Global economic trends reveal a growing tension between deglobalization and open market strategies, with countries reevaluating trade dependencies and supply chains in response to geopolitical shifts and protectionist policies. While deglobalization emphasizes national sovereignty and localized production to mitigate risks, open markets promote international trade, innovation, and economic growth through interconnected economies. Explore how these divergent approaches impact global economic stability and development.
Why it is important
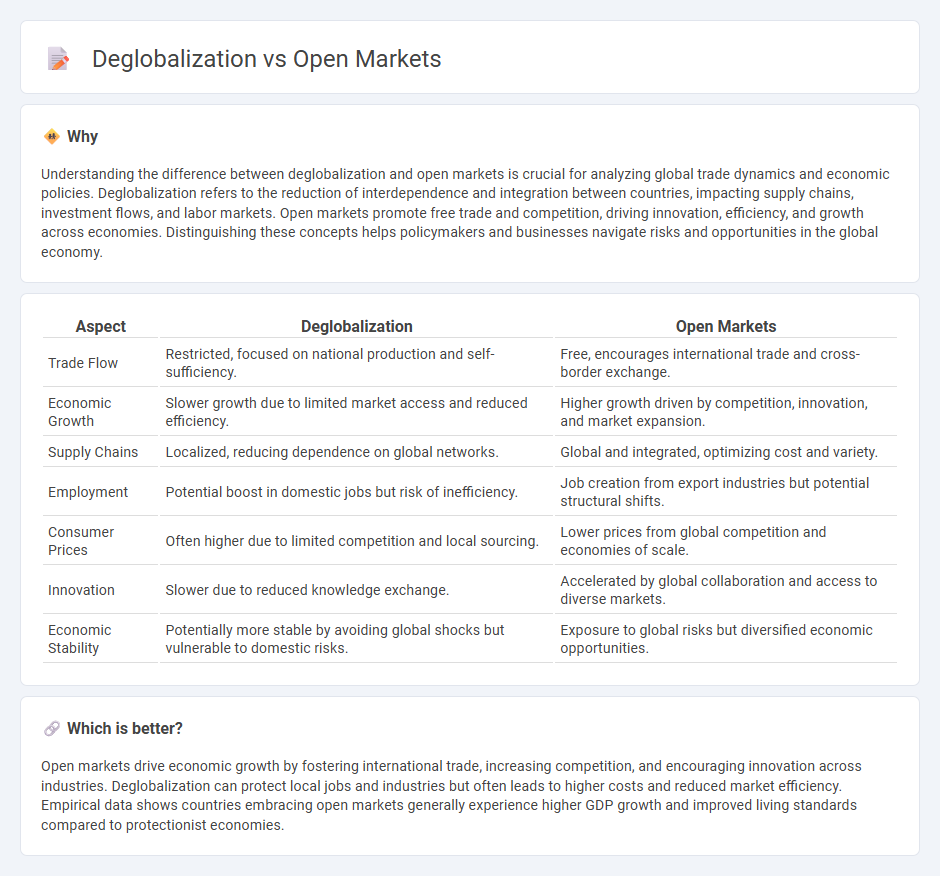
Understanding the difference between deglobalization and open markets is crucial for analyzing global trade dynamics and economic policies. Deglobalization refers to the reduction of interdependence and integration between countries, impacting supply chains, investment flows, and labor markets. Open markets promote free trade and competition, driving innovation, efficiency, and growth across economies. Distinguishing these concepts helps policymakers and businesses navigate risks and opportunities in the global economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deglobalization | Open Markets |
|---|---|---|
| Trade Flow | Restricted, focused on national production and self-sufficiency. | Free, encourages international trade and cross-border exchange. |
| Economic Growth | Slower growth due to limited market access and reduced efficiency. | Higher growth driven by competition, innovation, and market expansion. |
| Supply Chains | Localized, reducing dependence on global networks. | Global and integrated, optimizing cost and variety. |
| Employment | Potential boost in domestic jobs but risk of inefficiency. | Job creation from export industries but potential structural shifts. |
| Consumer Prices | Often higher due to limited competition and local sourcing. | Lower prices from global competition and economies of scale. |
| Innovation | Slower due to reduced knowledge exchange. | Accelerated by global collaboration and access to diverse markets. |
| Economic Stability | Potentially more stable by avoiding global shocks but vulnerable to domestic risks. | Exposure to global risks but diversified economic opportunities. |
Which is better?
Open markets drive economic growth by fostering international trade, increasing competition, and encouraging innovation across industries. Deglobalization can protect local jobs and industries but often leads to higher costs and reduced market efficiency. Empirical data shows countries embracing open markets generally experience higher GDP growth and improved living standards compared to protectionist economies.
Connection
Deglobalization challenges the expansion of open markets by promoting localized production and trade barriers, which can reduce global economic integration. Open markets rely on the free flow of goods, services, and capital across borders, fostering competitive advantages and economic growth. Shifts toward deglobalization often result in protectionist policies that disrupt supply chains and limit market access, counteracting the principles of open market economies.
Key Terms
Trade Liberalization
Trade liberalization drives economic growth by reducing tariffs, promoting free-market competition, and facilitating cross-border investment, which open markets strongly support. Deglobalization trends often lead to protectionist policies, higher trade barriers, and restricted market access, hindering efficient resource allocation and global supply chain integration. Explore how trade liberalization policies shape the balance between open markets and deglobalization to understand their impact on global economic dynamics.
Protectionism
Protectionism involves government policies such as tariffs, import quotas, and subsidies designed to shield domestic industries from foreign competition, contrasting sharply with the principles of open markets that favor free trade and minimal restrictions. The recent trend of deglobalization has amplified protectionist measures as countries seek to preserve economic sovereignty and reduce dependency on global supply chains. Explore the nuances of protectionism and its impact on global economic dynamics to understand this critical shift in international trade.
Supply Chain Resilience
Open markets enhance supply chain resilience by enabling diversified sourcing and flexible logistics, reducing dependency on single regions vulnerable to disruptions. Deglobalization triggers reshoring and regionalization trends, aiming to shorten supply chains but often increasing costs and limiting market access. Explore how balancing openness with strategic localization optimizes resilience in evolving global trade dynamics.
Source and External Links
OpenMarkets | Simplifying Healthcare Equipment Purchasing - A platform that streamlines the buying and selling of healthcare equipment and services for greater efficiency in the healthcare industry.
Open Market Definition & Operations | Study.com - In economics, an open market is characterized by free competition, prices set by supply and demand, and minimal regulatory restrictions, distinguishing it from closed markets with heavy regulations.
OPEN MARKET - A Los Angeles corner store specializing in a curated selection of natural, organic, and sustainable wines, sojus, sakes, and beers from independent producers worldwide.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com