Quiet vacationing offers employees mental rejuvenation and sustained productivity, contributing positively to overall economic stability. In contrast, job hopping can stimulate labor market dynamism and wage growth but may lead to workforce volatility and reduced long-term organizational investment. Explore the implications of these trends on economic performance and individual career development.
Why it is important
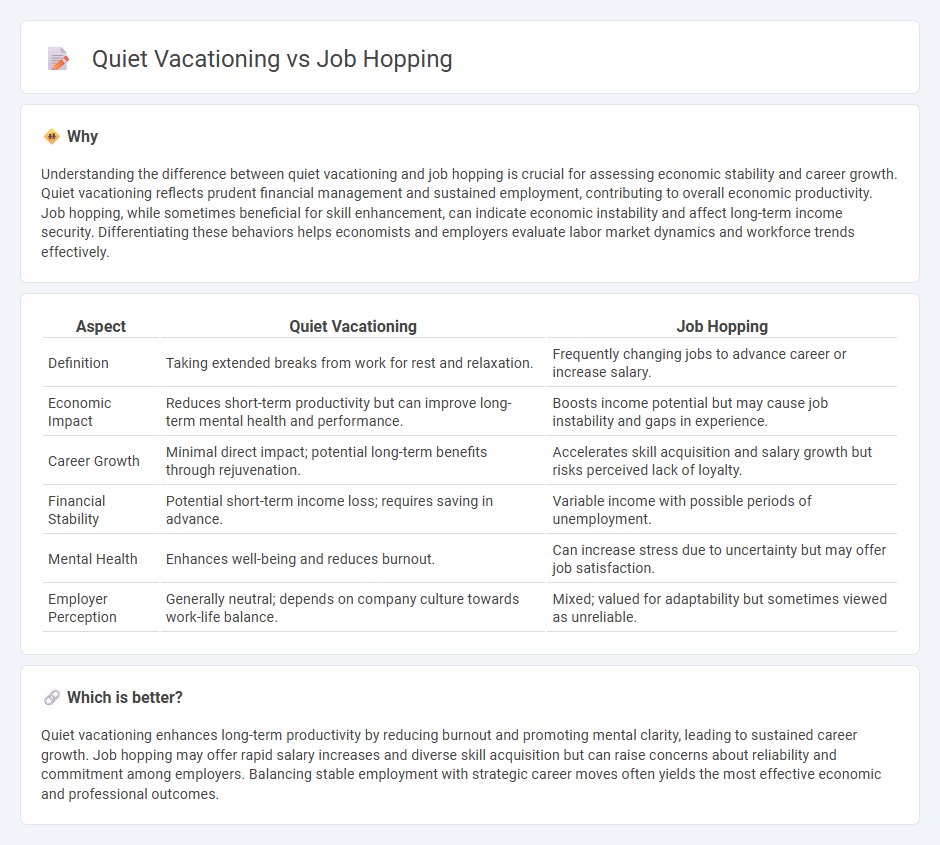
Understanding the difference between quiet vacationing and job hopping is crucial for assessing economic stability and career growth. Quiet vacationing reflects prudent financial management and sustained employment, contributing to overall economic productivity. Job hopping, while sometimes beneficial for skill enhancement, can indicate economic instability and affect long-term income security. Differentiating these behaviors helps economists and employers evaluate labor market dynamics and workforce trends effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Vacationing | Job Hopping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Taking extended breaks from work for rest and relaxation. | Frequently changing jobs to advance career or increase salary. |
| Economic Impact | Reduces short-term productivity but can improve long-term mental health and performance. | Boosts income potential but may cause job instability and gaps in experience. |
| Career Growth | Minimal direct impact; potential long-term benefits through rejuvenation. | Accelerates skill acquisition and salary growth but risks perceived lack of loyalty. |
| Financial Stability | Potential short-term income loss; requires saving in advance. | Variable income with possible periods of unemployment. |
| Mental Health | Enhances well-being and reduces burnout. | Can increase stress due to uncertainty but may offer job satisfaction. |
| Employer Perception | Generally neutral; depends on company culture towards work-life balance. | Mixed; valued for adaptability but sometimes viewed as unreliable. |
Which is better?
Quiet vacationing enhances long-term productivity by reducing burnout and promoting mental clarity, leading to sustained career growth. Job hopping may offer rapid salary increases and diverse skill acquisition but can raise concerns about reliability and commitment among employers. Balancing stable employment with strategic career moves often yields the most effective economic and professional outcomes.
Connection
Quiet vacationing promotes mental well-being and reduces burnout, enabling employees to perform better and seek new opportunities more confidently. Job hopping reflects a dynamic labor market where workers prioritize growth, skill acquisition, and work-life balance often supported by restorative breaks. Together, these trends highlight the interplay between personal well-being and career mobility in the modern economy.
Key Terms
Employee Turnover
Employee turnover significantly impacts organizational stability, with job hopping often leading to frequent departures while quiet vacationing reflects longer tenures and lower turnover rates. Companies experience higher recruitment costs and loss of institutional knowledge due to job hopping, whereas quiet vacationing fosters employee loyalty and sustained productivity. Explore deeper insights on how these behaviors influence workforce management and retention strategies.
Productivity
Job hopping can boost productivity by exposing employees to diverse skills and new challenges, leading to faster professional growth and innovation. Quiet vacationing, emphasizing rest and mental clarity, enhances long-term focus and reduces burnout, resulting in sustained high performance. Explore strategies for balancing career moves and restorative breaks to maximize your productivity potential.
Workplace Engagement
Job hopping often stimulates workplace engagement by exposing employees to diverse roles and challenges, accelerating skill development and professional growth. Quiet vacationing, characterized by taking intentional breaks without frequent job changes, supports long-term engagement by promoting mental well-being and preventing burnout. Explore deeper insights on how these strategies impact employee motivation and productivity in modern work environments.
Source and External Links
Job Hopper: definition, synonyms and explanation - HeroHunt.ai - Job hoppers are individuals who frequently change jobs, often within short periods, and may be perceived as risky hires due to their lack of long-term commitment, but can also be seen as adaptable and skilled from diverse experiences.
What Is Job Hopping? (Plus Advantages and Disadvantages) - Indeed - Job hopping is the practice of working at multiple companies over a relatively short span, a trend that has become more common and can be driven by desire for advancement, dissatisfaction, or external factors like layoffs.
Job-Hopping With Intention: Pros, Cons, and Considerations - FlexJobs - Job hopping typically means staying in a job for one to two years and can lead to faster career growth by gaining diverse skills and experiences, though some employers may still view it negatively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com