Locavesting focuses on investing in local businesses and communities to stimulate regional economic growth, often emphasizing shorter supply chains and local resource utilization. Sustainable investing prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to achieve long-term financial returns while promoting ethical practices and mitigating environmental impact. Explore deeper insights into how these investment strategies shape economic and social outcomes.
Why it is important
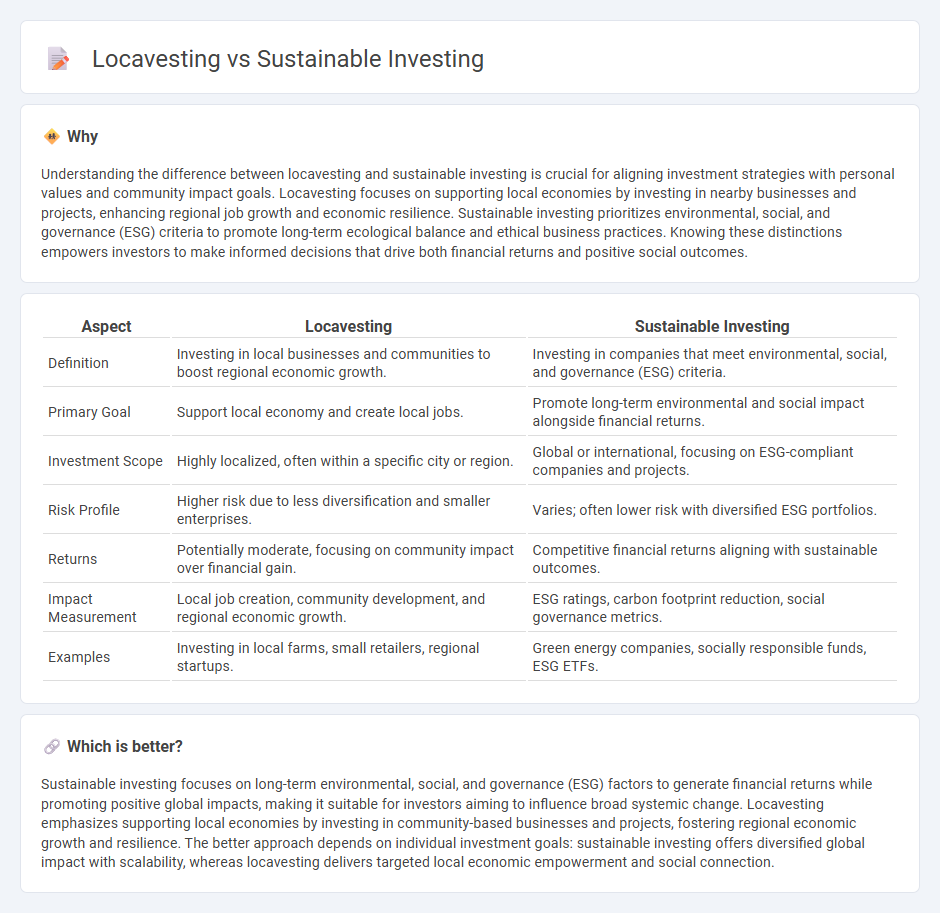
Understanding the difference between locavesting and sustainable investing is crucial for aligning investment strategies with personal values and community impact goals. Locavesting focuses on supporting local economies by investing in nearby businesses and projects, enhancing regional job growth and economic resilience. Sustainable investing prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term ecological balance and ethical business practices. Knowing these distinctions empowers investors to make informed decisions that drive both financial returns and positive social outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Locavesting | Sustainable Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing in local businesses and communities to boost regional economic growth. | Investing in companies that meet environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. |
| Primary Goal | Support local economy and create local jobs. | Promote long-term environmental and social impact alongside financial returns. |
| Investment Scope | Highly localized, often within a specific city or region. | Global or international, focusing on ESG-compliant companies and projects. |
| Risk Profile | Higher risk due to less diversification and smaller enterprises. | Varies; often lower risk with diversified ESG portfolios. |
| Returns | Potentially moderate, focusing on community impact over financial gain. | Competitive financial returns aligning with sustainable outcomes. |
| Impact Measurement | Local job creation, community development, and regional economic growth. | ESG ratings, carbon footprint reduction, social governance metrics. |
| Examples | Investing in local farms, small retailers, regional startups. | Green energy companies, socially responsible funds, ESG ETFs. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing focuses on long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to generate financial returns while promoting positive global impacts, making it suitable for investors aiming to influence broad systemic change. Locavesting emphasizes supporting local economies by investing in community-based businesses and projects, fostering regional economic growth and resilience. The better approach depends on individual investment goals: sustainable investing offers diversified global impact with scalability, whereas locavesting delivers targeted local economic empowerment and social connection.
Connection
Locavesting focuses on investing in local businesses to stimulate regional economic growth and community resilience. Sustainable investing prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, often overlapping with locavesting's goal of supporting eco-friendly and socially responsible enterprises. Both approaches drive capital toward projects that promote long-term economic sustainability and reduce carbon footprints within specific geographic areas.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Sustainable investing prioritizes ESG factors by integrating environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and strong governance practices into portfolio decisions to drive long-term value and reduce risks. Locavesting emphasizes investing in local businesses and communities, fostering economic growth and social impact at a regional level while also considering ESG criteria. Explore the distinct advantages and methodologies of sustainable investing versus locavesting to enhance your impact-driven investment strategy.
Community Development
Sustainable investing emphasizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term value while promoting global ethical practices. Locavesting prioritizes investing in local businesses and projects to directly bolster community economic growth and resilience. Explore how these strategies uniquely impact community development and contribute to a healthier economy.
Local Supply Chains
Sustainable investing emphasizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to support long-term global impact, while locavesting concentrates on strengthening local supply chains and boosting regional economies. By investing in local businesses and producers, locavesting fosters community resilience, reduces carbon footprints, and promotes economic self-sufficiency. Explore the benefits of both strategies to better understand their roles in advancing responsible investment practices.
Source and External Links
What Is Sustainable Investing? - This article explains sustainable investing as a practice that combines financial returns with long-term environmental and social value, using strategies like ESG integration.
Sustainable Investing - This resource provides an overview of sustainable investing, including common strategies like negative screening, positive screening, ESG integration, and impact investing.
Sustainability Solutions - MSCI offers solutions for integrating sustainability into investment processes, including risk management and sustainability reporting across various asset classes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com