Carbon farming and reforestation are critical strategies in the global economy aimed at reducing atmospheric CO2 levels and combating climate change. Carbon farming involves agricultural practices that increase carbon capture in soil, while reforestation focuses on planting trees to absorb CO2 over time. Explore how these approaches impact economic sustainability and environmental health.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between carbon farming and reforestation is crucial for effective climate finance and sustainable investment strategies. Carbon farming involves agricultural practices that increase soil carbon sequestration, directly impacting crop yields and farmer incomes, whereas reforestation focuses on tree planting to absorb CO2 over larger ecosystems. Policymakers and investors rely on these distinctions to allocate funds correctly and measure economic returns linked to carbon credits. Clear differentiation enhances the accuracy of environmental impact assessments and supports targeted economic incentives in green markets.
Comparison Table
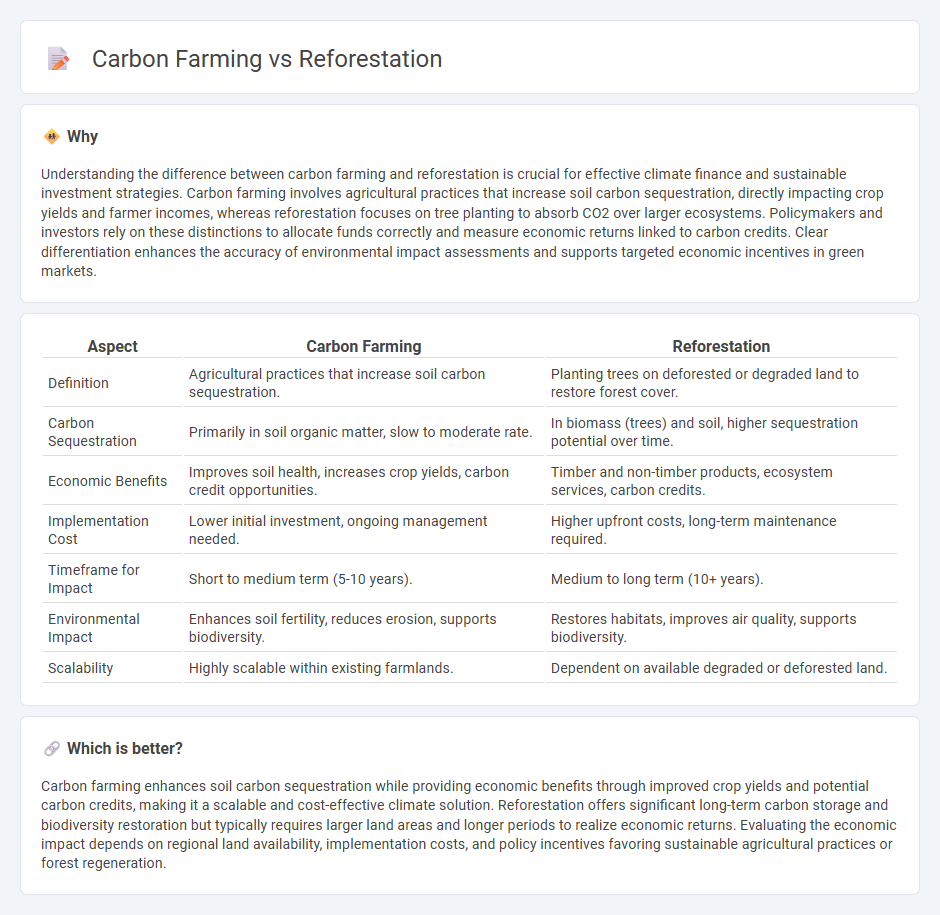
| Aspect | Carbon Farming | Reforestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agricultural practices that increase soil carbon sequestration. | Planting trees on deforested or degraded land to restore forest cover. |
| Carbon Sequestration | Primarily in soil organic matter, slow to moderate rate. | In biomass (trees) and soil, higher sequestration potential over time. |
| Economic Benefits | Improves soil health, increases crop yields, carbon credit opportunities. | Timber and non-timber products, ecosystem services, carbon credits. |
| Implementation Cost | Lower initial investment, ongoing management needed. | Higher upfront costs, long-term maintenance required. |
| Timeframe for Impact | Short to medium term (5-10 years). | Medium to long term (10+ years). |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances soil fertility, reduces erosion, supports biodiversity. | Restores habitats, improves air quality, supports biodiversity. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable within existing farmlands. | Dependent on available degraded or deforested land. |
Which is better?
Carbon farming enhances soil carbon sequestration while providing economic benefits through improved crop yields and potential carbon credits, making it a scalable and cost-effective climate solution. Reforestation offers significant long-term carbon storage and biodiversity restoration but typically requires larger land areas and longer periods to realize economic returns. Evaluating the economic impact depends on regional land availability, implementation costs, and policy incentives favoring sustainable agricultural practices or forest regeneration.
Connection
Carbon farming and reforestation are connected through their shared goal of enhancing carbon sequestration to mitigate climate change impacts. Carbon farming practices, such as agroforestry and sustainable land management, increase soil carbon storage, while reforestation directly expands forested areas that absorb atmospheric CO2. Both approaches generate economic opportunities via carbon credits and ecosystem services, aligning environmental benefits with sustainable economic growth.
Key Terms
Carbon Credits
Reforestation involves planting trees to restore ecosystems and sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide, while carbon farming employs agricultural techniques like cover cropping and soil enrichment to capture carbon in the soil. Both methods generate carbon credits by quantifying and verifying the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the atmosphere, which can then be sold in voluntary or compliance markets. Explore the detailed processes and benefits of reforestation and carbon farming to maximize your carbon credit strategies.
Ecosystem Services
Reforestation enhances ecosystem services by restoring biodiversity, improving soil health, and regulating water cycles through tree planting initiatives. Carbon farming focuses on agricultural practices that increase soil carbon sequestration and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, thereby improving soil fertility and crop resilience. Discover how both approaches contribute to sustainable ecosystems and climate mitigation strategies.
Sustainable Land Management
Reforestation involves planting trees to restore ecosystems and sequester carbon, while carbon farming employs agricultural practices that increase soil carbon storage and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Both strategies contribute significantly to Sustainable Land Management by enhancing biodiversity, improving soil health, and promoting climate resilience. Explore how integrating reforestation and carbon farming can optimize land use and environmental benefits.
Source and External Links
What is reforestation? Benefits and types - Reforestation is the recovery of forested areas through planting trees and sowing seeds, with urban and rural types focused on improving environments, reducing pollution, and supporting biodiversity and local economies.
Why Plant Trees? - Reforestation restores forest cover to improve air quality, watershed health, forest resilience, and wildlife habitats, especially after disturbances like wildfires and disease in National Forests.
Reforestation | US Forest Service - USDA - The USDA Forest Service uses reforestation through natural regeneration or tree planting to accelerate forest ecosystem recovery, enhance species diversity, and mitigate climate change impacts by sequestering carbon.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com