De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in global trade and finance, aiming to stabilize national economies against dollar volatility. The gold standard, historically used to back currency with a fixed amount of gold, offers long-term price stability but limits monetary policy flexibility. Explore the implications of these monetary frameworks for today's economy to understand their potential impacts.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and the gold standard is crucial for analyzing global economic stability and monetary policy shifts. De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and reserves, impacting currency markets and geopolitical power dynamics. The gold standard ties a country's currency value directly to gold, influencing inflation control and long-term fiscal discipline. Knowing these distinctions helps policymakers and investors anticipate economic risks and opportunities in evolving financial systems.
Comparison Table
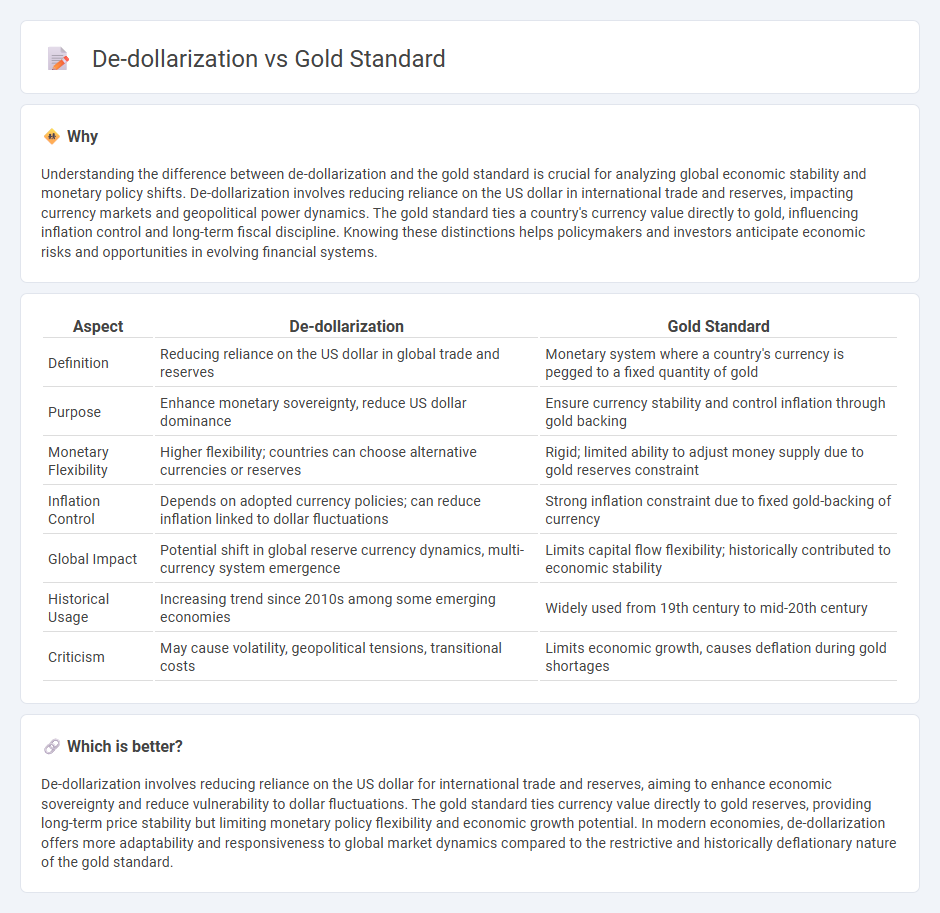
| Aspect | De-dollarization | Gold Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on the US dollar in global trade and reserves | Monetary system where a country's currency is pegged to a fixed quantity of gold |
| Purpose | Enhance monetary sovereignty, reduce US dollar dominance | Ensure currency stability and control inflation through gold backing |
| Monetary Flexibility | Higher flexibility; countries can choose alternative currencies or reserves | Rigid; limited ability to adjust money supply due to gold reserves constraint |
| Inflation Control | Depends on adopted currency policies; can reduce inflation linked to dollar fluctuations | Strong inflation constraint due to fixed gold-backing of currency |
| Global Impact | Potential shift in global reserve currency dynamics, multi-currency system emergence | Limits capital flow flexibility; historically contributed to economic stability |
| Historical Usage | Increasing trend since 2010s among some emerging economies | Widely used from 19th century to mid-20th century |
| Criticism | May cause volatility, geopolitical tensions, transitional costs | Limits economic growth, causes deflation during gold shortages |
Which is better?
De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar for international trade and reserves, aiming to enhance economic sovereignty and reduce vulnerability to dollar fluctuations. The gold standard ties currency value directly to gold reserves, providing long-term price stability but limiting monetary policy flexibility and economic growth potential. In modern economies, de-dollarization offers more adaptability and responsiveness to global market dynamics compared to the restrictive and historically deflationary nature of the gold standard.
Connection
De-dollarization refers to the process of reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance, promoting alternative currencies or commodities like gold. The gold standard, a monetary system where currency value is directly linked to gold, presents a tangible asset-based alternative that supports currency stability and trust. Both concepts aim to enhance economic sovereignty and minimize exposure to dollar-driven financial volatility.
Key Terms
Reserve Currency
The gold standard, a monetary system where currency value is directly linked to gold, contrasts sharply with the modern trend of de-dollarization, which aims to reduce reliance on the US dollar as the world's reserve currency. Countries pursuing de-dollarization often diversify their reserves into alternative currencies or assets, challenging the dollar's dominance established post-Bretton Woods. Explore how these dynamics reshape global financial stability and the future of reserve currencies.
Fixed Exchange Rate
The gold standard, a fixed exchange rate system where currency value is directly linked to gold, contrasts sharply with de-dollarization efforts aimed at reducing reliance on the US dollar as a global reserve currency. Fixed exchange rates under the gold standard provided monetary stability by limiting inflation and exchange rate volatility, while de-dollarization seeks to diversify currency reserves and promote national economic sovereignty. Explore how these strategies impact global trade and financial stability in greater detail.
Monetary Sovereignty
The gold standard imposes strict constraints on monetary policy by tying currency value to physical gold reserves, limiting central banks' ability to respond to economic fluctuations. De-dollarization enhances monetary sovereignty by reducing reliance on the US dollar, enabling countries to regain control over exchange rates and inflation management. Explore the implications of these monetary frameworks to understand their impact on national economic independence.
Source and External Links
What is the Gold Standard System? - The gold standard is a monetary system where currency value is directly linked to gold, limiting money supply to the amount of gold reserves and using gold flows to correct international payment imbalances through price and interest rate adjustments.
Gold Standard - Econlib - The gold standard was a commitment by countries to fix their currency prices to a specific amount of gold, with money freely convertible into gold at a fixed price, leading to relatively stable exchange rates and economic growth from the 19th century to early 20th century.
Gold standard - A monetary system based on a fixed quantity of gold, the gold standard provided long-term price stability, reduced currency crises, and credible commitment against inflation and financial repression by linking money to gold and enabling automatic economic adjustments through gold flows.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com