Gigification transforms the economy by enabling flexible, on-demand work through digital platforms that connect freelancers with clients, fostering rapid service exchange and entrepreneurial opportunities. Cooperatives emphasize collective ownership and democratic decision-making, focusing on long-term economic sustainability and equitable profit distribution among members. Explore the contrasting impacts of gigification and cooperatives on economic structures and workforce dynamics.
Why it is important
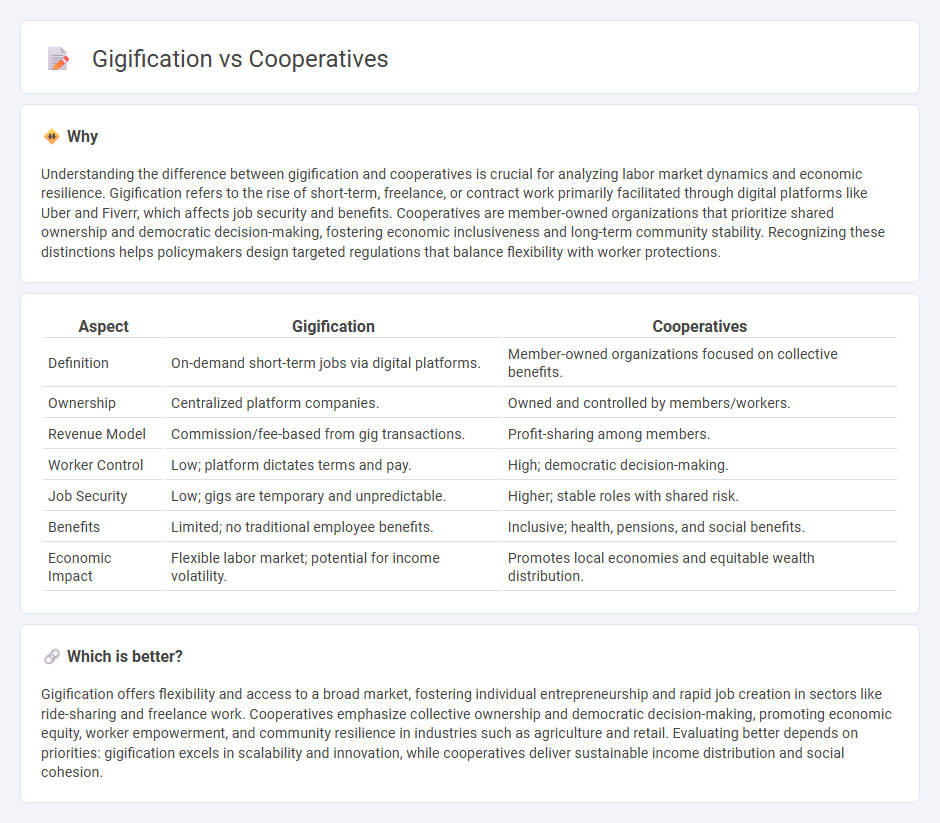
Understanding the difference between gigification and cooperatives is crucial for analyzing labor market dynamics and economic resilience. Gigification refers to the rise of short-term, freelance, or contract work primarily facilitated through digital platforms like Uber and Fiverr, which affects job security and benefits. Cooperatives are member-owned organizations that prioritize shared ownership and democratic decision-making, fostering economic inclusiveness and long-term community stability. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers design targeted regulations that balance flexibility with worker protections.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gigification | Cooperatives |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | On-demand short-term jobs via digital platforms. | Member-owned organizations focused on collective benefits. |
| Ownership | Centralized platform companies. | Owned and controlled by members/workers. |
| Revenue Model | Commission/fee-based from gig transactions. | Profit-sharing among members. |
| Worker Control | Low; platform dictates terms and pay. | High; democratic decision-making. |
| Job Security | Low; gigs are temporary and unpredictable. | Higher; stable roles with shared risk. |
| Benefits | Limited; no traditional employee benefits. | Inclusive; health, pensions, and social benefits. |
| Economic Impact | Flexible labor market; potential for income volatility. | Promotes local economies and equitable wealth distribution. |
Which is better?
Gigification offers flexibility and access to a broad market, fostering individual entrepreneurship and rapid job creation in sectors like ride-sharing and freelance work. Cooperatives emphasize collective ownership and democratic decision-making, promoting economic equity, worker empowerment, and community resilience in industries such as agriculture and retail. Evaluating better depends on priorities: gigification excels in scalability and innovation, while cooperatives deliver sustainable income distribution and social cohesion.
Connection
Gigification transforms traditional employment by promoting flexible, task-based work, which challenges workers' stability and benefits access. Cooperatives offer a collective alternative, enabling gig workers to band together for shared ownership, equitable profit distribution, and mutual support. This synergy enhances economic resilience by merging gig economy flexibility with cooperative security and democratic governance.
Key Terms
Collective Ownership
Collective ownership in cooperatives ensures that members share equal stakes and democratic control, contrasting sharply with gigification, which emphasizes individual contracts and fragmented work. Cooperatives foster sustainable economic models by reinvesting profits into the community and strengthening member bonds. Explore how collective ownership shapes resilient and inclusive work ecosystems.
Platform Labor
Cooperatives offer platform workers collective ownership and democratic decision-making, contrasting with the gigification trend that often emphasizes individual, on-demand labor without job security. Platform labor in cooperatives ensures fair wages, benefits, and improved working conditions by pooling resources and sharing profits among members. Explore how cooperative models challenge gigification and promote sustainable platform labor for a fairer future.
Profit Distribution
Cooperatives prioritize equitable profit distribution among members, ensuring earnings reflect their contribution and fostering collective ownership. Gigification often centralizes profits with platforms, offering minimal revenue sharing to workers despite their significant roles. Explore how profit-sharing models impact worker empowerment and economic fairness in both systems.
Source and External Links
What is a Cooperative? - A cooperative is an organization owned and democratically controlled by its members to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs, sharing profits and decision-making equally among members without discrimination.
What are Cooperatives? | Business Enterprise Institute - Cooperatives are member-owned businesses operated democratically to serve members' interests and distribute earnings back to member-owners while adhering to the 7 Cooperative Principles such as voluntary membership and concern for community.
Cooperative - Wikipedia - A cooperative is a legal entity owned and controlled by members who benefit proportionally to their participation, existing in types like worker, consumer, producer, purchasing, and housing cooperatives, balancing profit-making with community interests.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com