Scrap metal arbitrage exploits price differences in scrap metal markets across regions, capitalizing on variations in demand, quality, and local regulations to generate profit. Triangular arbitrage involves currency trading by exploiting discrepancies in exchange rates between three currencies, allowing traders to make risk-free profits through simultaneous trades. Discover the intricacies behind these economic strategies and how they influence global markets.
Why it is important
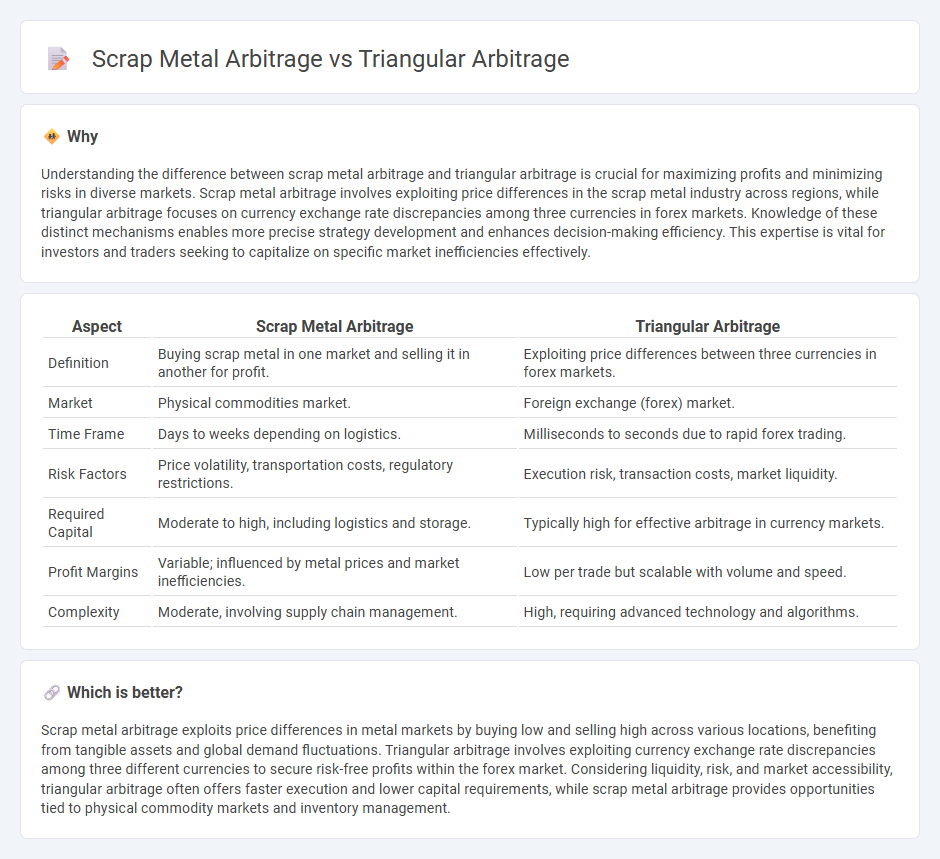
Understanding the difference between scrap metal arbitrage and triangular arbitrage is crucial for maximizing profits and minimizing risks in diverse markets. Scrap metal arbitrage involves exploiting price differences in the scrap metal industry across regions, while triangular arbitrage focuses on currency exchange rate discrepancies among three currencies in forex markets. Knowledge of these distinct mechanisms enables more precise strategy development and enhances decision-making efficiency. This expertise is vital for investors and traders seeking to capitalize on specific market inefficiencies effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Scrap Metal Arbitrage | Triangular Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying scrap metal in one market and selling it in another for profit. | Exploiting price differences between three currencies in forex markets. |
| Market | Physical commodities market. | Foreign exchange (forex) market. |
| Time Frame | Days to weeks depending on logistics. | Milliseconds to seconds due to rapid forex trading. |
| Risk Factors | Price volatility, transportation costs, regulatory restrictions. | Execution risk, transaction costs, market liquidity. |
| Required Capital | Moderate to high, including logistics and storage. | Typically high for effective arbitrage in currency markets. |
| Profit Margins | Variable; influenced by metal prices and market inefficiencies. | Low per trade but scalable with volume and speed. |
| Complexity | Moderate, involving supply chain management. | High, requiring advanced technology and algorithms. |
Which is better?
Scrap metal arbitrage exploits price differences in metal markets by buying low and selling high across various locations, benefiting from tangible assets and global demand fluctuations. Triangular arbitrage involves exploiting currency exchange rate discrepancies among three different currencies to secure risk-free profits within the forex market. Considering liquidity, risk, and market accessibility, triangular arbitrage often offers faster execution and lower capital requirements, while scrap metal arbitrage provides opportunities tied to physical commodity markets and inventory management.
Connection
Scrap metal arbitrage and triangular arbitrage both exploit price differentials across markets to generate risk-free profits, highlighting inefficiencies in the global trading system. Scrap metal arbitrage involves buying scrap metal in a low-priced market and selling it where prices are higher, while triangular arbitrage capitalizes on discrepancies in foreign exchange rates through three currency transactions. Both strategies rely on swift execution and accurate market data to capitalize on transient opportunities in commodity and currency markets.
Key Terms
Exchange rates
Triangular arbitrage exploits discrepancies in exchange rates among three different currencies to generate risk-free profits by simultaneously buying and selling these currencies in a loop. Scrap metal arbitrage involves capitalizing on price differences of metal commodities across various markets, but it is subject to physical constraints and market liquidity unlike currency arbitrage. Discover how understanding these distinctions in exchange rate dynamics can enhance your arbitrage strategy effectiveness.
Pricing inefficiencies
Triangular arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies within currency exchange rates across three different currencies to achieve risk-free profit through simultaneous trades. Scrap metal arbitrage capitalizes on price discrepancies in scrap metal markets, often driven by regional demand-supply imbalances and varying purity standards. Explore detailed strategies and market dynamics to understand how these arbitrage methods optimize profitability.
Commodities
Triangular arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between three currency pairs in the forex market, leveraging the simultaneous buying and selling of currencies to lock in risk-free profits without exposure to commodities. Scrap metal arbitrage involves capitalizing on regional price variations in recyclable metals like copper, aluminum, and steel, often factoring in transportation costs and market demand fluctuations within the commodities sector. Explore detailed strategies and market dynamics to understand how these arbitrage opportunities operate within their distinct financial landscapes.
Source and External Links
Triangular arbitrage - Wikipedia - Triangular arbitrage exploits pricing discrepancies across three currency pairs to earn risk-free profits by sequentially converting an initial currency into a second, then into a third, and finally back to the original currency.
Triangular Arbitrage Opportunity - Definition and Example - This strategy involves trading three currencies when the market exchange rate does not match the implied cross-rate, allowing traders to profit from momentary mispricings typically lasting only fractions of a second.
Triangular Arbitrage Explained | Example With Bid & Ask - YouTube - Triangular arbitrage requires identifying opportunities using bid and ask prices across three currency pairs and executing trades quickly before the market corrects the mispricing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com