Unretirement involves individuals returning to the workforce after retirement, often seeking meaningful work or supplemental income, while bridge employment refers to temporary or part-time jobs that ease the transition from full-time work to retirement. Both approaches address financial security and personal fulfillment in later life stages. Explore the differences and benefits of unretirement and bridge employment to better understand their impact on the economy.
Why it is important
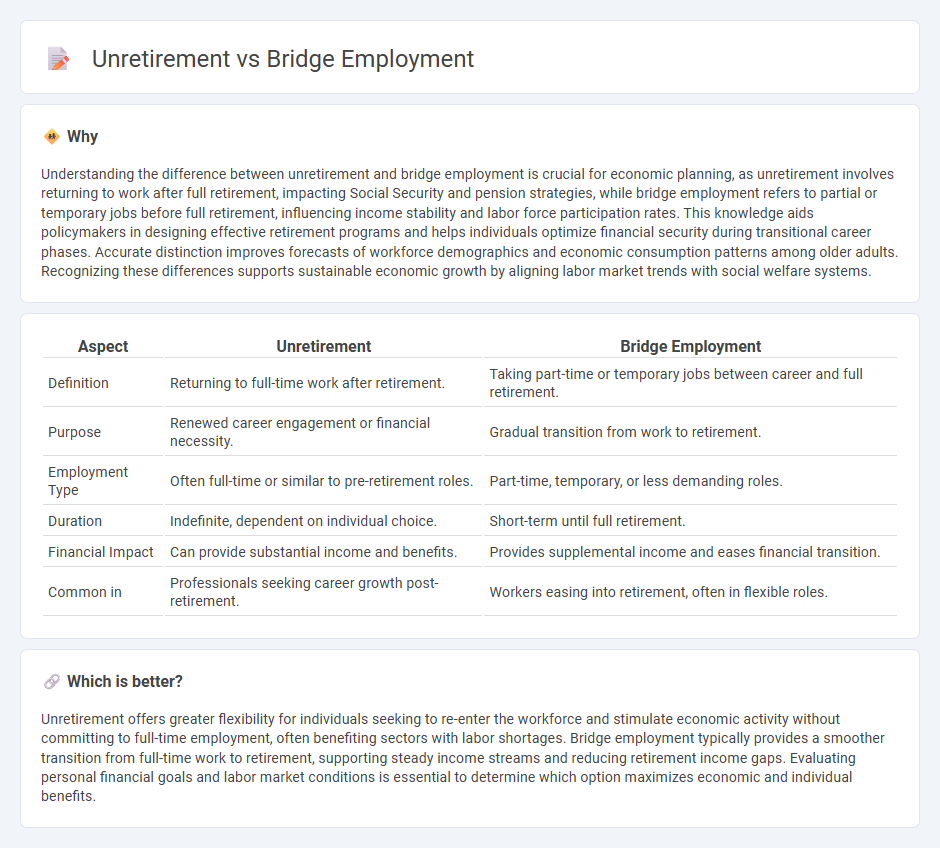
Understanding the difference between unretirement and bridge employment is crucial for economic planning, as unretirement involves returning to work after full retirement, impacting Social Security and pension strategies, while bridge employment refers to partial or temporary jobs before full retirement, influencing income stability and labor force participation rates. This knowledge aids policymakers in designing effective retirement programs and helps individuals optimize financial security during transitional career phases. Accurate distinction improves forecasts of workforce demographics and economic consumption patterns among older adults. Recognizing these differences supports sustainable economic growth by aligning labor market trends with social welfare systems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Unretirement | Bridge Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Returning to full-time work after retirement. | Taking part-time or temporary jobs between career and full retirement. |
| Purpose | Renewed career engagement or financial necessity. | Gradual transition from work to retirement. |
| Employment Type | Often full-time or similar to pre-retirement roles. | Part-time, temporary, or less demanding roles. |
| Duration | Indefinite, dependent on individual choice. | Short-term until full retirement. |
| Financial Impact | Can provide substantial income and benefits. | Provides supplemental income and eases financial transition. |
| Common in | Professionals seeking career growth post-retirement. | Workers easing into retirement, often in flexible roles. |
Which is better?
Unretirement offers greater flexibility for individuals seeking to re-enter the workforce and stimulate economic activity without committing to full-time employment, often benefiting sectors with labor shortages. Bridge employment typically provides a smoother transition from full-time work to retirement, supporting steady income streams and reducing retirement income gaps. Evaluating personal financial goals and labor market conditions is essential to determine which option maximizes economic and individual benefits.
Connection
Unretirement and bridge employment are interconnected phenomena in the evolving labor market where retirees re-enter the workforce, often seeking part-time or temporary roles to supplement retirement income. Bridge employment serves as a transitional phase, allowing individuals to gradually reduce work hours while maintaining financial stability and social engagement. This trend reflects demographic shifts and changes in retirement patterns, impacting economic productivity and labor force dynamics.
Key Terms
Labor Force Participation
Bridge employment refers to part-time or temporary work taken after full-time retirement, helping older workers maintain Labor Force Participation (LFP) without committing to a full career. Unretirement occurs when retirees fully return to the workforce, often in roles similar to their previous careers, significantly impacting LFP rates among older adults. Explore deeper insights into how these employment patterns shape the dynamics of older workers' engagement in the labor market.
Retirement Transition
Bridge employment offers retirees part-time or temporary work to ease the transition from full-time career roles, providing financial stability and maintaining professional identity. Unretirement refers to re-entering the workforce after a period of full retirement, often driven by financial needs or personal fulfillment. Explore detailed strategies and benefits of both approaches for a smoother retirement transition.
Post-Retirement Employment
Post-retirement employment includes bridge employment, a temporary or part-time job taken before full retirement, and unretirement, where retirees re-enter the workforce after a period of full retirement. Bridge employment often serves as a transition phase to ease into retirement, offering financial stability and work-life balance, whereas unretirement reflects a decision to resume career activities for purpose, social engagement, or income. Discover more about how these employment choices impact retirement planning and lifestyle adjustments.
Source and External Links
Bridge Job | Definition, Types, Transition, & Maximizing Benefits - A bridge job is a short-term, temporary, or transitional position that helps individuals transition between two stages of their career or life, often used to delay full retirement, explore new industries, or maintain work-life balance.
Bridge Employment or Encore Career? Examining Predictors That ... - Bridge employment is one of the common retirement pathways defined by transitional work after a full-time career, with predictors including health, human capital, and retirement status influencing workers' choices to pursue such paths.
The new meaning of retirement for bridge employees: Situating... - Bridge employment describes retirees who re-enter the workforce while identifying as retired or collecting retirement benefits, reflecting evolving work motives and aspirations distinct from traditional retirement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com