Living wage ensures workers earn enough to cover basic living expenses without government aid, promoting economic self-sufficiency and reducing poverty. Subsidized wage involves financial support from the government or organizations to supplement income, aiming to assist low-income individuals but potentially creating dependency. Explore how these wage models impact economic stability and social welfare.
Why it is important
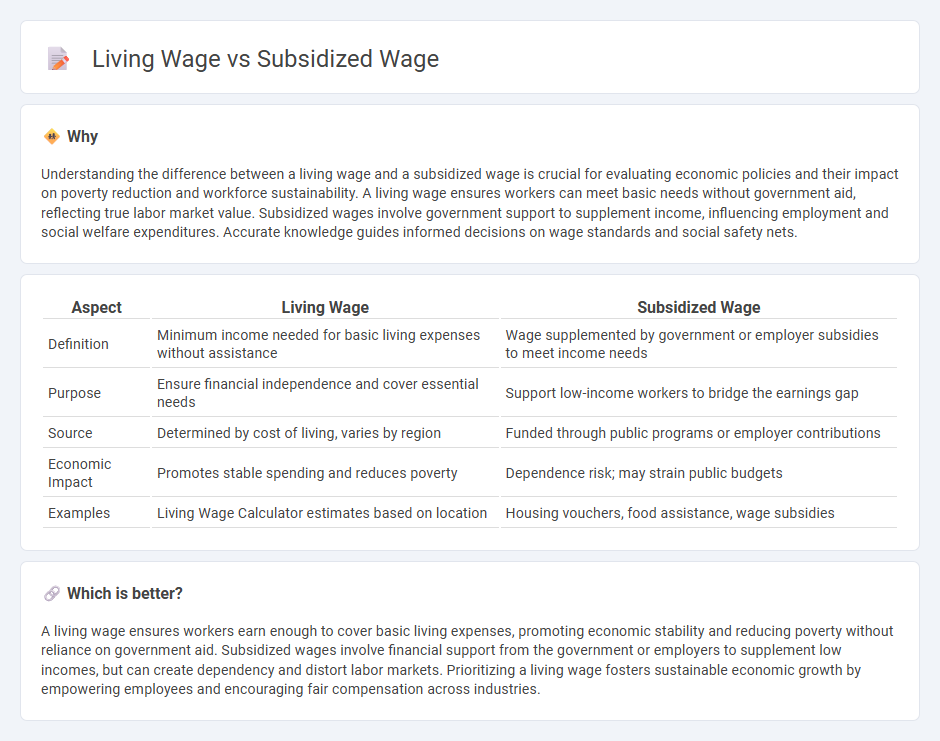
Understanding the difference between a living wage and a subsidized wage is crucial for evaluating economic policies and their impact on poverty reduction and workforce sustainability. A living wage ensures workers can meet basic needs without government aid, reflecting true labor market value. Subsidized wages involve government support to supplement income, influencing employment and social welfare expenditures. Accurate knowledge guides informed decisions on wage standards and social safety nets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Living Wage | Subsidized Wage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimum income needed for basic living expenses without assistance | Wage supplemented by government or employer subsidies to meet income needs |
| Purpose | Ensure financial independence and cover essential needs | Support low-income workers to bridge the earnings gap |
| Source | Determined by cost of living, varies by region | Funded through public programs or employer contributions |
| Economic Impact | Promotes stable spending and reduces poverty | Dependence risk; may strain public budgets |
| Examples | Living Wage Calculator estimates based on location | Housing vouchers, food assistance, wage subsidies |
Which is better?
A living wage ensures workers earn enough to cover basic living expenses, promoting economic stability and reducing poverty without reliance on government aid. Subsidized wages involve financial support from the government or employers to supplement low incomes, but can create dependency and distort labor markets. Prioritizing a living wage fosters sustainable economic growth by empowering employees and encouraging fair compensation across industries.
Connection
Living wage and subsidized wage are interconnected as subsidies help bridge the gap between low wages and the cost of living, ensuring workers can meet basic needs. Governments or organizations provide wage subsidies to supplement low incomes, promoting economic stability and reducing poverty. This connection supports a sustainable labor market by aligning income levels with the real expenses of housing, food, and healthcare.
Key Terms
Government intervention
Government intervention in subsidized wage programs aims to reduce labor costs for employers by providing financial assistance, often resulting in wages below the living wage standard. Living wage policies, however, emphasize ensuring workers earn enough to meet basic living expenses without external subsidies, promoting economic self-sufficiency and reducing poverty. Explore the effects of these wage policies on economic equity and employment by learning more about government role and labor market outcomes.
Minimum wage
Subsidized wage programs supplement income for workers earning minimum wage, aiming to reduce poverty without increasing employer costs, while a living wage reflects the actual income needed to cover basic living expenses like housing, food, and healthcare. The minimum wage is often set below the living wage, leading to a gap that subsidies attempt to fill, though critics argue it does not address underlying wage inadequacies. Explore the impact of minimum wage policies and living wage calculations for a deeper understanding of economic justice.
Cost of living
Subsidized wages are often set below the living wage, relying on government or employer support to supplement income, which may not fully cover the cost of living including housing, food, and healthcare expenses. Living wages are calculated based on the actual cost of living in a specific area, ensuring workers earn enough to meet basic needs without external assistance. Explore how different wage policies impact economic stability and worker well-being in your region.
Source and External Links
Wage subsidy - Wikipedia - A wage subsidy is a payment from the government--directly to workers or via employers--aimed at redistributing income, reducing unemployment, and helping workers avoid welfare traps by supplementing earnings from paid employment.
Wage Subsidy Program -- The Work First - This program places low-income individuals into temporary, subsidized jobs by reimbursing employers for up to 75% of wages, providing on-the-job training and a pathway to long-term employment and self-sufficiency.
Wage subsidy programmes - Youth Futures Foundation - Wage subsidy programs pay employers to hire individuals from under-resourced groups, generally offering short-term experience that can lead to longer-term employment, with subsidies covering some or all wage costs either by direct payment or tax reduction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com