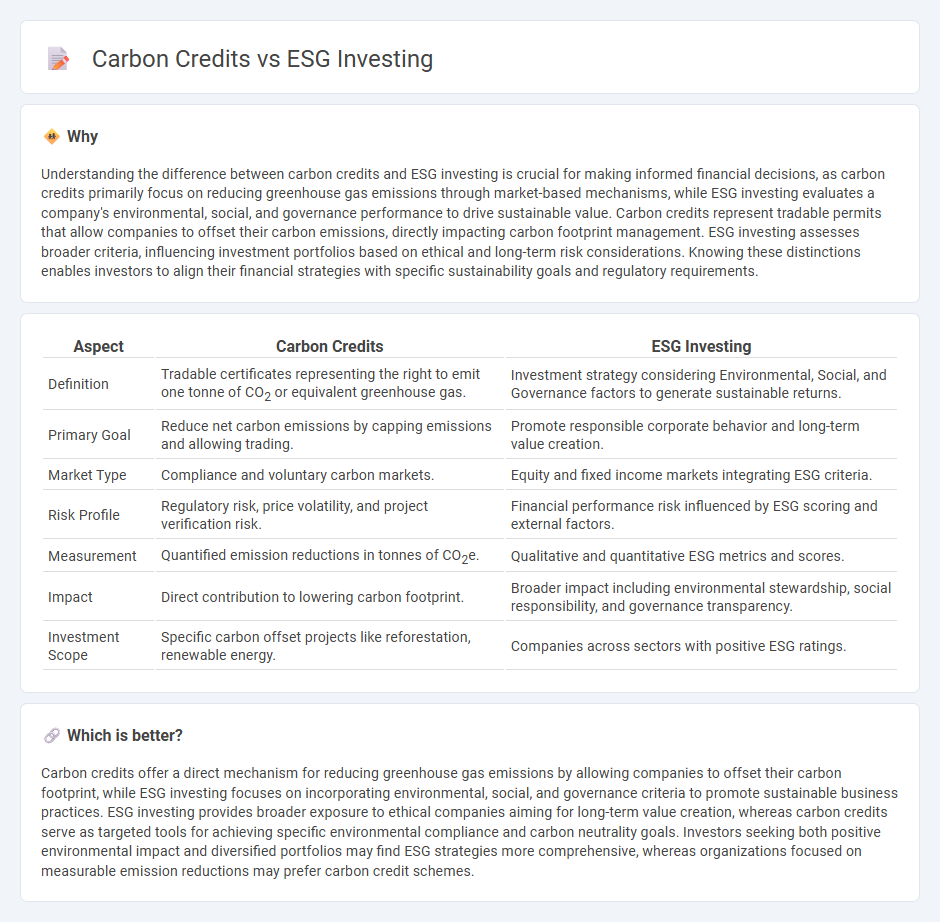
Understanding the difference between carbon credits and ESG investing is crucial for making informed financial decisions, as carbon credits primarily focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions through market-based mechanisms, while ESG investing evaluates a company's environmental, social, and governance performance to drive sustainable value. Carbon credits represent tradable permits that allow companies to offset their carbon emissions, directly impacting carbon footprint management. ESG investing assesses broader criteria, influencing investment portfolios based on ethical and long-term risk considerations. Knowing these distinctions enables investors to align their financial strategies with specific sustainability goals and regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Credits | ESG Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tradable certificates representing the right to emit one tonne of CO2 or equivalent greenhouse gas. | Investment strategy considering Environmental, Social, and Governance factors to generate sustainable returns. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce net carbon emissions by capping emissions and allowing trading. | Promote responsible corporate behavior and long-term value creation. |
| Market Type | Compliance and voluntary carbon markets. | Equity and fixed income markets integrating ESG criteria. |
| Risk Profile | Regulatory risk, price volatility, and project verification risk. | Financial performance risk influenced by ESG scoring and external factors. |
| Measurement | Quantified emission reductions in tonnes of CO2e. | Qualitative and quantitative ESG metrics and scores. |
| Impact | Direct contribution to lowering carbon footprint. | Broader impact including environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and governance transparency. |
| Investment Scope | Specific carbon offset projects like reforestation, renewable energy. | Companies across sectors with positive ESG ratings. |
Which is better?
Carbon credits offer a direct mechanism for reducing greenhouse gas emissions by allowing companies to offset their carbon footprint, while ESG investing focuses on incorporating environmental, social, and governance criteria to promote sustainable business practices. ESG investing provides broader exposure to ethical companies aiming for long-term value creation, whereas carbon credits serve as targeted tools for achieving specific environmental compliance and carbon neutrality goals. Investors seeking both positive environmental impact and diversified portfolios may find ESG strategies more comprehensive, whereas organizations focused on measurable emission reductions may prefer carbon credit schemes.
Connection
Carbon credits represent a measurable reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, serving as a key component in ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing strategies by enabling companies to offset their environmental impact. ESG investing prioritizes companies with strong sustainability practices, where carbon credit usage demonstrates commitment to environmental responsibility and risk management. Integrating carbon credits into ESG portfolios supports global climate goals while enhancing long-term financial performance and investor appeal.
Key Terms
Sustainability
ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance criteria to evaluate companies' long-term sustainability and ethical impact, influencing capital allocation towards responsible businesses. Carbon credits function as market-based instruments allowing companies to offset their greenhouse gas emissions by purchasing credits generated from emission-reducing projects. Explore further insights into how ESG investing and carbon credits drive sustainable finance and corporate accountability.
Emissions Reduction
ESG investing prioritizes companies with strong environmental, social, and governance practices, targeting long-term sustainability and reduced carbon footprints. Carbon credits enable organizations to offset their emissions by funding projects that reduce greenhouse gases, directly contributing to climate impact mitigation. Explore the differences in emissions reduction strategies to understand their roles in combating climate change.
Greenwashing
ESG investing aims to promote sustainable business practices by evaluating environmental, social, and governance criteria, but it often faces criticism for greenwashing when companies exaggerate their eco-friendly initiatives. Carbon credits serve as a market-based mechanism to offset carbon emissions but may also be exploited for superficial environmental claims without real impact. Explore how these strategies tackle the challenges of authentic sustainability and greenwashing in today's corporate world.
Source and External Links
Embracing Sustainable Investment Practices with ESG Investing - ESG investing is a strategy that evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance factors, aiming to account for risks and positive impacts related to climate, social justice, and corporate practices, and it has shown strong growth and resilience in financial markets.
What is ESG Investing? - ESG investing, also called socially responsible or sustainable investing, prioritizes environmental, social, and governance outcomes, reflecting long-standing ethical investment traditions and growing influence from international guidelines like the UN Principles for Responsible Investment.
What is ESG investing? - Deutsche Bank Wealth Management - ESG investing incorporates environmental, social, and governance criteria alongside financial factors to promote investments that align with societal and ecological sustainability goals, and by 2020, over $35 trillion globally were invested with ESG principles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com