De-dollarization aims to reduce reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance, strengthening national currencies and promoting financial sovereignty. Demonetization involves the withdrawal of a currency unit from circulation, often to combat inflation or corruption and encourage digital payments. Explore the economic impacts and strategic goals behind de-dollarization and demonetization to understand their roles in global finance.
Why it is important
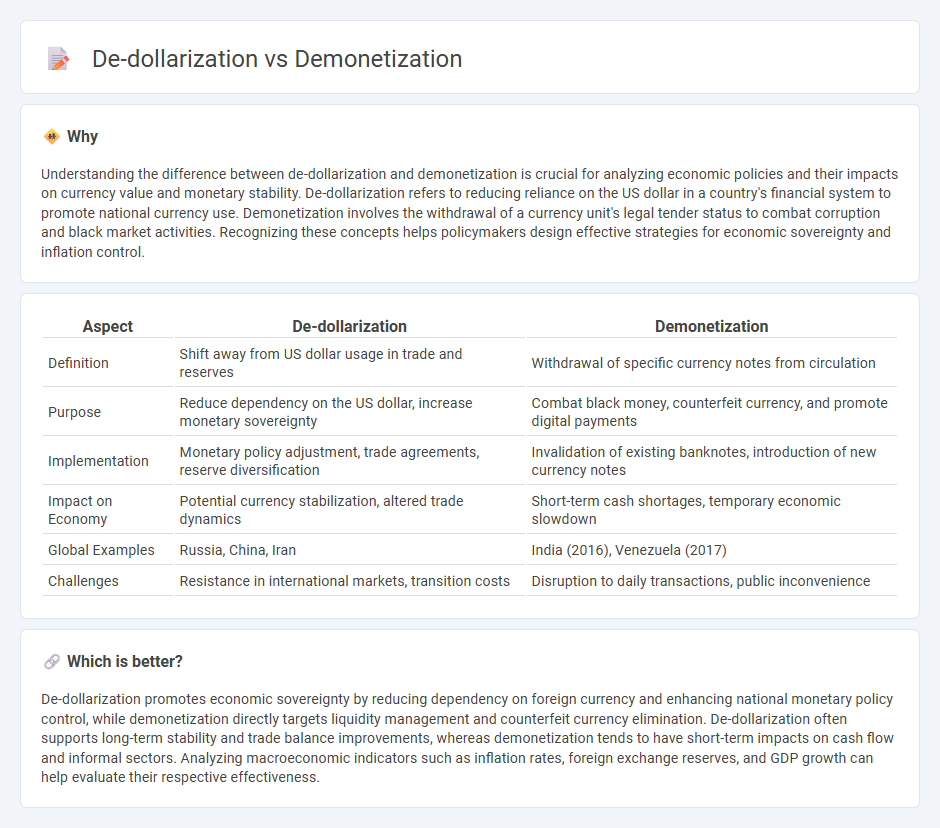
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and demonetization is crucial for analyzing economic policies and their impacts on currency value and monetary stability. De-dollarization refers to reducing reliance on the US dollar in a country's financial system to promote national currency use. Demonetization involves the withdrawal of a currency unit's legal tender status to combat corruption and black market activities. Recognizing these concepts helps policymakers design effective strategies for economic sovereignty and inflation control.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-dollarization | Demonetization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shift away from US dollar usage in trade and reserves | Withdrawal of specific currency notes from circulation |
| Purpose | Reduce dependency on the US dollar, increase monetary sovereignty | Combat black money, counterfeit currency, and promote digital payments |
| Implementation | Monetary policy adjustment, trade agreements, reserve diversification | Invalidation of existing banknotes, introduction of new currency notes |
| Impact on Economy | Potential currency stabilization, altered trade dynamics | Short-term cash shortages, temporary economic slowdown |
| Global Examples | Russia, China, Iran | India (2016), Venezuela (2017) |
| Challenges | Resistance in international markets, transition costs | Disruption to daily transactions, public inconvenience |
Which is better?
De-dollarization promotes economic sovereignty by reducing dependency on foreign currency and enhancing national monetary policy control, while demonetization directly targets liquidity management and counterfeit currency elimination. De-dollarization often supports long-term stability and trade balance improvements, whereas demonetization tends to have short-term impacts on cash flow and informal sectors. Analyzing macroeconomic indicators such as inflation rates, foreign exchange reserves, and GDP growth can help evaluate their respective effectiveness.
Connection
De-dollarization reduces dependence on the US dollar for international trade and reserves, weakening the dollar's global dominance and influencing currency stability. Demonetization, which involves withdrawing a currency's legal tender status, disrupts cash liquidity and accelerates the transition to digital or alternative payment systems. Both processes impact monetary policy effectiveness and financial system resilience by altering currency usage patterns and reducing reliance on traditional fiat currencies.
Key Terms
Currency replacement
Demonetization involves the government withdrawing the legal tender status of certain currency denominations, forcing replacement with new currency to curb black money and counterfeit notes. De-dollarization refers to reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and domestic transactions, promoting local currency usage to enhance monetary sovereignty. Explore the impacts and strategies of currency replacement in both processes to understand their economic significance.
Monetary policy
Demonetization involves the withdrawal of a country's currency from circulation to curb black money and counterfeit notes, directly impacting liquidity and consumer behavior. De-dollarization refers to reducing reliance on the US dollar in domestic and international transactions, aiming to strengthen national currency and enhance monetary sovereignty. Explore the nuances of these monetary policies and their implications on global economic stability.
Reserve currency
Demonetization involves the withdrawal of a currency's legal tender status, often disrupting domestic cash flow, while de-dollarization refers to reducing reliance on the US dollar as the global reserve currency to enhance national economic sovereignty. Countries pursue de-dollarization to mitigate exchange rate risks and gain greater control over monetary policy in the face of shifting geopolitical dynamics. Explore detailed strategies and impacts of both to understand their influence on global financial stability.
Source and External Links
Demonetization - Demonetization is an economic process where a country's currency unit is removed as legal tender, often to replace it with a new form of currency.
Demonetization - This economic process involves revoking a currency's legal tender status to address economic challenges such as inflation or to introduce new monetary systems.
2016 Indian banknote demonetisation - This event involved the demonetization of Rs500 and Rs1,000 banknotes in India to combat illegal activities and promote digital transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com