Soft saving focuses on gradually building financial reserves through low-risk investments and consistent budgeting, promoting long-term stability and reduced economic volatility. Hard spending, characterized by aggressive expenditure and high-consumption patterns, can stimulate short-term economic growth but risks increasing debt and inflation. Discover how balancing these strategies can optimize personal and national economic health.
Why it is important
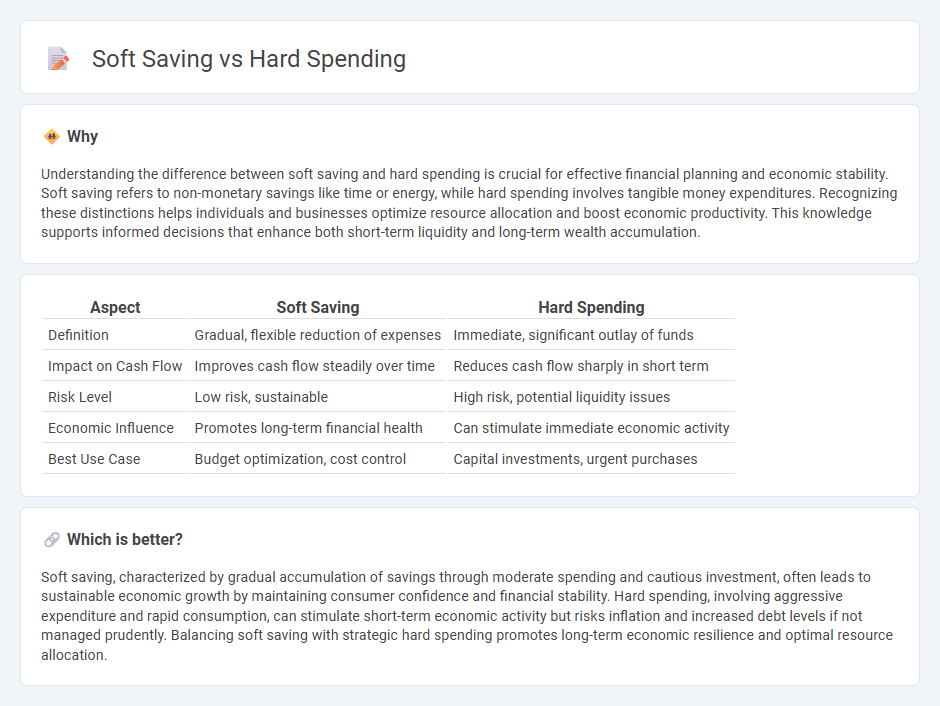
Understanding the difference between soft saving and hard spending is crucial for effective financial planning and economic stability. Soft saving refers to non-monetary savings like time or energy, while hard spending involves tangible money expenditures. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals and businesses optimize resource allocation and boost economic productivity. This knowledge supports informed decisions that enhance both short-term liquidity and long-term wealth accumulation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Saving | Hard Spending |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual, flexible reduction of expenses | Immediate, significant outlay of funds |
| Impact on Cash Flow | Improves cash flow steadily over time | Reduces cash flow sharply in short term |
| Risk Level | Low risk, sustainable | High risk, potential liquidity issues |
| Economic Influence | Promotes long-term financial health | Can stimulate immediate economic activity |
| Best Use Case | Budget optimization, cost control | Capital investments, urgent purchases |
Which is better?
Soft saving, characterized by gradual accumulation of savings through moderate spending and cautious investment, often leads to sustainable economic growth by maintaining consumer confidence and financial stability. Hard spending, involving aggressive expenditure and rapid consumption, can stimulate short-term economic activity but risks inflation and increased debt levels if not managed prudently. Balancing soft saving with strategic hard spending promotes long-term economic resilience and optimal resource allocation.
Connection
Soft saving involves gradually accumulating funds through small, consistent deposits, which enhances financial stability over time. Hard spending, characterized by significant, often impulsive expenses, can undermine these savings if not carefully managed. Balancing soft saving with mindful hard spending is crucial for sustaining long-term economic health and avoiding debt accumulation.
Key Terms
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy distinguishes hard spending as government expenditures on infrastructure, defense, and social programs that directly stimulate economic growth, while soft saving refers to budgetary measures like deferred spending or reserve accumulation aimed at maintaining fiscal stability. Hard spending injects capital into the economy, boosting demand and employment, whereas soft saving emphasizes fiscal prudence to control deficits and manage long-term debt. Explore further to understand how balancing these strategies affects national economic health and policy outcomes.
Consumption
Hard spending emphasizes significant expenditures on essential goods and services, directly impacting consumption patterns by prioritizing durable and non-durable products. Soft saving involves subtle reductions in discretionary spending, promoting gradual accumulation of savings without drastically altering daily consumption habits. Explore more about how these strategies influence financial behavior and long-term economic stability.
Savings Rate
Hard spending refers to necessary and non-negotiable expenses such as rent, utilities, and groceries, which directly impact your savings rate by limiting the amount available to save. Soft saving involves discretionary spending cuts and lifestyle adjustments like dining out less or canceling subscriptions, designed to improve savings rate by increasing the surplus income. Explore strategies to optimize your savings rate effectively and balance hard spending and soft saving for financial growth.
Source and External Links
10 Smart Ways To Spend Your Hard-Earned Money - This article provides insights into smart spending strategies that can save money and improve well-being in the long run.
The Psychology of Spending Money: 4 Common Challenges - This piece explores common challenges people face when spending money and offers solutions to these issues.
What Is Doom Spending and How Can You Stop It? - This article discusses the problem of doom spending and provides strategies for managing such behavior to achieve financial stability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com