Funflation refers to the rising prices of entertainment and leisure activities driven by increased demand and limited supply, impacting consumer spending patterns. Cost-push inflation occurs when production costs, such as wages and raw materials, rise, leading businesses to increase prices to maintain profit margins. Explore how these distinct inflation types affect economic growth and household budgets.
Why it is important
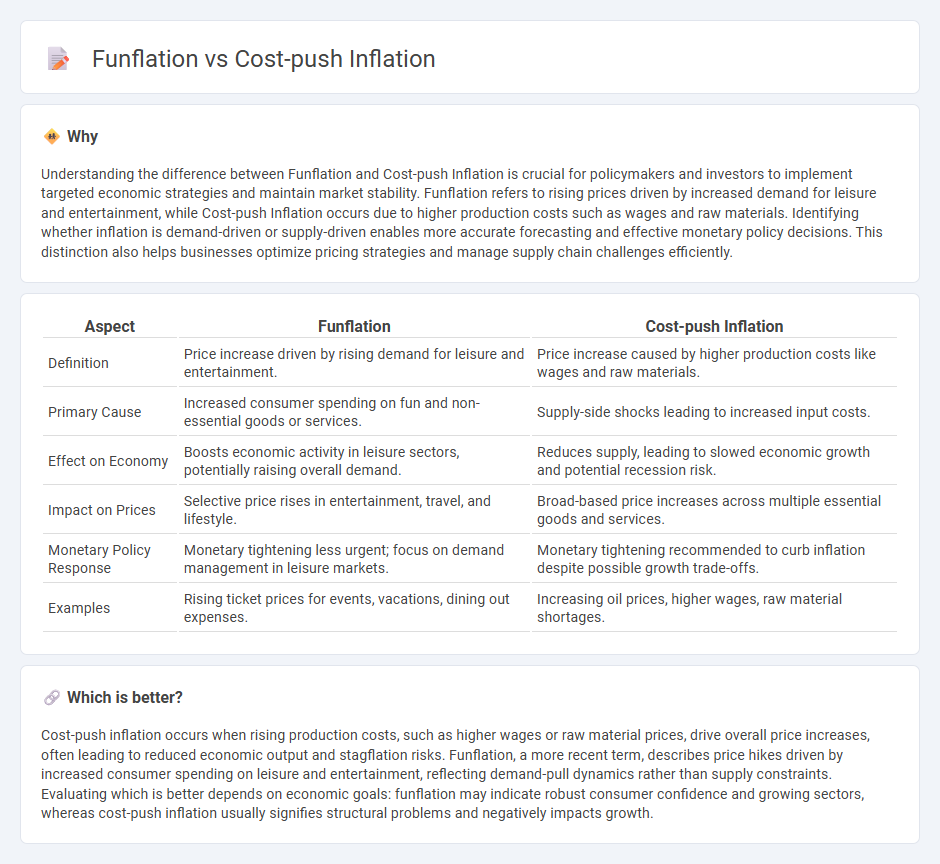
Understanding the difference between Funflation and Cost-push Inflation is crucial for policymakers and investors to implement targeted economic strategies and maintain market stability. Funflation refers to rising prices driven by increased demand for leisure and entertainment, while Cost-push Inflation occurs due to higher production costs such as wages and raw materials. Identifying whether inflation is demand-driven or supply-driven enables more accurate forecasting and effective monetary policy decisions. This distinction also helps businesses optimize pricing strategies and manage supply chain challenges efficiently.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Funflation | Cost-push Inflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price increase driven by rising demand for leisure and entertainment. | Price increase caused by higher production costs like wages and raw materials. |
| Primary Cause | Increased consumer spending on fun and non-essential goods or services. | Supply-side shocks leading to increased input costs. |
| Effect on Economy | Boosts economic activity in leisure sectors, potentially raising overall demand. | Reduces supply, leading to slowed economic growth and potential recession risk. |
| Impact on Prices | Selective price rises in entertainment, travel, and lifestyle. | Broad-based price increases across multiple essential goods and services. |
| Monetary Policy Response | Monetary tightening less urgent; focus on demand management in leisure markets. | Monetary tightening recommended to curb inflation despite possible growth trade-offs. |
| Examples | Rising ticket prices for events, vacations, dining out expenses. | Increasing oil prices, higher wages, raw material shortages. |
Which is better?
Cost-push inflation occurs when rising production costs, such as higher wages or raw material prices, drive overall price increases, often leading to reduced economic output and stagflation risks. Funflation, a more recent term, describes price hikes driven by increased consumer spending on leisure and entertainment, reflecting demand-pull dynamics rather than supply constraints. Evaluating which is better depends on economic goals: funflation may indicate robust consumer confidence and growing sectors, whereas cost-push inflation usually signifies structural problems and negatively impacts growth.
Connection
Funflation, driven by increased consumer spending on entertainment and leisure, intensifies demand pressures that contribute to cost-push inflation by causing businesses to raise prices in response to higher operational costs. Both phenomena reflect supply chain constraints and rising wages, which push production expenses upward, creating a feedback loop that accelerates overall price inflation. Understanding the interplay between funflation-induced demand spikes and cost-push supply shocks is crucial for policymakers aiming to stabilize economic growth and control inflation rates.
Key Terms
Production Costs
Cost-push inflation arises from rising production costs such as wages, raw materials, and energy prices, leading to higher prices for finished goods. Funflation, a newer term, describes price increases driven by companies adding entertainment or experiential value to products, often justified by enhanced consumer satisfaction rather than cost pressures. Explore the dynamics of cost-push inflation versus funflation to understand their distinct impacts on pricing strategies and consumer behavior.
Aggregate Supply
Cost-push inflation occurs when rising production costs, such as wages and raw materials, reduce aggregate supply, leading to higher prices. Funflation, a newer concept, refers to increased spending on leisure and entertainment driving demand without supply keeping pace, indirectly affecting aggregate supply constraints. Explore how these inflation types impact economic policy and market dynamics for deeper insights.
Consumer Demand
Cost-push inflation occurs when rising production costs, such as higher wages or raw material prices, drive overall price increases, reducing consumer purchasing power. Funflation, a phenomenon where demand for entertainment and leisure activities surges post-pandemic, leads to higher prices in experiential sectors despite stable supply costs. Explore these dynamics to understand how consumer demand shapes various inflationary pressures in today's economy.
Source and External Links
Cost-Push Inflation - Cost-push inflation occurs when rising production costs and raw material prices cause firms to increase prices, leading to higher overall inflation and reduced economic growth due to supply-side constraints.
Causes of Inflation | Explainer | Education - Cost-push inflation arises when aggregate supply falls because of higher production costs, pushing prices up while demand remains steady, such as through increased oil prices or supply disruptions.
Cost-push inflation - A type of inflation caused by increased costs of key inputs like oil, which forces businesses to raise prices, exemplified by the 1970s oil crisis, and can lead to a wage-price spiral prolonging inflation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com