Slowbalization reflects a gradual reduction in global trade integration due to rising geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions, while nationalization emphasizes increasing domestic control over critical industries to boost economic sovereignty. This dynamic shift impacts international investment flows, trade policies, and labor markets worldwide. Explore how these trends reshape the global economy and influence future growth trajectories.
Why it is important
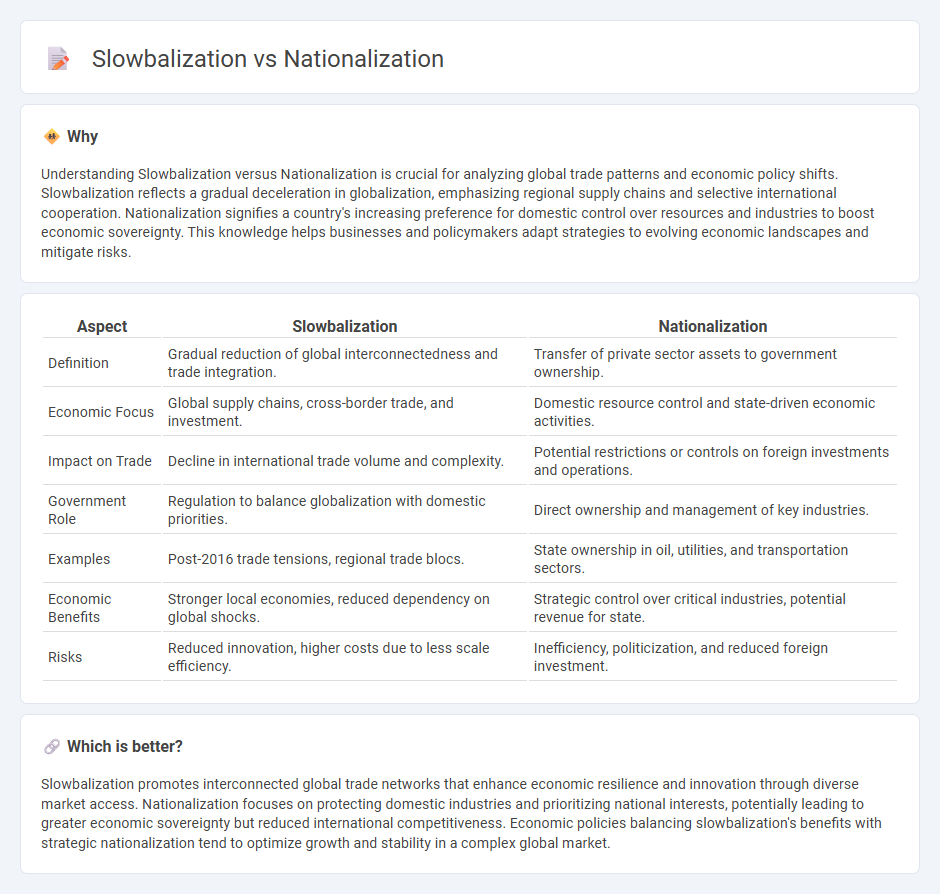
Understanding Slowbalization versus Nationalization is crucial for analyzing global trade patterns and economic policy shifts. Slowbalization reflects a gradual deceleration in globalization, emphasizing regional supply chains and selective international cooperation. Nationalization signifies a country's increasing preference for domestic control over resources and industries to boost economic sovereignty. This knowledge helps businesses and policymakers adapt strategies to evolving economic landscapes and mitigate risks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Slowbalization | Nationalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual reduction of global interconnectedness and trade integration. | Transfer of private sector assets to government ownership. |
| Economic Focus | Global supply chains, cross-border trade, and investment. | Domestic resource control and state-driven economic activities. |
| Impact on Trade | Decline in international trade volume and complexity. | Potential restrictions or controls on foreign investments and operations. |
| Government Role | Regulation to balance globalization with domestic priorities. | Direct ownership and management of key industries. |
| Examples | Post-2016 trade tensions, regional trade blocs. | State ownership in oil, utilities, and transportation sectors. |
| Economic Benefits | Stronger local economies, reduced dependency on global shocks. | Strategic control over critical industries, potential revenue for state. |
| Risks | Reduced innovation, higher costs due to less scale efficiency. | Inefficiency, politicization, and reduced foreign investment. |
Which is better?
Slowbalization promotes interconnected global trade networks that enhance economic resilience and innovation through diverse market access. Nationalization focuses on protecting domestic industries and prioritizing national interests, potentially leading to greater economic sovereignty but reduced international competitiveness. Economic policies balancing slowbalization's benefits with strategic nationalization tend to optimize growth and stability in a complex global market.
Connection
Slowbalization, characterized by the deceleration of global trade and investment flows, drives nations to adopt nationalization strategies to protect domestic industries and secure critical resources. This economic shift emphasizes self-reliance, reducing dependency on international supply chains and encouraging local production. Consequently, nationalization becomes a response to the vulnerabilities exposed by slowbalization, fostering economic sovereignty.
Key Terms
State Ownership
State ownership plays a critical role in shaping nationalization policies that prioritize domestic control over key industries, contrasting with slowbalization's gradual globalization emphasizing interconnected markets yet cautious sovereignty. Nationalization ensures strategic sectors remain under government regulatory frameworks, impacting economic stability and social welfare, while slowbalization balances global collaboration with protective measures against rapid market fluctuations. Explore how state ownership dynamics influence economic strategies in evolving global landscapes.
Global Supply Chains
Nationalization of global supply chains emphasizes reshoring production and reducing dependency on foreign suppliers to enhance national security and economic resilience. Slowbalization promotes a gradual deceleration of global trade integration, encouraging regionalization and diversification to mitigate risks associated with overdependence on distant markets. Explore deeper insights into how these contrasting strategies impact global supply chain dynamics and economic sustainability.
Trade Liberalization
Nationalization often leads to increased state control over strategic industries, reducing foreign investment and limiting trade liberalization efforts. Slowbalization describes a gradual slowdown in globalization, marked by protective trade policies and regionalism that hinder free trade expansion. Explore the nuanced impacts of these trends on global trade policies and economic growth.
Source and External Links
Nationalization | EBSCO Research Starters - This webpage provides an overview of nationalization, highlighting its role in government control, particularly in the energy sector, and its historical examples in countries like Mexico and Venezuela.
Nationalization - Definition, How It Works, Examples - This article defines nationalization as the process of governments taking control of specific companies or industries to shift profits and control from private to public hands.
Nationalization - Wikipedia - This Wikipedia entry explains nationalization as the transformation of private assets into public assets under government control, affecting industries such as energy, telecommunications, and banking.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com