The shrinking middle class has contributed to increased income inequality and economic instability, challenging the effectiveness of existing social safety nets designed to support vulnerable populations. Limited access to affordable healthcare, education, and housing exacerbates financial insecurity for many households. Explore how policy reforms and economic measures can strengthen social protection and promote economic resilience.
Why it is important
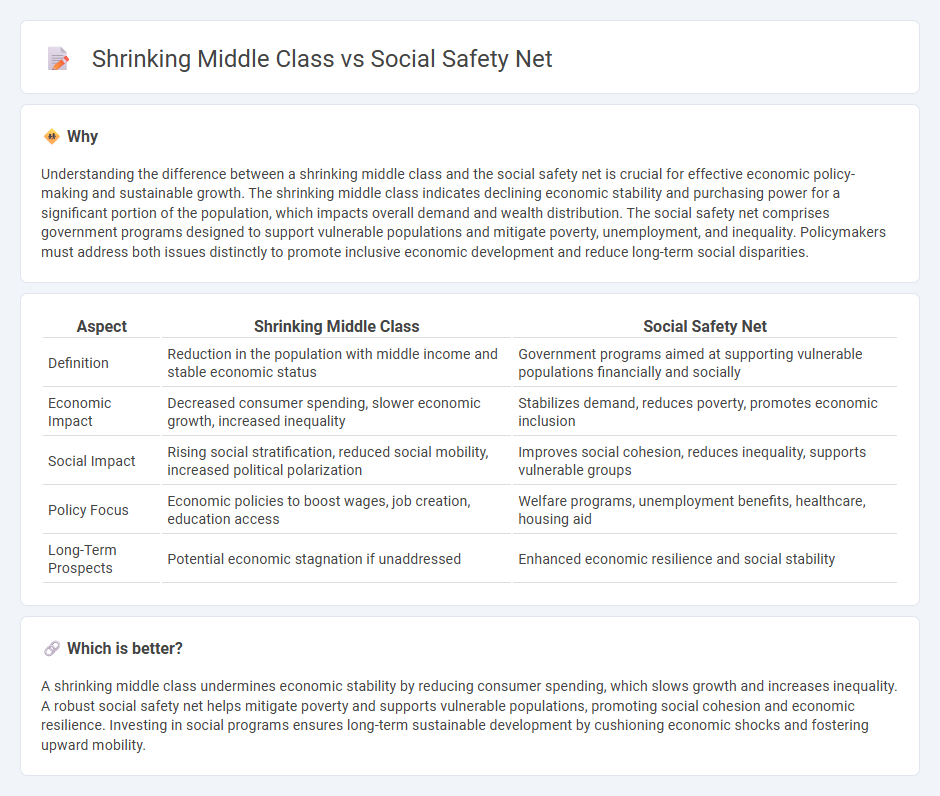
Understanding the difference between a shrinking middle class and the social safety net is crucial for effective economic policy-making and sustainable growth. The shrinking middle class indicates declining economic stability and purchasing power for a significant portion of the population, which impacts overall demand and wealth distribution. The social safety net comprises government programs designed to support vulnerable populations and mitigate poverty, unemployment, and inequality. Policymakers must address both issues distinctly to promote inclusive economic development and reduce long-term social disparities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shrinking Middle Class | Social Safety Net |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction in the population with middle income and stable economic status | Government programs aimed at supporting vulnerable populations financially and socially |
| Economic Impact | Decreased consumer spending, slower economic growth, increased inequality | Stabilizes demand, reduces poverty, promotes economic inclusion |
| Social Impact | Rising social stratification, reduced social mobility, increased political polarization | Improves social cohesion, reduces inequality, supports vulnerable groups |
| Policy Focus | Economic policies to boost wages, job creation, education access | Welfare programs, unemployment benefits, healthcare, housing aid |
| Long-Term Prospects | Potential economic stagnation if unaddressed | Enhanced economic resilience and social stability |
Which is better?
A shrinking middle class undermines economic stability by reducing consumer spending, which slows growth and increases inequality. A robust social safety net helps mitigate poverty and supports vulnerable populations, promoting social cohesion and economic resilience. Investing in social programs ensures long-term sustainable development by cushioning economic shocks and fostering upward mobility.
Connection
A shrinking middle class reduces the tax base that funds social safety net programs, leading to budget constraints and diminished support for vulnerable populations. As economic inequality grows, fewer people contribute sufficiently to social insurance systems, weakening their sustainability. This cycle exacerbates financial insecurity for lower-income groups, increasing dependence on already strained social safety nets.
Key Terms
Income Inequality
Income inequality intensifies as the middle class shrinks, undermining economic stability and social mobility. Strengthening social safety nets such as unemployment benefits, healthcare access, and affordable housing programs can mitigate the financial vulnerability faced by lower-income groups. Explore effective policy solutions to address income disparity and support a resilient middle class.
Welfare Programs
Welfare programs serve as critical components of the social safety net, aiming to provide financial assistance, healthcare access, and food security to vulnerable populations amid economic disparities. The shrinking middle class faces increased reliance on these programs due to wage stagnation and rising living costs, highlighting gaps in social equity and economic mobility. Explore how evolving welfare policies address the challenges of a diminishing middle class and strengthen social protections.
Labor Market Polarization
Labor market polarization exacerbates the shrinking middle class by increasing demand for high-skill and low-skill jobs while diminishing middle-skill employment opportunities, thereby stressing social safety nets like unemployment insurance and welfare programs. The erosion of middle-income jobs intensifies income inequality and heightens reliance on government assistance, challenging policymakers to design responsive labor market interventions. Explore how targeted social safety nets can mitigate the impacts of labor market polarization on middle-class stability.
Source and External Links
Social Safety Net - A social safety net consists of non-contributory assistance designed to improve the lives of vulnerable families and individuals experiencing poverty or destitution.
Program Participation, U.S. Social Safety Net - This webpage provides information on various U.S. social safety net programs that offer critical support to individuals during economic hardship.
Safety Nets Overview - World Bank - The World Bank supports numerous social safety net programs worldwide, helping protect families from economic shocks and crises.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com