Unretirement reflects the growing economic trend of retirees reentering the workforce to supplement income and maintain financial stability, driven by increasing life expectancy and rising living costs. Encore careers focus on pursuing purpose-driven work often in nonprofit, education, or creative sectors, aligning personal fulfillment with economic contribution during later stages of life. Explore these evolving economic patterns to understand how unretirement and encore careers reshape retirement landscapes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between unretirement and encore career is crucial for economic planning and workforce development. Unretirement refers to retirees returning to work temporarily or part-time, while encore careers involve a permanent shift to a new profession, often in social impact roles. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers design targeted employment programs and retirement policies that address diverse labor market needs and support financial security. Awareness also guides individuals in aligning their work-life balance with economic opportunities and personal fulfillment.
Comparison Table
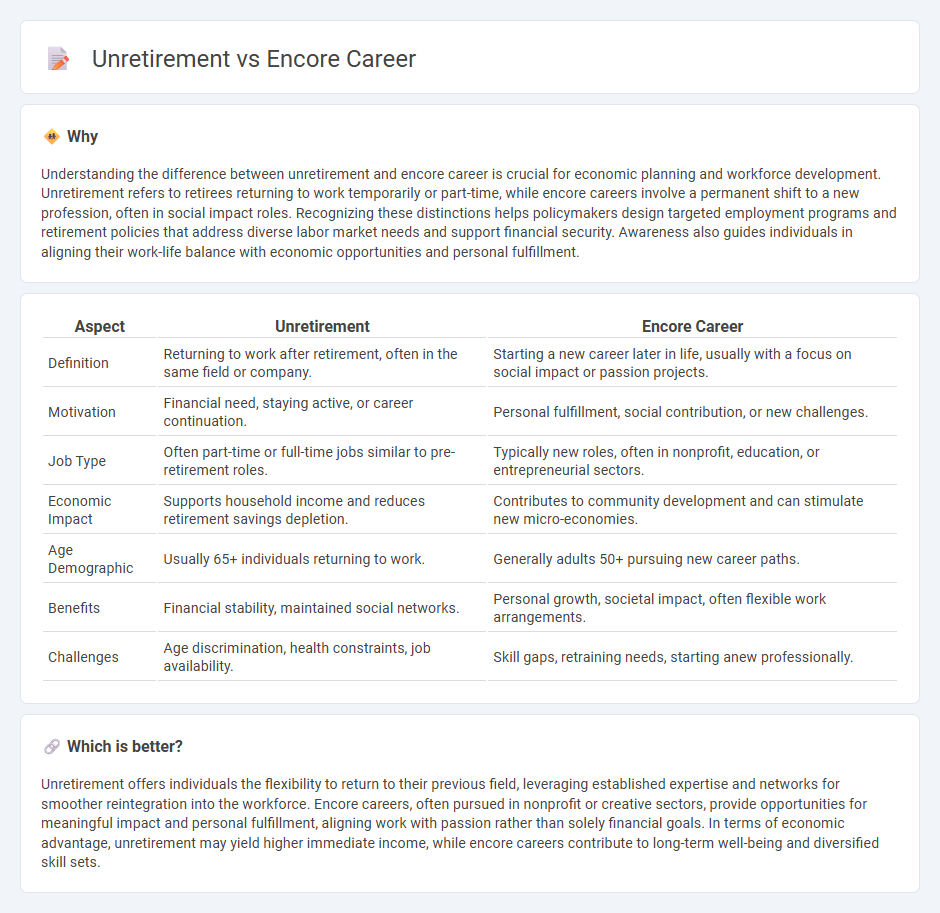
| Aspect | Unretirement | Encore Career |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Returning to work after retirement, often in the same field or company. | Starting a new career later in life, usually with a focus on social impact or passion projects. |
| Motivation | Financial need, staying active, or career continuation. | Personal fulfillment, social contribution, or new challenges. |
| Job Type | Often part-time or full-time jobs similar to pre-retirement roles. | Typically new roles, often in nonprofit, education, or entrepreneurial sectors. |
| Economic Impact | Supports household income and reduces retirement savings depletion. | Contributes to community development and can stimulate new micro-economies. |
| Age Demographic | Usually 65+ individuals returning to work. | Generally adults 50+ pursuing new career paths. |
| Benefits | Financial stability, maintained social networks. | Personal growth, societal impact, often flexible work arrangements. |
| Challenges | Age discrimination, health constraints, job availability. | Skill gaps, retraining needs, starting anew professionally. |
Which is better?
Unretirement offers individuals the flexibility to return to their previous field, leveraging established expertise and networks for smoother reintegration into the workforce. Encore careers, often pursued in nonprofit or creative sectors, provide opportunities for meaningful impact and personal fulfillment, aligning work with passion rather than solely financial goals. In terms of economic advantage, unretirement may yield higher immediate income, while encore careers contribute to long-term well-being and diversified skill sets.
Connection
Unretirement and encore careers are interconnected trends reflecting a shift in retirement patterns where individuals re-enter the workforce or pursue new professional ventures after leaving traditional employment. Economic factors like rising living costs and desire for financial security drive this phenomenon, while encore careers often focus on purpose-driven roles or entrepreneurship that leverage accumulated skills. This dynamic impacts labor market participation rates, reshaping workforce demographics and stimulating economic growth through increased consumer spending and innovation.
Key Terms
Labor Force Participation
Encore career refers to pursuing new work opportunities after traditional retirement, often driven by passion or supplemental income needs, while unretirement involves rejoining the labor force after a period of full retirement. Both trends contribute to rising labor force participation rates among older adults, reflecting shifts in economic necessity and personal fulfillment. Explore how these changing workforce dynamics impact economic growth and social well-being.
Human Capital
Encore careers leverage existing human capital by allowing professionals to apply accumulated skills and experiences in new or related fields, promoting continued personal and economic growth. Unretirement often involves returning to previous industries or roles to maintain financial stability and harness established expertise. Discover how both paths optimize human capital and influence workforce trends by exploring detailed analyses and case studies.
Income Security
An encore career involves transitioning into a new profession after traditional retirement, often aimed at personal fulfillment and supplemental income. Unretirement refers to returning to a previous job or workforce after exiting retirement to regain financial stability. Explore strategies to optimize income security through both encore careers and unretirement options.
Source and External Links
Encore career - Wikipedia - An encore career is paid work later in life that combines continued income, greater personal meaning, and social impact, often in public interest fields such as education, health, and social services, and is a way for older adults to "give back" through meaningful work.
What Is an Encore Career? Redefining Your Career After 55 - An encore career can mean starting a new career, business, or consulting later in life and offers benefits such as earning additional income, building community, and making a positive difference, often with flexible or part-time work options.
What employers need to know about encore careers - An encore career usually involves a career change later in life where individuals pursue new professional interests, often bringing valuable experience and professionalism, and may seek more flexible or less stressful roles while continuing to contribute and mentor younger workers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com