Onshoring involves relocating business operations to the company's home country, boosting local employment and ensuring tighter control over quality and supply chains. Offshoring shifts production or services to foreign countries to capitalize on cost reductions, skilled labor, and market expansion opportunities. Explore how these strategies impact global trade dynamics and corporate competitiveness.
Why it is important
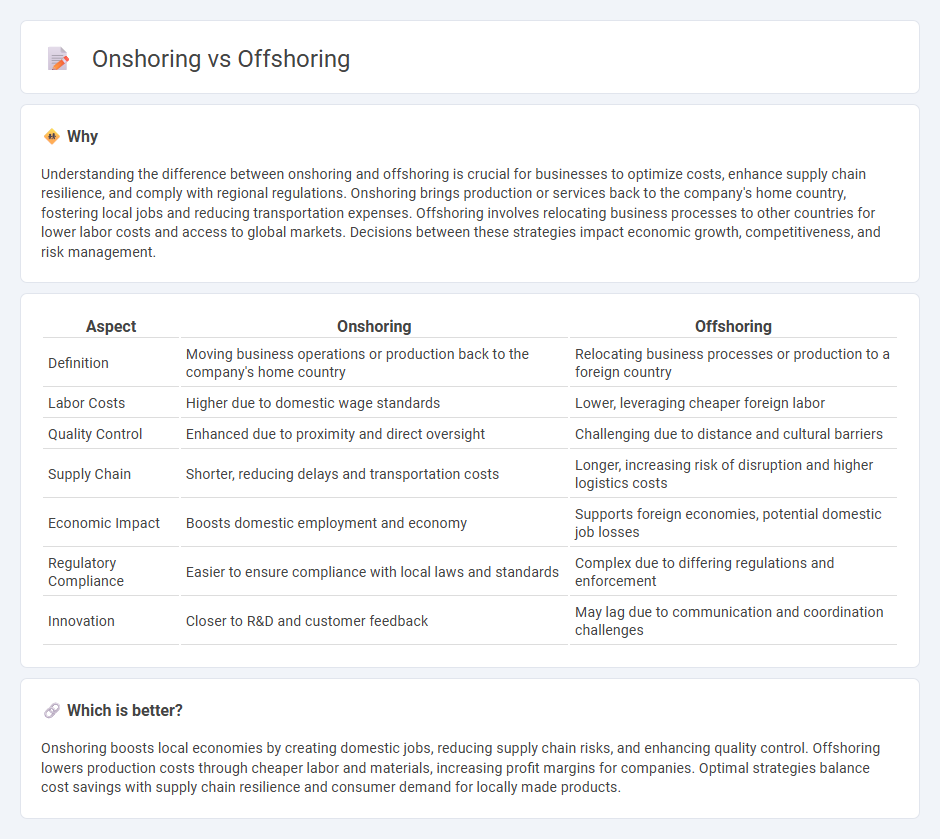
Understanding the difference between onshoring and offshoring is crucial for businesses to optimize costs, enhance supply chain resilience, and comply with regional regulations. Onshoring brings production or services back to the company's home country, fostering local jobs and reducing transportation expenses. Offshoring involves relocating business processes to other countries for lower labor costs and access to global markets. Decisions between these strategies impact economic growth, competitiveness, and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Onshoring | Offshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Moving business operations or production back to the company's home country | Relocating business processes or production to a foreign country |
| Labor Costs | Higher due to domestic wage standards | Lower, leveraging cheaper foreign labor |
| Quality Control | Enhanced due to proximity and direct oversight | Challenging due to distance and cultural barriers |
| Supply Chain | Shorter, reducing delays and transportation costs | Longer, increasing risk of disruption and higher logistics costs |
| Economic Impact | Boosts domestic employment and economy | Supports foreign economies, potential domestic job losses |
| Regulatory Compliance | Easier to ensure compliance with local laws and standards | Complex due to differing regulations and enforcement |
| Innovation | Closer to R&D and customer feedback | May lag due to communication and coordination challenges |
Which is better?
Onshoring boosts local economies by creating domestic jobs, reducing supply chain risks, and enhancing quality control. Offshoring lowers production costs through cheaper labor and materials, increasing profit margins for companies. Optimal strategies balance cost savings with supply chain resilience and consumer demand for locally made products.
Connection
Onshoring and offshoring are interconnected strategies that businesses use to optimize production costs and supply chain efficiency by relocating operations either domestically or internationally. Offshoring typically lowers labor and operational expenses by shifting processes to countries with cheaper costs, while onshoring enhances control over quality, reduces logistical risks, and supports local job markets. The dynamic balance between onshoring and offshoring decisions directly impacts global trade patterns, economic resilience, and competitive advantage in the evolving marketplace.
Key Terms
Labor Costs
Labor costs significantly differ between offshoring and onshoring, with offshoring often providing access to lower wages in countries like India, the Philippines, or Vietnam, which can reduce operational expenses substantially. Onshoring, while typically involving higher labor costs due to wages and benefits in domestic markets such as the United States or Western Europe, offers advantages like improved communication, faster turnaround times, and greater quality control. Explore detailed comparisons of labor cost impacts and strategic benefits for your business decisions.
Supply Chain
Offshoring in supply chain management involves relocating production or procurement processes to foreign countries, often to leverage lower labor costs and access global resources. Onshoring focuses on bringing these operations closer to the parent company's location to enhance control, reduce lead times, and improve supply chain responsiveness. Explore the detailed trade-offs between offshoring and onshoring to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Trade Policy
Trade policy significantly influences the decision between offshoring and onshoring by shaping tariffs, import-export regulations, and trade agreements that affect cost efficiency and market access. Countries with favorable trade policies and incentives often attract onshoring initiatives to reduce supply chain risks and leverage local production advantages. Explore detailed impacts of trade policies on global business strategies to optimize operational decisions.
Source and External Links
Offshoring - Wikipedia - Offshoring is the relocation of business processes, such as manufacturing or services, from one country to another to reduce costs, access talent, or shorten time to market, and it is distinct from outsourcing though these can overlap.
Offshoring: Definition, Overview, Pros and Cons - Velocity Global - Offshoring involves moving business operations to another country to leverage lower labor costs, gain access to specialized skills, or expand global presence, often improving efficiency and profitability.
What Is Offshoring? With Definition, Benefits and Tips | Indeed.com - Offshoring means establishing business units or functions in lower-cost countries while maintaining remaining operations at home, differing from outsourcing by the internal handling of operations without transfer to a third party.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com