Workation blends remote work with travel by staying temporarily in one location, fostering productivity alongside leisure. Digital nomadism involves continuous movement across multiple destinations, emphasizing a location-independent lifestyle driven by technology. Explore how these trends reshape modern economic behaviors and work-life balance.
Why it is important
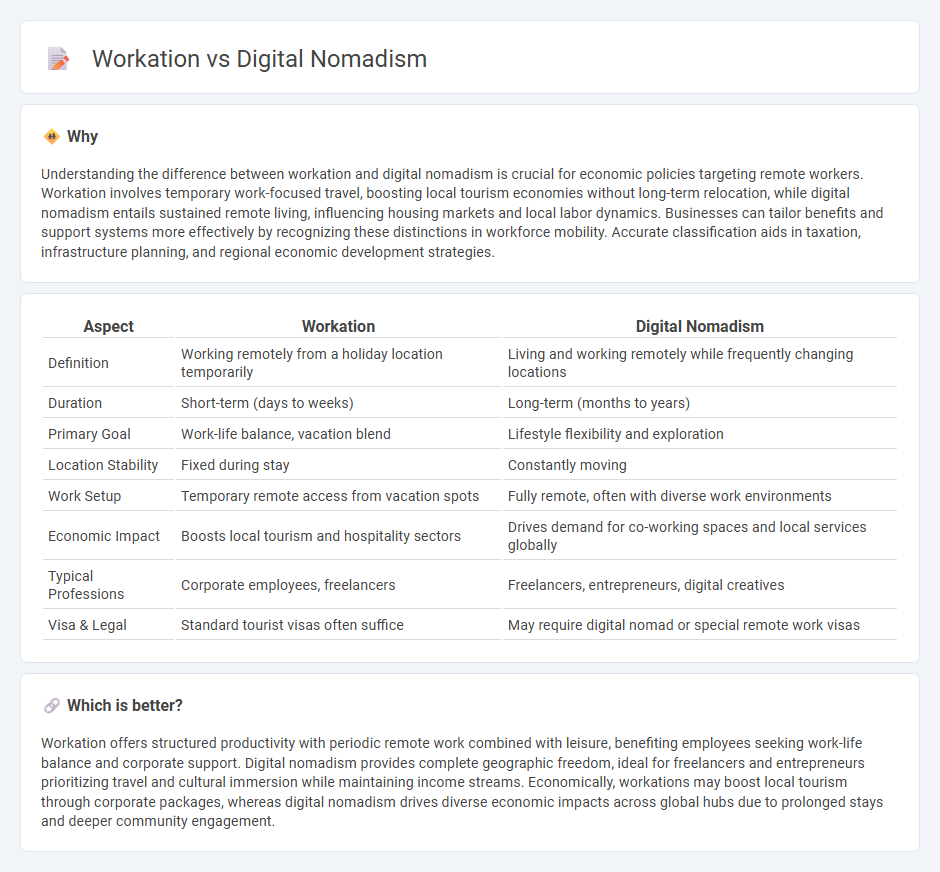
Understanding the difference between workation and digital nomadism is crucial for economic policies targeting remote workers. Workation involves temporary work-focused travel, boosting local tourism economies without long-term relocation, while digital nomadism entails sustained remote living, influencing housing markets and local labor dynamics. Businesses can tailor benefits and support systems more effectively by recognizing these distinctions in workforce mobility. Accurate classification aids in taxation, infrastructure planning, and regional economic development strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Workation | Digital Nomadism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Working remotely from a holiday location temporarily | Living and working remotely while frequently changing locations |
| Duration | Short-term (days to weeks) | Long-term (months to years) |
| Primary Goal | Work-life balance, vacation blend | Lifestyle flexibility and exploration |
| Location Stability | Fixed during stay | Constantly moving |
| Work Setup | Temporary remote access from vacation spots | Fully remote, often with diverse work environments |
| Economic Impact | Boosts local tourism and hospitality sectors | Drives demand for co-working spaces and local services globally |
| Typical Professions | Corporate employees, freelancers | Freelancers, entrepreneurs, digital creatives |
| Visa & Legal | Standard tourist visas often suffice | May require digital nomad or special remote work visas |
Which is better?
Workation offers structured productivity with periodic remote work combined with leisure, benefiting employees seeking work-life balance and corporate support. Digital nomadism provides complete geographic freedom, ideal for freelancers and entrepreneurs prioritizing travel and cultural immersion while maintaining income streams. Economically, workations may boost local tourism through corporate packages, whereas digital nomadism drives diverse economic impacts across global hubs due to prolonged stays and deeper community engagement.
Connection
Workation and digital nomadism drive economic growth by boosting demand in local hospitality, coworking spaces, and service sectors. Increased remote work flexibility enables professionals to choose diverse geographic locations, stimulating regional economies with sustained spending. This shift promotes global talent redistribution and supports the rise of location-independent entrepreneurship.
Key Terms
Remote Work
Digital nomadism involves individuals working remotely while continuously traveling and living in various locations, embracing a flexible lifestyle without a fixed base. In contrast, workation blends remote work with vacation by allowing professionals to temporarily work from a leisure destination, balancing productivity with relaxation. Explore detailed distinctions and benefits between digital nomadism and workation to enhance your remote work experience.
Mobility
Digital nomadism emphasizes continuous mobility, allowing individuals to work from various global locations without a fixed base, leveraging remote work technologies to maintain productivity. Workation typically involves combining work with leisure at a single destination for a limited period, prioritizing comfort over extensive travel. Explore the distinctions and benefits of both lifestyles to optimize your mobile work experience.
Local Economic Impact
Digital nomadism significantly boosts local economies by increasing demand for long-term housing, coworking spaces, and services, fostering sustainable growth especially in emerging tourist destinations. Workations primarily benefit short-term hospitality sectors such as hotels, restaurants, and event venues, generating immediate but often less sustained economic activity. Explore how both trends reshape local markets and community development in greater detail.
Source and External Links
Digital nomad - A digital nomad is someone who travels freely while working remotely, using technology like the Internet, often living minimally and working from temporary locations like cafes or co-working spaces; the community has grown significantly, with 18.1 million American digital nomads in 2024, valuing travel, location independence, and lower living costs.
The New Reality of Digital Nomads - Digital nomadism is a rising lifestyle that leverages remote work for living in diverse, affordable locations worldwide, expanding beyond tech professionals to families and retirees, partly due to easier access to digital nomad visas after the pandemic.
2024 Digital Nomads Trends Report - Digital nomads often practice geo-arbitrage by living in low-cost areas while earning from higher-wage employers, enjoying flexibility and autonomy, with 95% planning to continue nomadism at least temporarily and expressing optimism about their careers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com