Greenflation describes rising costs linked to environmental policies and clean energy transition, impacting sectors like manufacturing and energy production. Sustainable finance focuses on directing investments towards environmentally responsible projects, promoting long-term economic resilience and reduced carbon footprints. Explore how these dynamics shape the future of global markets and investment strategies.
Why it is important
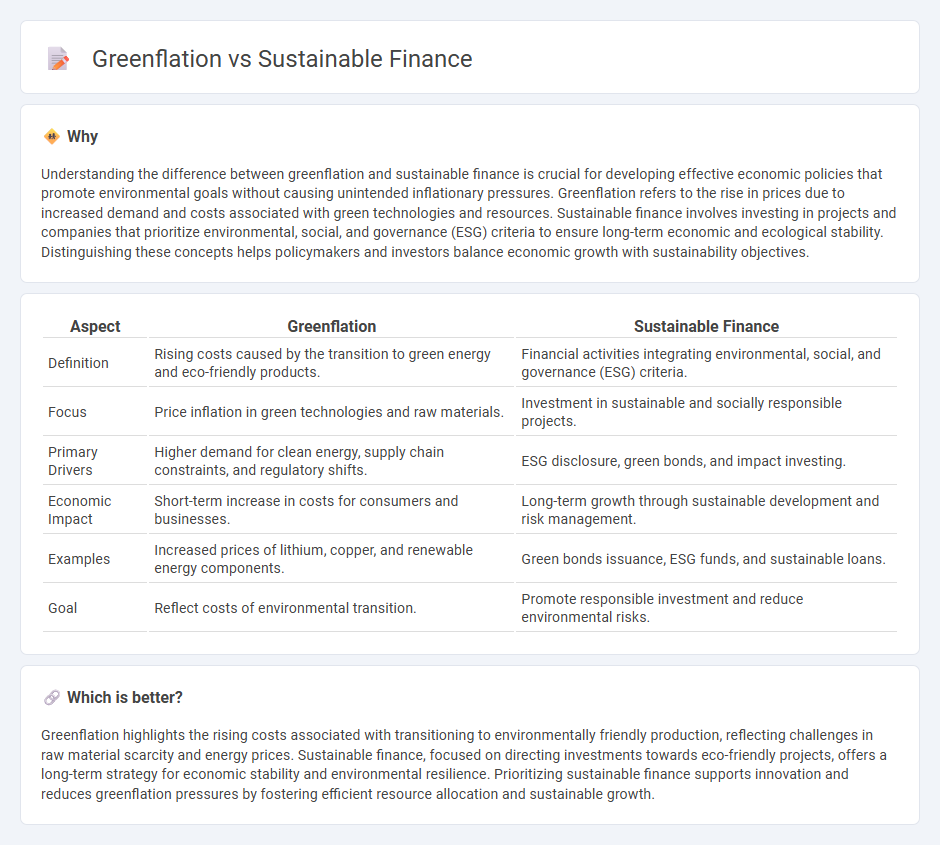
Understanding the difference between greenflation and sustainable finance is crucial for developing effective economic policies that promote environmental goals without causing unintended inflationary pressures. Greenflation refers to the rise in prices due to increased demand and costs associated with green technologies and resources. Sustainable finance involves investing in projects and companies that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to ensure long-term economic and ecological stability. Distinguishing these concepts helps policymakers and investors balance economic growth with sustainability objectives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenflation | Sustainable Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rising costs caused by the transition to green energy and eco-friendly products. | Financial activities integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. |
| Focus | Price inflation in green technologies and raw materials. | Investment in sustainable and socially responsible projects. |
| Primary Drivers | Higher demand for clean energy, supply chain constraints, and regulatory shifts. | ESG disclosure, green bonds, and impact investing. |
| Economic Impact | Short-term increase in costs for consumers and businesses. | Long-term growth through sustainable development and risk management. |
| Examples | Increased prices of lithium, copper, and renewable energy components. | Green bonds issuance, ESG funds, and sustainable loans. |
| Goal | Reflect costs of environmental transition. | Promote responsible investment and reduce environmental risks. |
Which is better?
Greenflation highlights the rising costs associated with transitioning to environmentally friendly production, reflecting challenges in raw material scarcity and energy prices. Sustainable finance, focused on directing investments towards eco-friendly projects, offers a long-term strategy for economic stability and environmental resilience. Prioritizing sustainable finance supports innovation and reduces greenflation pressures by fostering efficient resource allocation and sustainable growth.
Connection
Greenflation, driven by rising costs of raw materials essential for renewable energy technologies, directly impacts the financial sector's approach to sustainable investment. Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to allocate capital efficiently while mitigating inflationary pressures linked to the green transition. This connection compels investors to develop innovative financing mechanisms that support decarbonization without exacerbating economic instability.
Key Terms
Sustainable Finance:
Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to promote long-term ecological balance and responsible economic growth. It channels capital towards renewable energy, clean technologies, and sustainable infrastructure, addressing climate risks while fostering green innovations. Discover more about the impact of sustainable finance on global markets and sustainable development goals.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Sustainable finance integrates ESG criteria to promote investments that generate positive environmental and social impacts while managing financial risks, whereas greenflation refers to rising costs driven by environmental regulations and green technology demands affecting market prices. ESG-focused strategies prioritize transparency, ethical governance, and long-term value creation amid evolving regulatory landscapes and shifting investor preferences. Explore the dynamics of sustainable finance and greenflation to understand their implications on future investment trends and economic sustainability.
Green Bonds
Green bonds are financial instruments designed to fund projects with positive environmental impacts, aligning investment strategies with sustainability goals. Sustainable finance broadly encompasses these instruments, integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term ecological balance, while greenflation refers to the inflationary pressures arising from the rising costs of green technologies and resources. Explore how green bonds navigate both sustainable finance ambitions and the challenges posed by greenflation to maximize environmental and economic benefits.
Source and External Links
Sustainable finance - Sustainable finance involves financial practices and products that pursue both financial returns and environmental or social goals, integral to global efforts like the Paris Agreement and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for fostering a sustainable economy.
Sustainable finance explained: Why it matters and how your business can lead - Sustainable finance aligns investments and decision-making with the SDGs, mobilizing capital to support inclusive growth, climate action, and social equity, with businesses urged to set and report measurable SDG-focused targets.
Overview of sustainable finance - European Commission - Sustainable finance entails integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions to encourage long-term sustainable economic activities, playing a key role in the European Green Deal and the EU's climate goals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com