Zero-day work contracts allow employees to work without guaranteed hours, creating flexible yet unpredictable income streams, while temporary agency work involves hiring through staffing firms that provide fixed-term assignments with more structured hours and employee benefits. The economic impact of zero-day contracts reflects growing labor market flexibility but raises concerns about job security and social protection. Explore the nuances and implications of these evolving employment models to better understand their roles in modern economies.
Why it is important
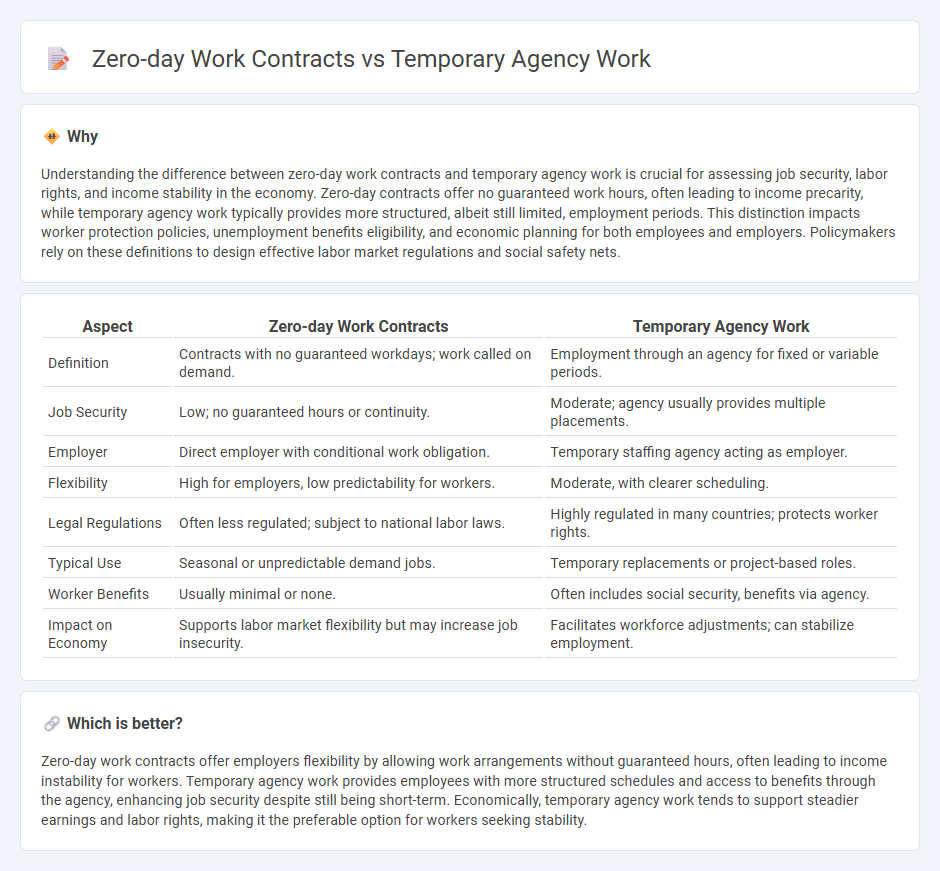
Understanding the difference between zero-day work contracts and temporary agency work is crucial for assessing job security, labor rights, and income stability in the economy. Zero-day contracts offer no guaranteed work hours, often leading to income precarity, while temporary agency work typically provides more structured, albeit still limited, employment periods. This distinction impacts worker protection policies, unemployment benefits eligibility, and economic planning for both employees and employers. Policymakers rely on these definitions to design effective labor market regulations and social safety nets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero-day Work Contracts | Temporary Agency Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contracts with no guaranteed workdays; work called on demand. | Employment through an agency for fixed or variable periods. |
| Job Security | Low; no guaranteed hours or continuity. | Moderate; agency usually provides multiple placements. |
| Employer | Direct employer with conditional work obligation. | Temporary staffing agency acting as employer. |
| Flexibility | High for employers, low predictability for workers. | Moderate, with clearer scheduling. |
| Legal Regulations | Often less regulated; subject to national labor laws. | Highly regulated in many countries; protects worker rights. |
| Typical Use | Seasonal or unpredictable demand jobs. | Temporary replacements or project-based roles. |
| Worker Benefits | Usually minimal or none. | Often includes social security, benefits via agency. |
| Impact on Economy | Supports labor market flexibility but may increase job insecurity. | Facilitates workforce adjustments; can stabilize employment. |
Which is better?
Zero-day work contracts offer employers flexibility by allowing work arrangements without guaranteed hours, often leading to income instability for workers. Temporary agency work provides employees with more structured schedules and access to benefits through the agency, enhancing job security despite still being short-term. Economically, temporary agency work tends to support steadier earnings and labor rights, making it the preferable option for workers seeking stability.
Connection
Zero-day work contracts and temporary agency work are connected through their shared focus on flexible labor arrangements that prioritize short-term employment without long-term commitments. Both mechanisms offer employers rapid workforce adjustments and cost savings by circumventing standard employment protections, often impacting job security and employee benefits. Temporary agency work typically utilizes zero-day contracts to assign workers to various assignments on demand, emphasizing immediate deployment over stable employment.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Temporary agency work offers enhanced flexibility by allowing employees to move between assignments with varying durations, enabling businesses to quickly adjust workforce levels based on demand fluctuations. Zero-day work contracts, often characterized by their immediate start and end dates, provide ultra-short-term engagement but may limit continuity and long-term planning. Explore the advantages and constraints of each to determine the optimal flexibility solution for your workforce needs.
Employment relationship
Temporary agency work involves a tripartite employment relationship where the agency employs the worker and assigns them to a client company, maintaining legal responsibility for wages and working conditions. Zero-day work contracts, often used for sporadic or occasional labor, establish a direct bilateral employment relationship with the employer, activating only on days the worker is called in without guaranteed hours. Explore the distinctions and legal implications surrounding these employment relationships for better workforce management insights.
Job security
Temporary agency work offers more job security than zero-day work contracts due to regulated assignment durations and social protection under labor laws in many countries. Zero-day contracts, with no guaranteed workdays, lead to unpredictable income and limited access to benefits, increasing employment instability. Explore detailed comparisons of job security measures between these two contract types to understand their implications for workforce stability.
Source and External Links
Labor Finders - Offers flexible and stable temporary and permanent job opportunities across the country, connecting job seekers with companies looking to fill positions quickly.
Adecco - Provides a wide range of direct hire and temporary jobs, managing the recruitment process from application to placement for candidates and employers in various industries.
PeopleReady - Specializes in on-demand temporary staffing for industries like construction, manufacturing, and hospitality, using a digital platform to match job seekers with local opportunities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com