Slowbalization describes the gradual reduction of global economic integration, marked by slower trade growth and increased focus on regional markets, while economic decoupling refers to the deliberate separation of intertwined economies, often driven by geopolitical tensions between major powers like the US and China. Both phenomena reshape supply chains, investment flows, and technological exchanges, impacting global economic stability and growth trajectories. Explore the detailed implications of slowbalization and economic decoupling on modern economies for deeper insights.
Why it is important
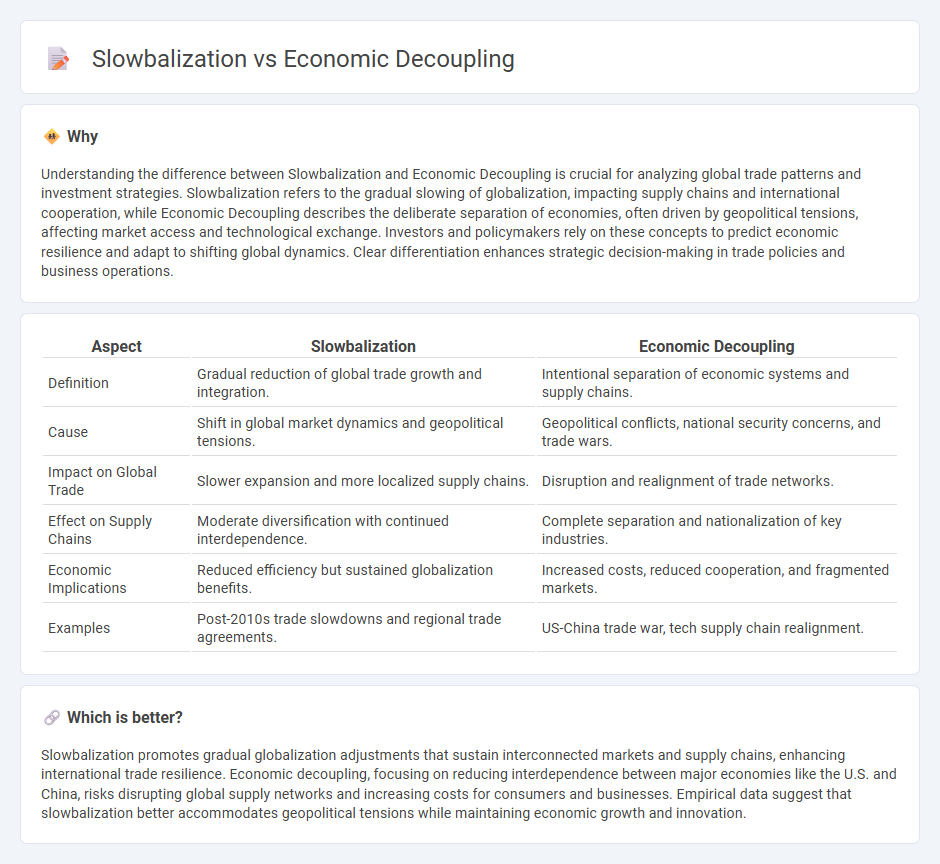
Understanding the difference between Slowbalization and Economic Decoupling is crucial for analyzing global trade patterns and investment strategies. Slowbalization refers to the gradual slowing of globalization, impacting supply chains and international cooperation, while Economic Decoupling describes the deliberate separation of economies, often driven by geopolitical tensions, affecting market access and technological exchange. Investors and policymakers rely on these concepts to predict economic resilience and adapt to shifting global dynamics. Clear differentiation enhances strategic decision-making in trade policies and business operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Slowbalization | Economic Decoupling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual reduction of global trade growth and integration. | Intentional separation of economic systems and supply chains. |
| Cause | Shift in global market dynamics and geopolitical tensions. | Geopolitical conflicts, national security concerns, and trade wars. |
| Impact on Global Trade | Slower expansion and more localized supply chains. | Disruption and realignment of trade networks. |
| Effect on Supply Chains | Moderate diversification with continued interdependence. | Complete separation and nationalization of key industries. |
| Economic Implications | Reduced efficiency but sustained globalization benefits. | Increased costs, reduced cooperation, and fragmented markets. |
| Examples | Post-2010s trade slowdowns and regional trade agreements. | US-China trade war, tech supply chain realignment. |
Which is better?
Slowbalization promotes gradual globalization adjustments that sustain interconnected markets and supply chains, enhancing international trade resilience. Economic decoupling, focusing on reducing interdependence between major economies like the U.S. and China, risks disrupting global supply networks and increasing costs for consumers and businesses. Empirical data suggest that slowbalization better accommodates geopolitical tensions while maintaining economic growth and innovation.
Connection
Slowbalization, characterized by the gradual reduction in the pace of global economic integration, directly influences economic decoupling by encouraging countries to prioritize domestic markets and regional supply chains over global interdependence. Economic decoupling, marked by the deliberate separation of major economies like the US and China in trade, technology, and finance, accelerates this trend by fostering localized production and diversified economic alliances. Both concepts highlight a shift from globalization to a more fragmented world economy with increased risks and opportunities for national economic sovereignty.
Key Terms
Global Value Chains
Economic decoupling refers to the deliberate reduction of interdependence between major economies, often visible in reshoring manufacturing and diversifying supply chains to reduce reliance on specific countries. Slowbalization describes the gradual slowing of globalization, characterized by more cautious cross-border trade and investment growth influencing the structure and expansion of global value chains (GVCs). Explore the evolving dynamics of GVCs to understand how these trends reshape international trade and economic strategies.
Trade Barriers
Trade barriers such as tariffs, quotas, and regulatory measures impact economic decoupling by disrupting global supply chains and encouraging regional self-reliance among major economies, particularly between the US and China. Slowbalization reflects a gradual slowdown in global trade growth influenced by increased protectionism, shifts in geopolitical tensions, and a preference for localized production, resulting in a more fragmented global economic landscape. Explore how varying trade policies shape the future of international commerce and economic integration.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Economic decoupling refers to the intentional reduction of interdependencies between major economies, often leading to a decline in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows as countries seek to localize supply chains and protect strategic industries. Slowbalization describes a gradual slowdown in global economic integration, reflected in the stabilization or modest decrease of FDI growth rather than abrupt disruptions. Explore the implications of these trends on global FDI patterns and investment strategies to fully understand their impact.
Source and External Links
The economic costs of supply chain decoupling - Economic decoupling, especially in global value chains, results in substantial trade losses, reduced resilience to shocks, and real income losses in both developed and emerging economies.
Eco-economic decoupling - Wikipedia - Economic decoupling refers to an economy's ability to grow without increasing environmental pressures, often involving sustaining growth while reducing resource usage and emissions.
How might economic decoupling or de-risking impact the global economy? - Economic decoupling between China and the West would reduce trade and technology cooperation, disrupt supply chains, increase tariffs, and negatively affect global business and innovation ecosystems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com