Unretirement reflects a growing trend where individuals return to the workforce after retirement, driven by financial needs, personal fulfillment, or changes in economic conditions. This shift impacts labor markets, pension systems, and consumer behavior, highlighting evolving socioeconomic dynamics. Explore how unretirement reshapes economic landscapes and personal finance strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between unretirement and retirement is crucial for accurate financial planning and managing career transitions. Unretirement involves re-entering the workforce after a period of retirement, impacting income streams and social benefits differently than traditional retirement. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals optimize their savings, tax strategies, and healthcare planning. Clear knowledge ensures informed decisions to maintain financial stability in later life stages.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Unretirement | Retirement |
|---|---|---|
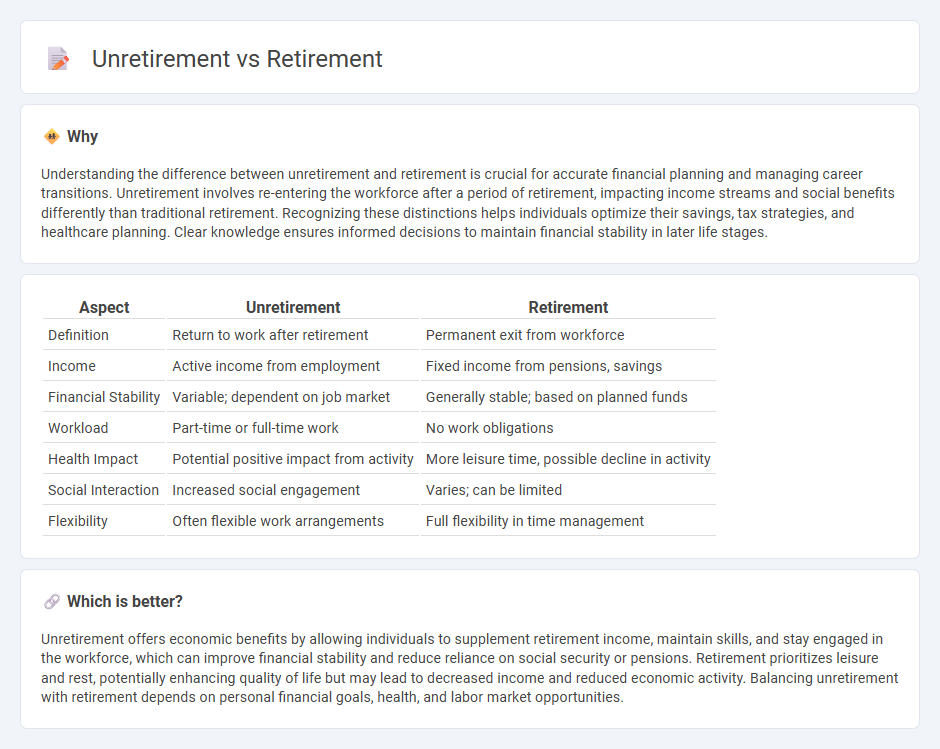
| Definition | Return to work after retirement | Permanent exit from workforce |
| Income | Active income from employment | Fixed income from pensions, savings |
| Financial Stability | Variable; dependent on job market | Generally stable; based on planned funds |
| Workload | Part-time or full-time work | No work obligations |
| Health Impact | Potential positive impact from activity | More leisure time, possible decline in activity |
| Social Interaction | Increased social engagement | Varies; can be limited |
| Flexibility | Often flexible work arrangements | Full flexibility in time management |
Which is better?
Unretirement offers economic benefits by allowing individuals to supplement retirement income, maintain skills, and stay engaged in the workforce, which can improve financial stability and reduce reliance on social security or pensions. Retirement prioritizes leisure and rest, potentially enhancing quality of life but may lead to decreased income and reduced economic activity. Balancing unretirement with retirement depends on personal financial goals, health, and labor market opportunities.
Connection
Unretirement reflects a growing trend where retirees re-enter the workforce, blending retirement with continued economic participation. This shift influences labor market dynamics and impacts retirement savings strategies, social security systems, and overall economic productivity. Understanding the linkage between retirement timing and unretirement behavior is crucial for policymakers addressing aging populations and workforce sustainability.
Key Terms
Pension
Pension benefits often differ significantly between retirement and unretirement, with many plans imposing restrictions or reduced payouts upon returning to work after retiring. Understanding how pension recalculations, eligibility criteria, and contribution requirements change during unretirement can protect one's financial security. Explore the detailed implications of pension options to make informed decisions about retiring or reentering the workforce.
Labor Force Participation
Labor force participation rates among retirees show a growing trend toward unretirement, where individuals re-enter the workforce after leaving full-time employment. Economic necessity, changes in health status, and evolving retirement preferences drive this shift, impacting social security dynamics and workforce demographics. Explore the factors influencing retirement and unretirement to better understand labor market transformations.
Social Security
Social Security benefits are crucial considerations in retirement planning, with claiming strategies significantly impacting monthly payments and lifetime income. Unretirement, or returning to work after retirement, can affect Social Security benefits through earnings limits and potential tax implications, possibly increasing long-term financial security. Explore tailored advice on maximizing your Social Security benefits during both retirement and unretirement phases.
Source and External Links
Retirement - Retirement is the withdrawal from one's occupation or active work life, often occurring due to age, health, or eligibility for pension benefits, with modern pension systems mostly introduced in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Social Security sets a new retirement age for 2026 - Starting in 2026, the Full Retirement Age (FRA) for Social Security benefits will be 67 for those born in 1960 or later, with benefits available as early as 62 but at reduced rates, and delayed claiming up to age 70 increasing benefits by up to 32%.
The Scariest Retirement Regrets You'll Never Hear - Delaying retirement benefits improves security in later years, helps maximize lifetime income, and stresses the importance of eliminating debt before retiring to avoid financial strain on a fixed income.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com