Fragmented supply chains often result in inefficiencies and increased vulnerability due to disjointed operations and limited coordination among suppliers. Distributed supply chains enhance resilience and flexibility by leveraging multiple, geographically dispersed nodes that improve responsiveness to demand fluctuations and disruptions. Explore how the shift toward distributed supply chains is transforming global economic stability and business continuity.
Why it is important
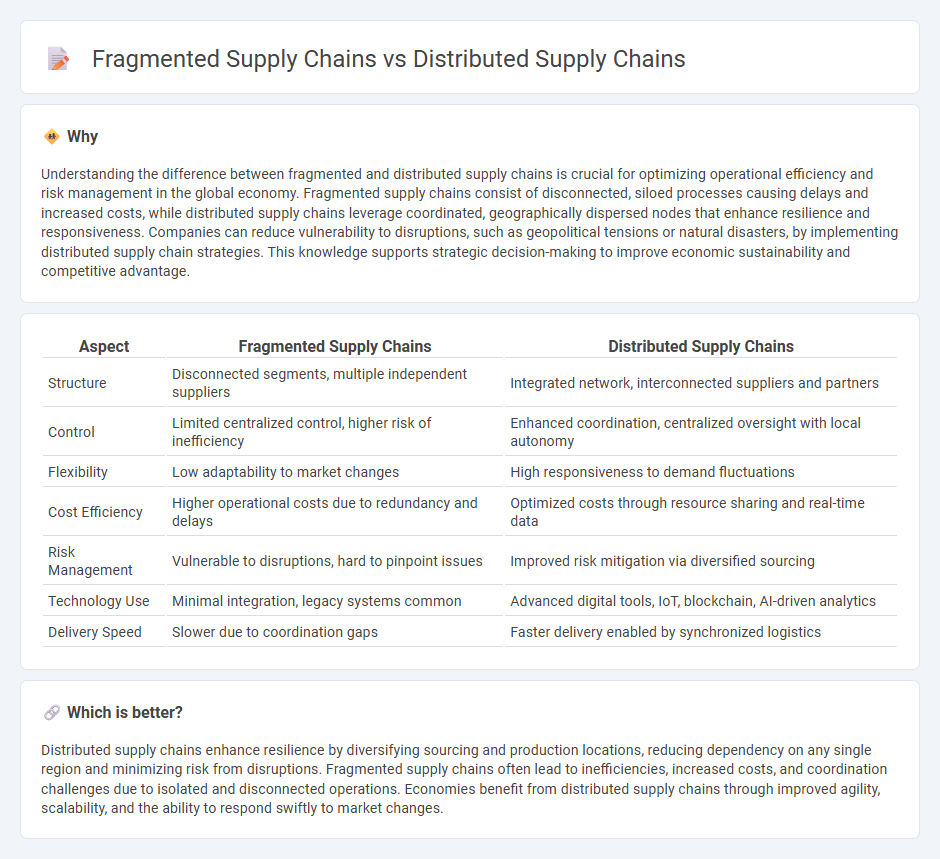
Understanding the difference between fragmented and distributed supply chains is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and risk management in the global economy. Fragmented supply chains consist of disconnected, siloed processes causing delays and increased costs, while distributed supply chains leverage coordinated, geographically dispersed nodes that enhance resilience and responsiveness. Companies can reduce vulnerability to disruptions, such as geopolitical tensions or natural disasters, by implementing distributed supply chain strategies. This knowledge supports strategic decision-making to improve economic sustainability and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fragmented Supply Chains | Distributed Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Disconnected segments, multiple independent suppliers | Integrated network, interconnected suppliers and partners |
| Control | Limited centralized control, higher risk of inefficiency | Enhanced coordination, centralized oversight with local autonomy |
| Flexibility | Low adaptability to market changes | High responsiveness to demand fluctuations |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to redundancy and delays | Optimized costs through resource sharing and real-time data |
| Risk Management | Vulnerable to disruptions, hard to pinpoint issues | Improved risk mitigation via diversified sourcing |
| Technology Use | Minimal integration, legacy systems common | Advanced digital tools, IoT, blockchain, AI-driven analytics |
| Delivery Speed | Slower due to coordination gaps | Faster delivery enabled by synchronized logistics |
Which is better?
Distributed supply chains enhance resilience by diversifying sourcing and production locations, reducing dependency on any single region and minimizing risk from disruptions. Fragmented supply chains often lead to inefficiencies, increased costs, and coordination challenges due to isolated and disconnected operations. Economies benefit from distributed supply chains through improved agility, scalability, and the ability to respond swiftly to market changes.
Connection
Fragmented supply chains consist of multiple independent entities operating in isolation, leading to inefficiencies and increased risks in production and distribution processes. Distributed supply chains, by contrast, leverage decentralized networks that enhance collaboration, flexibility, and resilience across global markets. Both models impact global trade, logistics management, and inventory optimization, influencing overall economic performance and supply chain sustainability.
Key Terms
Coordination
Distributed supply chains leverage interconnected networks of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to enhance coordination through real-time data sharing and collaborative planning. Fragmented supply chains suffer from siloed operations and poor communication, leading to inefficiencies and increased risk of delays. Explore strategies to improve supply chain coordination and optimize performance.
Visibility
Distributed supply chains leverage interconnected nodes across multiple locations to enhance end-to-end visibility, enabling real-time tracking and efficient inventory management. Fragmented supply chains often suffer from siloed data and limited transparency, leading to delayed responses and inventory discrepancies. Explore in-depth strategies to improve supply chain visibility and drive operational excellence.
Efficiency
Distributed supply chains leverage centralized coordination among multiple interconnected nodes, enhancing efficiency through real-time data sharing and streamlined operations. Fragmented supply chains, characterized by isolated and uncoordinated segments, often face inefficiencies like redundancy, delays, and higher operational costs. Explore how integrating distributed supply chain models can significantly boost overall business performance.
Source and External Links
Distribution strategies in supply chain management - Discusses how different distribution strategies, including direct and potentially distributed strategies, help improve efficiency, reduce costs, and manage delivery processes by either utilizing centralized or decentralized approaches directly from manufacturers to consumers.
Supply chain: distributed vs centralized - Explains the difference between distributed (decentralized) and centralized supply chain structures, where a distributed supply chain spreads decision-making and operations across multiple locations to enhance responsiveness and flexibility.
Supply chain - Describes supply chains as complex logistics systems that can be optimized through distributed approaches like multiple factories and warehouses to balance costs, reduce bottlenecks, and meet customer demand efficiently.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com