Greenflation refers to rising prices driven by increased costs in environmentally sustainable production methods and renewable energy investments, impacting sectors reliant on green technologies. Demand-pull inflation occurs when consumer demand outpaces supply, causing widespread price increases across the economy. Explore the distinct causes and impacts of greenflation versus demand-pull inflation for a deeper understanding of inflation dynamics.
Why it is important
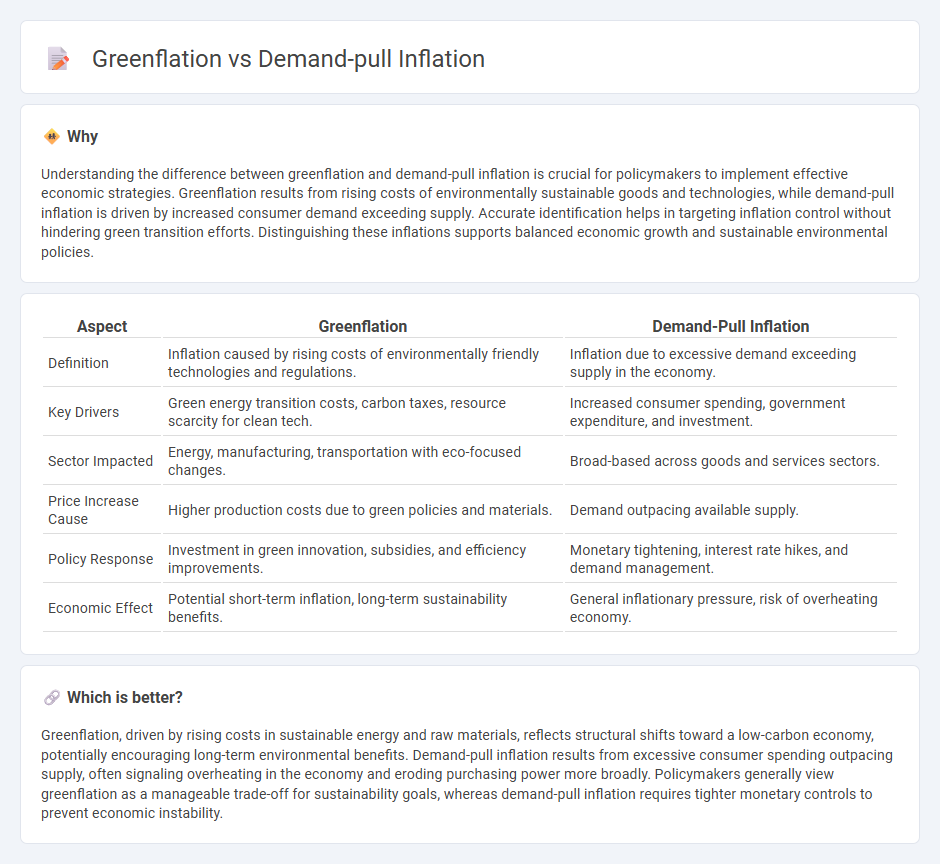
Understanding the difference between greenflation and demand-pull inflation is crucial for policymakers to implement effective economic strategies. Greenflation results from rising costs of environmentally sustainable goods and technologies, while demand-pull inflation is driven by increased consumer demand exceeding supply. Accurate identification helps in targeting inflation control without hindering green transition efforts. Distinguishing these inflations supports balanced economic growth and sustainable environmental policies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenflation | Demand-Pull Inflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflation caused by rising costs of environmentally friendly technologies and regulations. | Inflation due to excessive demand exceeding supply in the economy. |
| Key Drivers | Green energy transition costs, carbon taxes, resource scarcity for clean tech. | Increased consumer spending, government expenditure, and investment. |
| Sector Impacted | Energy, manufacturing, transportation with eco-focused changes. | Broad-based across goods and services sectors. |
| Price Increase Cause | Higher production costs due to green policies and materials. | Demand outpacing available supply. |
| Policy Response | Investment in green innovation, subsidies, and efficiency improvements. | Monetary tightening, interest rate hikes, and demand management. |
| Economic Effect | Potential short-term inflation, long-term sustainability benefits. | General inflationary pressure, risk of overheating economy. |
Which is better?
Greenflation, driven by rising costs in sustainable energy and raw materials, reflects structural shifts toward a low-carbon economy, potentially encouraging long-term environmental benefits. Demand-pull inflation results from excessive consumer spending outpacing supply, often signaling overheating in the economy and eroding purchasing power more broadly. Policymakers generally view greenflation as a manageable trade-off for sustainability goals, whereas demand-pull inflation requires tighter monetary controls to prevent economic instability.
Connection
Greenflation arises from increased production costs due to environmental regulations and renewable energy investments, which raise prices for raw materials and energy. Demand-pull inflation occurs when aggregate demand exceeds supply, pushing prices higher across the economy. Both phenomena interact as rising consumer demand for sustainable goods amplifies production costs, intensifying inflationary pressures in markets transitioning to green technologies.
Key Terms
Aggregate demand
Demand-pull inflation arises when aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply, leading to higher prices due to increased consumer spending and investment. Greenflation, a specific form of inflation linked to the transition to sustainable energy, is driven by rising costs in green technologies and raw materials, impacting aggregate demand through supply chain adjustments and investment shifts. Explore how these inflation types influence aggregate demand and economic policy further.
Renewable energy costs
Demand-pull inflation occurs when increased consumer demand drives up prices, impacting renewable energy by raising the cost of materials and services needed for production. Greenflation specifically refers to inflationary pressures stemming from the transition to renewable energy, where supply chain constraints and high demand for critical minerals like lithium and cobalt elevate costs. Explore the complex relationship between inflation types and renewable energy expenses to understand future economic impacts.
Supply constraints
Demand-pull inflation occurs when aggregate demand exceeds supply, pushing prices upward, while greenflation results from supply constraints linked to the transition to green energy, such as limited availability of critical minerals like lithium and cobalt. Supply chain disruptions, regulatory challenges, and increased production costs in renewable technologies exacerbate greenflation by restricting supply and raising prices. Explore further to understand how these supply constraints uniquely impact inflation dynamics in different economic contexts.
Source and External Links
Causes of Inflation | Explainer | Education | RBA - Demand-pull inflation arises when aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply, causing prices to rise as firms increase prices and wages to meet higher demand, leading to a cycle of rising incomes and further demand.
Demand-Pull Inflation: How Does It Work? - SmartAsset - Demand-pull inflation occurs when demand outpaces supply during strong economic growth, causing prices to rise as companies try to keep up, often creating a cycle of rising wages and prices.
Demand-pull inflation - Wikipedia - Demand-pull inflation happens when aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply, leading to inflation as output capacity is reached and prices rise, typically occurring at full employment in an overheating economy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com