Flash loan attacks exploit instant, uncollateralized loans to manipulate decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, leading to rapid financial exploitation. Governance attacks target voting mechanisms within blockchain ecosystems, allowing attackers to influence protocol decisions and redirect assets. Discover how these attack vectors impact financial security and strategies to mitigate risks.
Why it is important
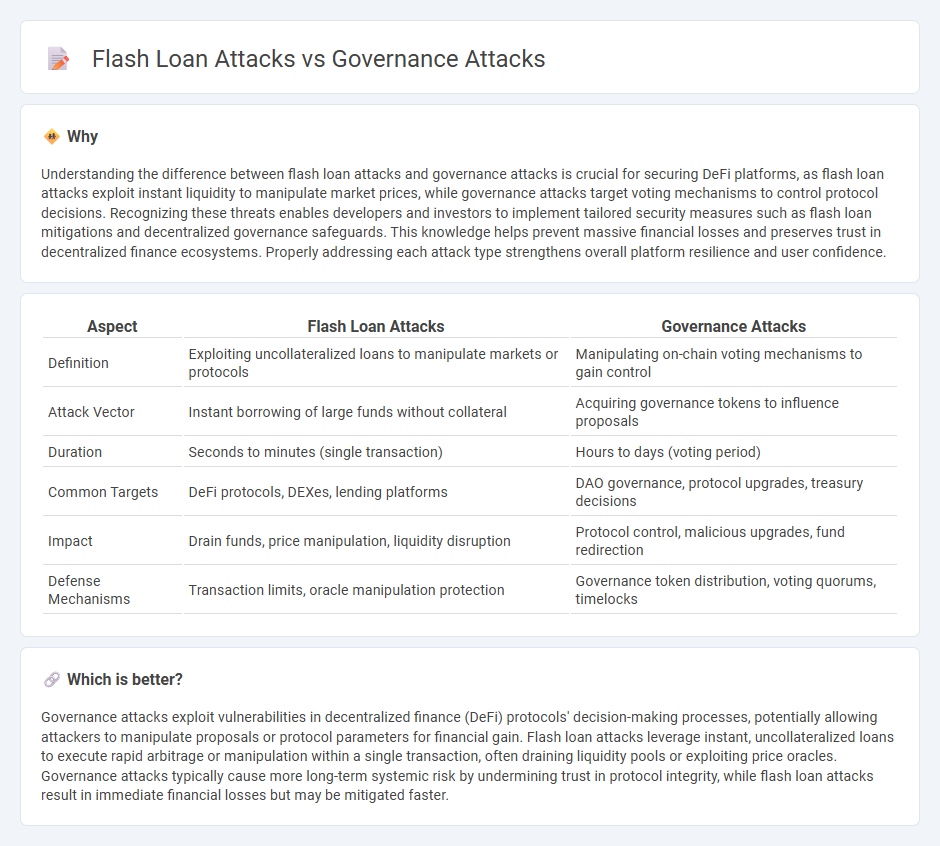
Understanding the difference between flash loan attacks and governance attacks is crucial for securing DeFi platforms, as flash loan attacks exploit instant liquidity to manipulate market prices, while governance attacks target voting mechanisms to control protocol decisions. Recognizing these threats enables developers and investors to implement tailored security measures such as flash loan mitigations and decentralized governance safeguards. This knowledge helps prevent massive financial losses and preserves trust in decentralized finance ecosystems. Properly addressing each attack type strengthens overall platform resilience and user confidence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flash Loan Attacks | Governance Attacks |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting uncollateralized loans to manipulate markets or protocols | Manipulating on-chain voting mechanisms to gain control |
| Attack Vector | Instant borrowing of large funds without collateral | Acquiring governance tokens to influence proposals |
| Duration | Seconds to minutes (single transaction) | Hours to days (voting period) |
| Common Targets | DeFi protocols, DEXes, lending platforms | DAO governance, protocol upgrades, treasury decisions |
| Impact | Drain funds, price manipulation, liquidity disruption | Protocol control, malicious upgrades, fund redirection |
| Defense Mechanisms | Transaction limits, oracle manipulation protection | Governance token distribution, voting quorums, timelocks |
Which is better?
Governance attacks exploit vulnerabilities in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols' decision-making processes, potentially allowing attackers to manipulate proposals or protocol parameters for financial gain. Flash loan attacks leverage instant, uncollateralized loans to execute rapid arbitrage or manipulation within a single transaction, often draining liquidity pools or exploiting price oracles. Governance attacks typically cause more long-term systemic risk by undermining trust in protocol integrity, while flash loan attacks result in immediate financial losses but may be mitigated faster.
Connection
Flash loan attacks exploit instant, uncollateralized borrowing to manipulate blockchain governance mechanisms by temporarily acquiring large voting power. Governance attacks leverage this temporary influence to pass malicious proposals or alter protocol rules, undermining decentralized finance (DeFi) security. Understanding the link between these attack vectors is crucial for developing robust DeFi governance protocols that resist exploitation and safeguard user assets.
Key Terms
Voting Power Manipulation (Governance Attacks)
Governance attacks exploit voting power manipulation by accumulating tokens through flash loans to influence decentralized protocol decisions without long-term stake commitment. Flash loan attacks rapidly borrow large sums to temporarily boost voting weight, enabling attackers to pass malicious proposals or disrupt governance processes. Explore deeper insights into safeguarding decentralized governance from such vulnerabilities.
Instant Liquidity Exploitation (Flash Loan Attacks)
Flash loan attacks leverage uncollateralized loans to manipulate DeFi protocols' instant liquidity, exploiting vulnerabilities in governance mechanisms and smart contracts for rapid financial gain. Governance attacks involve manipulating voting power, often through flash loans, to pass malicious proposals but rely on the same instant liquidity principle. Explore detailed insights into how these attacks impact decentralized finance security frameworks.
Protocol Vulnerabilities
Governance attacks exploit protocol vulnerabilities by manipulating voting mechanisms to gain control over decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, often through accumulation of governance tokens, which can be facilitated by flash loans. Flash loan attacks leverage these instant, uncollateralized loans to temporarily amass assets, enabling attackers to influence protocol governance or execute exploitative actions before the loan is repaid. Explore the mechanisms behind these attacks and how protocols can strengthen defenses against such vulnerabilities.
Source and External Links
Governance Attack - Cyfrin Glossary - A governance attack seeks to use malicious proposals in DAO smart contract governance systems to steal funds by gaining enough voting power often via flash loans to immediately vote on and implement harmful proposals.
Understanding Governance Attacks: A Case Study of Compound - Governance attacks manipulate decentralized protocols by acquiring majority voting power or swaying token holders to push harmful proposals, including through voting manipulation or proposal hijacking.
Governance Attacks in Smart Contracts - Metana - Governance attacks involve manipulating DAO governance mechanisms to seize control, as seen in real incidents like the Beanstalk flash loan attack that drained $181M, exposing vulnerabilities in DAO security.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com