Tipflation reflects rising costs driven by increased tipping expenses and consumer service charges, while slumpflation combines stagnant economic growth with persistent inflation, creating unique financial challenges. Understanding the distinctions between these inflation types helps analyze their impact on household budgets and market stability. Explore deeper insights into tipflation and slumpflation to better navigate evolving economic conditions.
Why it is important
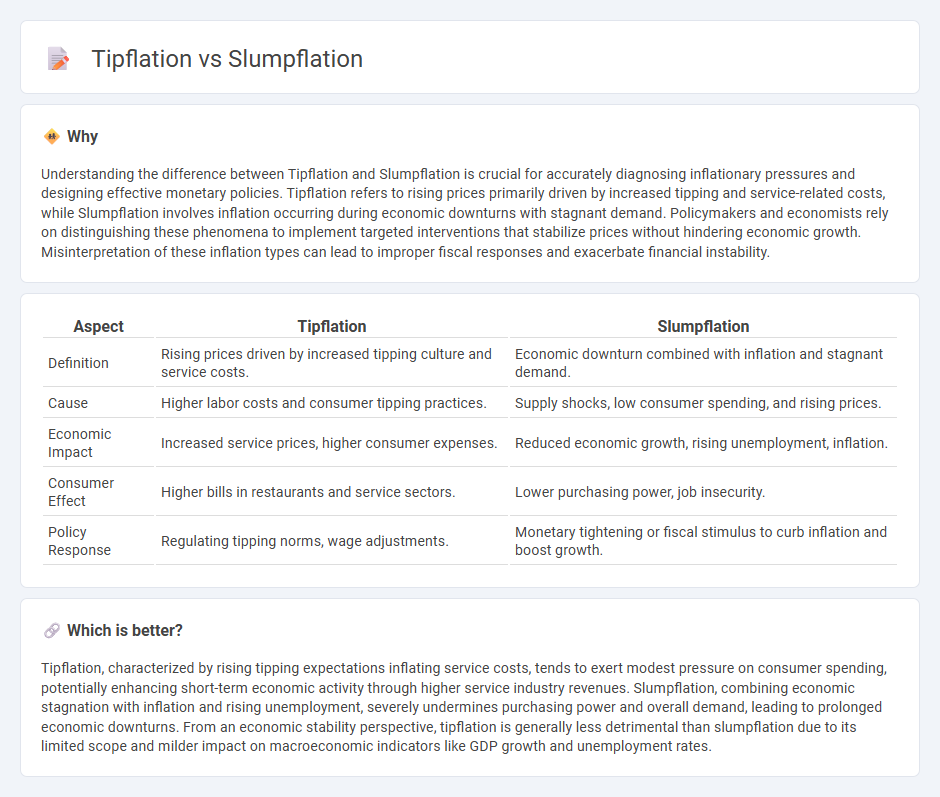
Understanding the difference between Tipflation and Slumpflation is crucial for accurately diagnosing inflationary pressures and designing effective monetary policies. Tipflation refers to rising prices primarily driven by increased tipping and service-related costs, while Slumpflation involves inflation occurring during economic downturns with stagnant demand. Policymakers and economists rely on distinguishing these phenomena to implement targeted interventions that stabilize prices without hindering economic growth. Misinterpretation of these inflation types can lead to improper fiscal responses and exacerbate financial instability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tipflation | Slumpflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rising prices driven by increased tipping culture and service costs. | Economic downturn combined with inflation and stagnant demand. |
| Cause | Higher labor costs and consumer tipping practices. | Supply shocks, low consumer spending, and rising prices. |
| Economic Impact | Increased service prices, higher consumer expenses. | Reduced economic growth, rising unemployment, inflation. |
| Consumer Effect | Higher bills in restaurants and service sectors. | Lower purchasing power, job insecurity. |
| Policy Response | Regulating tipping norms, wage adjustments. | Monetary tightening or fiscal stimulus to curb inflation and boost growth. |
Which is better?
Tipflation, characterized by rising tipping expectations inflating service costs, tends to exert modest pressure on consumer spending, potentially enhancing short-term economic activity through higher service industry revenues. Slumpflation, combining economic stagnation with inflation and rising unemployment, severely undermines purchasing power and overall demand, leading to prolonged economic downturns. From an economic stability perspective, tipflation is generally less detrimental than slumpflation due to its limited scope and milder impact on macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth and unemployment rates.
Connection
Tipflation and slumpflation both impact consumer spending behavior and reflect inflationary pressures within the economy. Tipflation, characterized by increased tipping amounts, often results from wage stagnation and rising prices, while slumpflation refers to inflation that occurs during economic downturns, leading to stagnant demand coupled with rising costs. The connection lies in their shared influence on overall consumer inflation expectations and real income erosion, affecting spending patterns and economic recovery prospects.
Key Terms
Recession
Slumpflation is characterized by stagnant economic growth combined with rising inflation, exacerbating recessionary pressures through reduced consumer spending and increased production costs. Tipflation, a less conventional term, refers to inflationary effects specifically driven by increased tipping, impacting service sectors disproportionately during economic downturns. Explore the nuanced differences between slumpflation and tipflation to better understand their distinct roles in recession dynamics.
Inflation
Slumpflation refers to the economic condition where high inflation occurs during a recession, characterized by stagnant demand and rising prices simultaneously. Tipflation represents the specific increase in costs associated with tipping services, contributing to overall inflationary pressures in the hospitality sector. Explore deeper insights into how these inflation types impact consumer behavior and economic policy.
Gratuity
Slumpflation describes an economic scenario characterized by stagnant demand and rising inflation, which can reduce real incomes and affect service industry tipping behavior. Tipflation specifically refers to the inflation-driven increase in gratuity amounts, where customers face higher tipping expectations as labor costs and prices rise. Explore the dynamics of gratuity trends amid economic shifts to understand how these phenomena impact tipping culture.
Source and External Links
SLUMPFLATION Definition & Meaning - Slumpflation is defined as a situation where economic depression is combined with increasing inflation.
slumpflation - Wiktionary - Slumpflation is an economic condition characterized by inflation accompanied by a slump in output and employment.
From greedflation to stagflation and then slumpflation - Slumpflation refers to a likely economic slump caused by sticky inflation and weak output growth, where central banks' interest rate hikes risk pushing economies into recession with rising unemployment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com