AI-driven portfolios leverage advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze large datasets and adapt to market changes dynamically, aiming to optimize returns and manage risks more effectively than traditional methods. In contrast, passive index portfolios track market indices with low fees and minimal turnover, offering broad market exposure and stable long-term growth. Explore how these investment strategies compare in performance, cost, and risk management to make informed financial decisions.
Why it is important
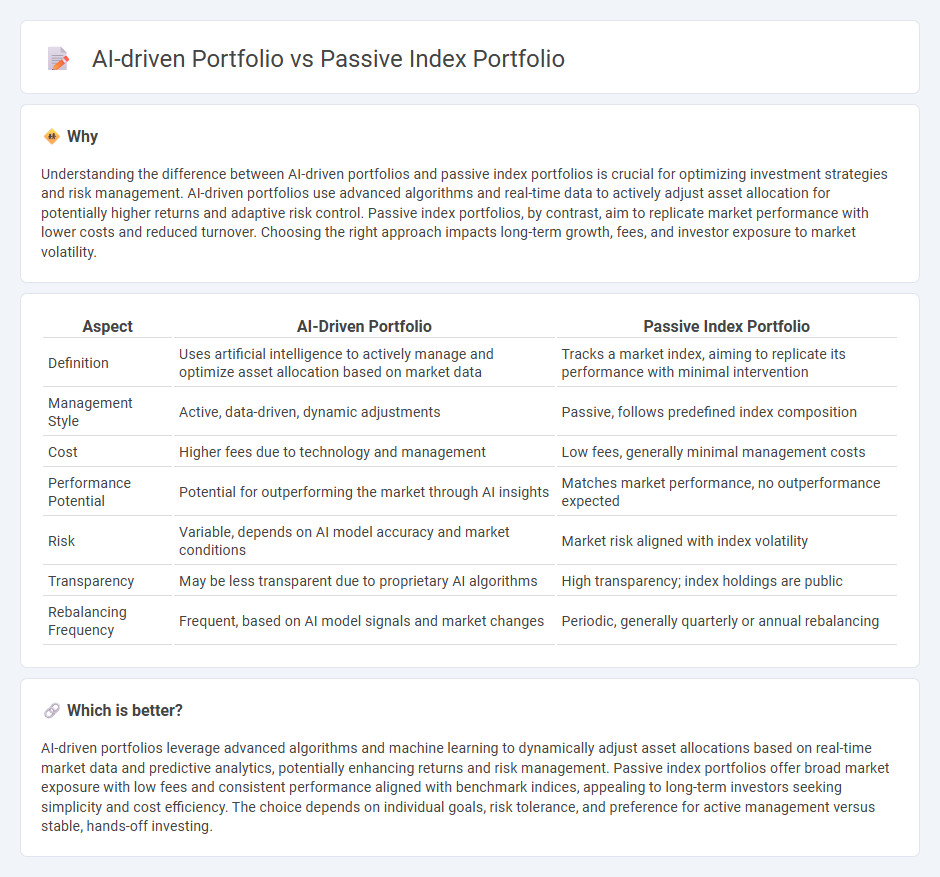
Understanding the difference between AI-driven portfolios and passive index portfolios is crucial for optimizing investment strategies and risk management. AI-driven portfolios use advanced algorithms and real-time data to actively adjust asset allocation for potentially higher returns and adaptive risk control. Passive index portfolios, by contrast, aim to replicate market performance with lower costs and reduced turnover. Choosing the right approach impacts long-term growth, fees, and investor exposure to market volatility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | AI-Driven Portfolio | Passive Index Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses artificial intelligence to actively manage and optimize asset allocation based on market data | Tracks a market index, aiming to replicate its performance with minimal intervention |
| Management Style | Active, data-driven, dynamic adjustments | Passive, follows predefined index composition |
| Cost | Higher fees due to technology and management | Low fees, generally minimal management costs |
| Performance Potential | Potential for outperforming the market through AI insights | Matches market performance, no outperformance expected |
| Risk | Variable, depends on AI model accuracy and market conditions | Market risk aligned with index volatility |
| Transparency | May be less transparent due to proprietary AI algorithms | High transparency; index holdings are public |
| Rebalancing Frequency | Frequent, based on AI model signals and market changes | Periodic, generally quarterly or annual rebalancing |
Which is better?
AI-driven portfolios leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning to dynamically adjust asset allocations based on real-time market data and predictive analytics, potentially enhancing returns and risk management. Passive index portfolios offer broad market exposure with low fees and consistent performance aligned with benchmark indices, appealing to long-term investors seeking simplicity and cost efficiency. The choice depends on individual goals, risk tolerance, and preference for active management versus stable, hands-off investing.
Connection
AI-driven portfolios enhance passive index portfolios by leveraging machine learning algorithms to optimize asset allocation and risk management, thereby improving returns while maintaining low costs. These AI models analyze vast datasets to identify subtle market patterns and dynamically adjust holdings within the passive index framework. This fusion enables investors to benefit from passive index diversification combined with AI's predictive analytics for more efficient portfolio performance.
Key Terms
Diversification
Passive index portfolios offer broad market exposure by tracking specific indices, ensuring diversified asset allocation with minimal management costs. AI-driven portfolios use advanced algorithms to analyze vast datasets, dynamically adjusting asset allocation to optimize risk and return diversification. Explore the advantages of each approach to determine the best fit for your investment strategy.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading in AI-driven portfolios leverages machine learning models and real-time data analysis to optimize asset selection and execution speed, contrasting with the static asset allocation in passive index portfolios. AI-driven strategies dynamically adjust to market volatility by identifying patterns and anomalies, potentially enhancing returns and reducing risk beyond traditional index tracking methods. Explore the benefits and challenges of integrating AI in portfolio management to understand its impact on modern investing.
Expense Ratio
Expense ratios significantly impact net returns in both passive index portfolios and AI-driven portfolios, with passive index funds typically offering lower expense ratios around 0.03% to 0.15%, while AI-driven portfolios may have higher fees due to active management and advanced analytics costs. Lower expense ratios in passive funds contribute to cost efficiency and long-term compounding advantages, whereas AI-driven portfolios aim to justify higher fees through enhanced performance and adaptive strategy optimization. Explore more to understand how expense ratios weigh in selecting the optimal investment approach.
Source and External Links
Passive Equity Investing | CFA Institute - Passive index portfolios aim to mimic benchmark indexes by constructing portfolios reflecting their characteristics, using methods like full replication or sampling, to track returns while controlling tracking error.
Guide to Passive Investing | Morningstar - Passive index portfolios replicate indexes using approaches such as full replication, sampling, or synthetic replication, focusing on minimizing tracking error and trading costs while managing index changes.
The Dirty Little Secret of Passive Investing | Research Affiliates - Passive index portfolios face implicit implementation costs from trading, which reduce gross returns more than apparent fees, a hidden cost to consider in passive investing strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com