Resilient supply chains focus on flexibility, risk management, and diversification to withstand disruptions, whereas just-in-time (JIT) supply chains prioritize minimizing inventory and reducing costs through precise timing. The shift towards resilient supply chains addresses vulnerabilities exposed by global events such as pandemics and geopolitical tensions. Explore how evolving strategies in supply chain management are shaping economic stability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between resilient supply chains and just-in-time supply chains is crucial for effective risk management and maintaining business continuity. Resilient supply chains prioritize flexibility and buffer stocks to absorb disruptions, while just-in-time supply chains focus on minimizing inventory to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Companies with resilient supply chains are better equipped to handle unexpected events like natural disasters or pandemics without severe operational delays. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses balance cost-efficiency with risk mitigation to optimize overall economic performance.
Comparison Table
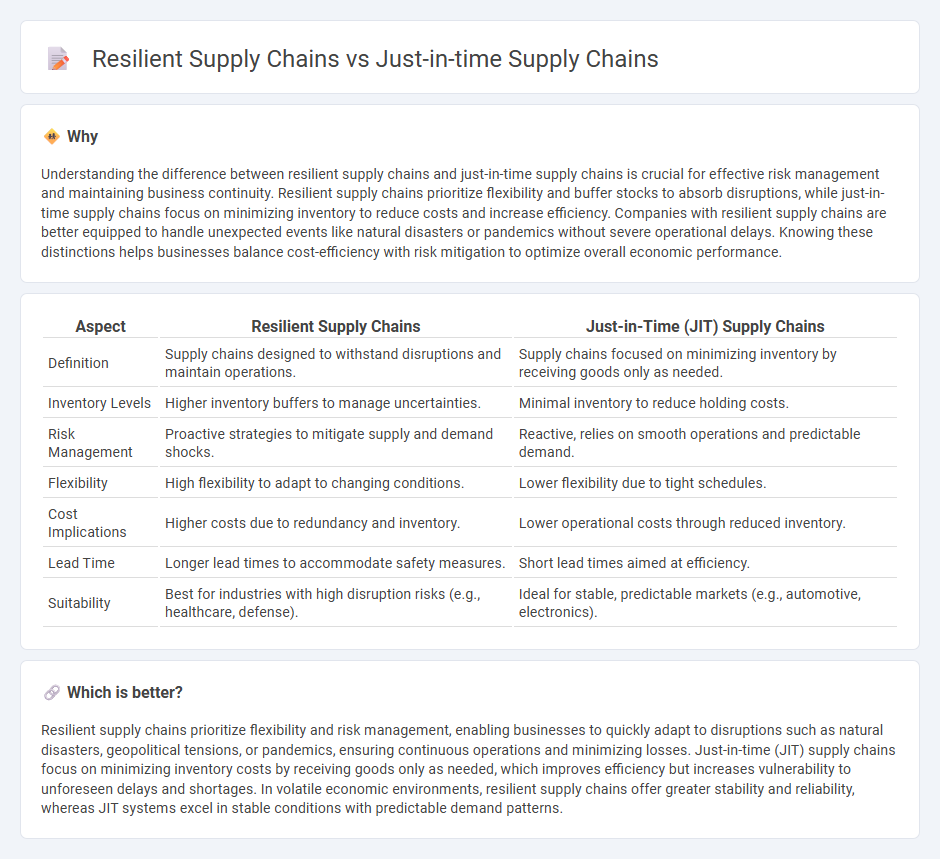
| Aspect | Resilient Supply Chains | Just-in-Time (JIT) Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supply chains designed to withstand disruptions and maintain operations. | Supply chains focused on minimizing inventory by receiving goods only as needed. |
| Inventory Levels | Higher inventory buffers to manage uncertainties. | Minimal inventory to reduce holding costs. |
| Risk Management | Proactive strategies to mitigate supply and demand shocks. | Reactive, relies on smooth operations and predictable demand. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to adapt to changing conditions. | Lower flexibility due to tight schedules. |
| Cost Implications | Higher costs due to redundancy and inventory. | Lower operational costs through reduced inventory. |
| Lead Time | Longer lead times to accommodate safety measures. | Short lead times aimed at efficiency. |
| Suitability | Best for industries with high disruption risks (e.g., healthcare, defense). | Ideal for stable, predictable markets (e.g., automotive, electronics). |
Which is better?
Resilient supply chains prioritize flexibility and risk management, enabling businesses to quickly adapt to disruptions such as natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or pandemics, ensuring continuous operations and minimizing losses. Just-in-time (JIT) supply chains focus on minimizing inventory costs by receiving goods only as needed, which improves efficiency but increases vulnerability to unforeseen delays and shortages. In volatile economic environments, resilient supply chains offer greater stability and reliability, whereas JIT systems excel in stable conditions with predictable demand patterns.
Connection
Resilient supply chains enhance just-in-time (JIT) supply chains by incorporating flexibility and risk management strategies to prevent disruptions that can halt production. JIT supply chains prioritize minimizing inventory and rely heavily on timely deliveries, making resilience critical to avoid costly delays. Integrating resilience measures such as diversified suppliers and real-time monitoring ensures JIT systems maintain efficiency while adapting to unpredictable market conditions.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Just-in-time (JIT) supply chains minimize inventory levels by synchronizing production schedules with demand, reducing holding costs but increasing vulnerability to disruptions. Resilient supply chains maintain higher safety stock and diversified sourcing to buffer against uncertainties and ensure continuous operations. Explore more insights to balance efficiency and resilience in inventory management strategies.
Supply Chain Disruption
Just-in-time supply chains prioritize minimizing inventory and reducing waste, making them vulnerable to supply chain disruptions such as natural disasters, geopolitical events, or sudden demand spikes. Resilient supply chains incorporate redundancy, flexibility, and risk management strategies to quickly adapt and recover from disruptions while maintaining operational continuity. Explore detailed strategies and case studies to better understand how to balance efficiency and resilience in supply chain planning.
Flexibility
Just-in-time supply chains prioritize minimizing inventory levels by delivering materials precisely when needed, enhancing operational efficiency but reducing flexibility to respond to disruptions. Resilient supply chains emphasize adaptability and buffer capacity, enabling quick adjustments to unexpected changes or delays, thereby maintaining continuity and reducing risk. Explore key strategies to balance flexibility between just-in-time efficiency and resilient robustness to optimize supply chain performance.
Source and External Links
The State of Just-in-time Supply Chains - Just-in-time (JIT) supply chains streamline production by ordering materials only as needed, reducing inventory and warehousing costs, but Covid-19 exposed vulnerabilities in this system due to supplier disruptions and sudden shifts in demand.
Just-in-Time (JIT): Agility and Efficiency in the Supply Chain - JIT aligns supply with actual demand to minimize waste and storage costs, enhances operational agility to quickly adapt to market changes, and promotes continuous improvement focused on efficiency and customer value.
What is Just in Time (JIT) Supply Chain Strategy? | GEP Glossary - JIT reduces inventory to near zero by timing material deliveries just before use, cutting storage costs, but recent supply volatility has led some to prefer just-in-case strategies that keep larger inventories.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com