The Shein effect reshapes the global economy by accelerating fast fashion, driving unprecedented growth through rapid production and digital marketing strategies that challenge traditional retail models. Retail apocalypse intensifies as brick-and-mortar stores face declining foot traffic, heightened e-commerce competition, and shifting consumer preferences favoring online shopping over physical outlets. Explore how Shein's rise disrupts established retail landscapes and transforms consumer behavior worldwide.
Why it is important
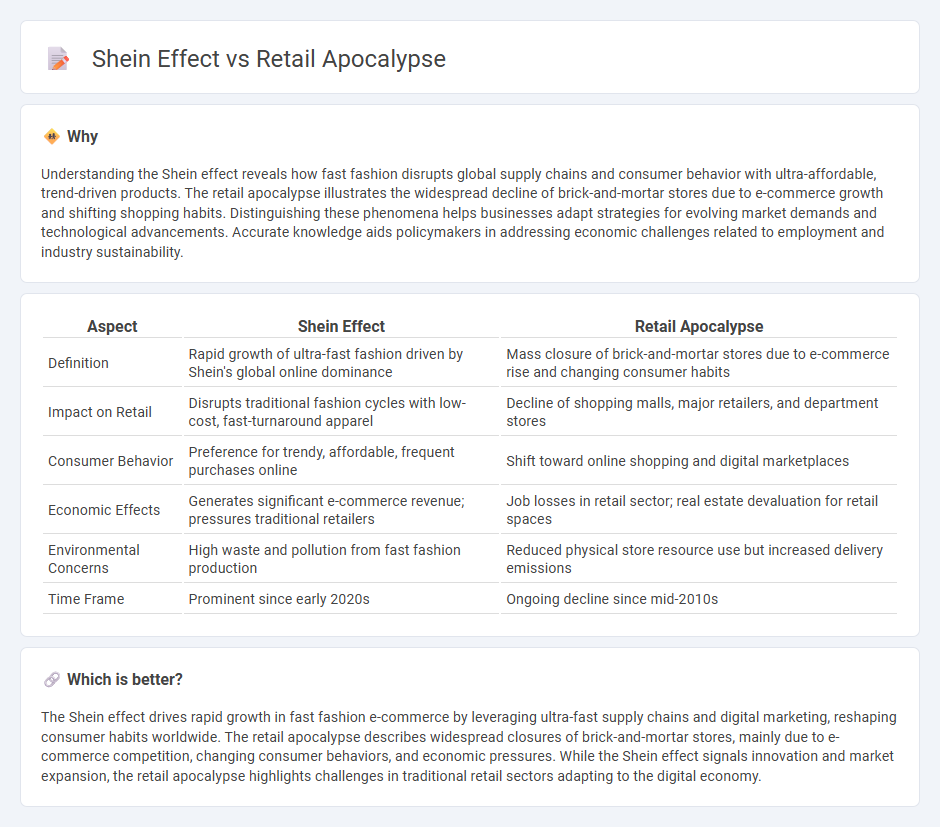
Understanding the Shein effect reveals how fast fashion disrupts global supply chains and consumer behavior with ultra-affordable, trend-driven products. The retail apocalypse illustrates the widespread decline of brick-and-mortar stores due to e-commerce growth and shifting shopping habits. Distinguishing these phenomena helps businesses adapt strategies for evolving market demands and technological advancements. Accurate knowledge aids policymakers in addressing economic challenges related to employment and industry sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shein Effect | Retail Apocalypse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid growth of ultra-fast fashion driven by Shein's global online dominance | Mass closure of brick-and-mortar stores due to e-commerce rise and changing consumer habits |
| Impact on Retail | Disrupts traditional fashion cycles with low-cost, fast-turnaround apparel | Decline of shopping malls, major retailers, and department stores |
| Consumer Behavior | Preference for trendy, affordable, frequent purchases online | Shift toward online shopping and digital marketplaces |
| Economic Effects | Generates significant e-commerce revenue; pressures traditional retailers | Job losses in retail sector; real estate devaluation for retail spaces |
| Environmental Concerns | High waste and pollution from fast fashion production | Reduced physical store resource use but increased delivery emissions |
| Time Frame | Prominent since early 2020s | Ongoing decline since mid-2010s |
Which is better?
The Shein effect drives rapid growth in fast fashion e-commerce by leveraging ultra-fast supply chains and digital marketing, reshaping consumer habits worldwide. The retail apocalypse describes widespread closures of brick-and-mortar stores, mainly due to e-commerce competition, changing consumer behaviors, and economic pressures. While the Shein effect signals innovation and market expansion, the retail apocalypse highlights challenges in traditional retail sectors adapting to the digital economy.
Connection
Shein's rapid global expansion has intensified competitive pressure on traditional retailers, accelerating the retail apocalypse by diverting consumer spending to fast fashion e-commerce. The company's data-driven supply chain and low-cost model have disrupted brick-and-mortar stores, causing widespread store closures and revenue declines. As a result, Shein exemplifies how digital-first platforms contribute to reshaping the retail economy and intensifying sectoral shifts.
Key Terms
Brick-and-mortar decline
The retail apocalypse highlights the ongoing decline of brick-and-mortar stores driven by shifts in consumer behavior and the rise of e-commerce. Shein's rapid growth and dominance in fast fashion exacerbate challenges for physical retailers by leveraging aggressive online marketing and supply chain efficiency. Explore how Shein's digital-first strategy reshapes the future of brick-and-mortar retail.
Fast fashion supply chain
The retail apocalypse, driven by declining brick-and-mortar sales, contrasts sharply with the Shein effect, which highlights the rapid growth of ultra-fast fashion supply chains emphasizing speed, agility, and low-cost production. Shein's model leverages advanced data analytics and agile manufacturing to shorten lead times from design to delivery, disrupting traditional retail models by flooding markets with frequent, trend-responsive collections. Explore how these supply chain innovations are reshaping the competitive landscape of fast fashion and retail sectors.
E-commerce disruption
The retail apocalypse, marked by widespread brick-and-mortar store closures, underscores the seismic shift driven by e-commerce giants like Shein, which thrives on ultra-fast fashion and digital-first strategies. Shein's advanced supply chain algorithms and aggressive global market penetration epitomize the disruptive force reshaping consumer habits and retail ecosystems. Explore how Shein's model is revolutionizing e-commerce and transforming the future of retail.
Source and External Links
What is Retail Apocalypse ? | Vue.ai - The retail apocalypse refers to the decline of brick-and-mortar retail in the US, driven primarily by the rapid growth of e-commerce, oversupply of malls, and shifting shopping habits towards online purchasing.
Retail apocalypse: Store closures surged 57% in 2024 - ABC 33/40 - In 2024, US store closures surged 57% to over 7,300, fueled by high inflation and competition from giants like Amazon and Walmart, including major closures from Family Dollar, Walgreens, CVS, Big Lots, and Party City.
Retail apocalypse - Wikipedia - The retail apocalypse involves widespread closures of physical retail stores in the US driven by e-commerce growth, mall oversupply, a shrinking middle class, and shifts in consumer spending preferences toward experiences over material goods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com