Tipflation describes rising prices driven by businesses adding extra service charges or tips, increasing consumers' overall expenses. Greedflation occurs when companies hike prices beyond cost increases to maximize profits, intensifying inflationary pressures. Explore these economic phenomena to understand their impact on market dynamics and consumer behavior.
Why it is important
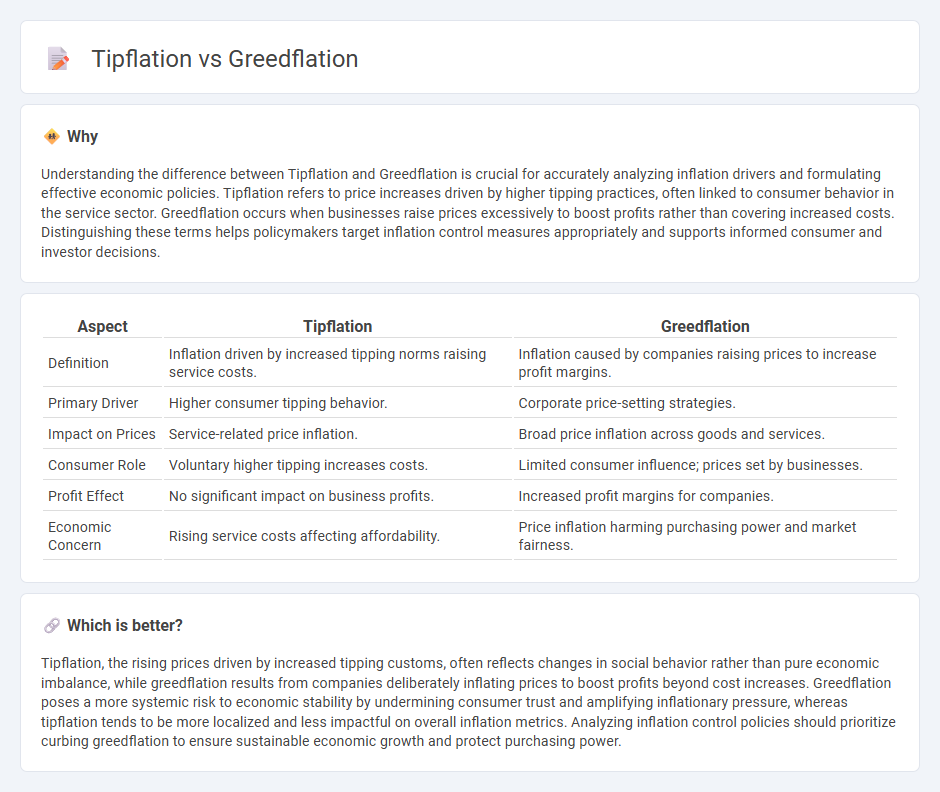
Understanding the difference between Tipflation and Greedflation is crucial for accurately analyzing inflation drivers and formulating effective economic policies. Tipflation refers to price increases driven by higher tipping practices, often linked to consumer behavior in the service sector. Greedflation occurs when businesses raise prices excessively to boost profits rather than covering increased costs. Distinguishing these terms helps policymakers target inflation control measures appropriately and supports informed consumer and investor decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tipflation | Greedflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflation driven by increased tipping norms raising service costs. | Inflation caused by companies raising prices to increase profit margins. |
| Primary Driver | Higher consumer tipping behavior. | Corporate price-setting strategies. |
| Impact on Prices | Service-related price inflation. | Broad price inflation across goods and services. |
| Consumer Role | Voluntary higher tipping increases costs. | Limited consumer influence; prices set by businesses. |
| Profit Effect | No significant impact on business profits. | Increased profit margins for companies. |
| Economic Concern | Rising service costs affecting affordability. | Price inflation harming purchasing power and market fairness. |
Which is better?
Tipflation, the rising prices driven by increased tipping customs, often reflects changes in social behavior rather than pure economic imbalance, while greedflation results from companies deliberately inflating prices to boost profits beyond cost increases. Greedflation poses a more systemic risk to economic stability by undermining consumer trust and amplifying inflationary pressure, whereas tipflation tends to be more localized and less impactful on overall inflation metrics. Analyzing inflation control policies should prioritize curbing greedflation to ensure sustainable economic growth and protect purchasing power.
Connection
Tipflation and Greedflation are interconnected economic phenomena where increased consumer tipping and corporate price hikes combine to drive overall inflation. Tipflation results from customers raising tips to compensate workers amid rising living costs, while greedflation occurs when companies exploit inflation by raising prices beyond necessary costs. Both contribute to sustained inflationary pressure, affecting purchasing power and economic stability.
Key Terms
Price Gouging
Greedflation refers to price increases driven by companies seeking higher profit margins rather than rising costs, while tipflation involves customers tipping more in response to overall inflation, indirectly affecting service prices. Both contribute to price gouging by amplifying consumer expenses beyond normal inflationary pressures. Explore our detailed analysis to understand the impact of these trends on your wallet.
Wage Stagnation
Greedflation refers to price increases driven by corporate profit-seeking amid wage stagnation, while tipflation arises from rising tipping expectations without corresponding wage growth. Both phenomena exacerbate the financial strain on workers whose wages have remained flat despite higher living costs and increased spending demands. Explore the economic impacts of greedflation and tipflation to understand their roles in today's wage stagnation challenges.
Consumer Behavior
Greedflation refers to businesses increasing prices beyond cost pressures to boost profits, while tipflation involves consumers voluntarily giving higher tips, inflating overall spending. Both phenomena reveal shifts in consumer behavior, with greedflation driven by corporate strategies and tipflation reflecting changing social norms around tipping. Explore the deeper economic impacts and behavioral trends behind these inflation dynamics to understand their effects on your spending habits.
Source and External Links
What is greedflation - and is it driving higher prices? - Greedflation refers to the idea that companies exploit inflation to generate excessive profits by keeping prices artificially high, a concept debated among economists with some arguing it is more a political meme than a primary cause of inflation.
Greedflation in the US and UK | NEB Digest - Greedflation has become a political focal point, particularly in the US where President Biden highlights corporate price gouging as a factor in inflation, while UK evidence points to corporate concentration and monopoly power as drivers of higher prices beyond traditional cost-push factors.
You Decide: Is 'Greedflation' Keeping Prices High? - Some economists dispute the greedflation theory, noting that competitive market forces and input costs explain much of the price increases, and businesses raising prices just reflect higher supplier costs rather than deliberate profit-seeking price hikes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com