Shrinkflation and product downsizing are two economic strategies companies use to cope with rising production costs without increasing retail prices. Shrinkflation reduces the quantity or size of a product while maintaining the same price, whereas product downsizing involves changing packaging or formulation to lower manufacturing expenses. Explore how these tactics impact consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Why it is important
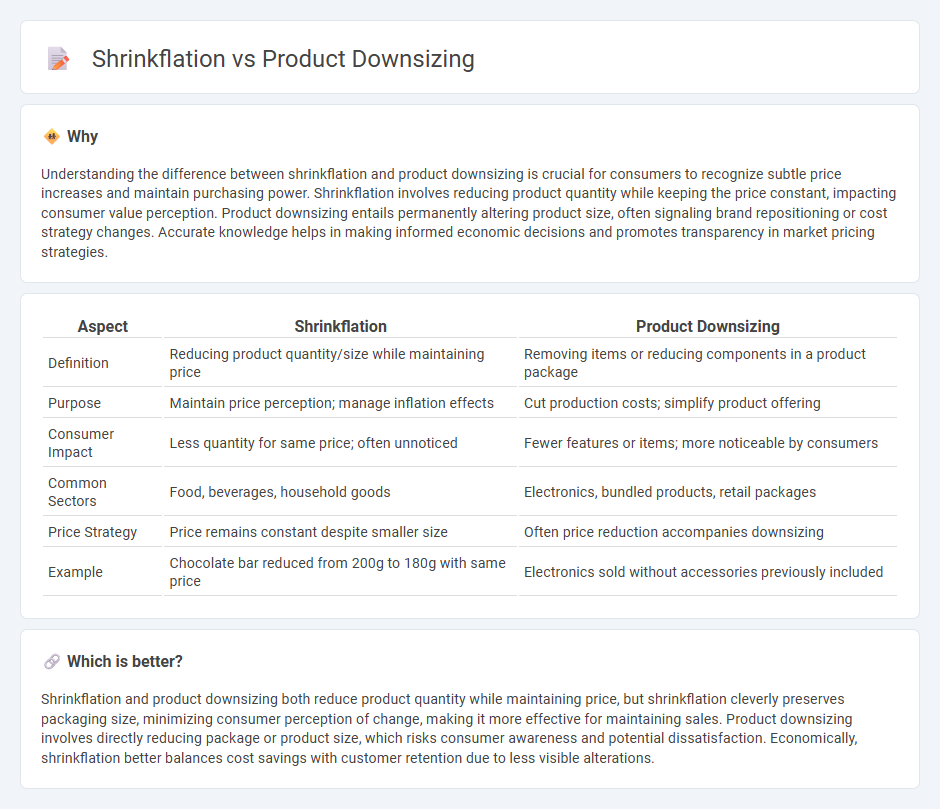
Understanding the difference between shrinkflation and product downsizing is crucial for consumers to recognize subtle price increases and maintain purchasing power. Shrinkflation involves reducing product quantity while keeping the price constant, impacting consumer value perception. Product downsizing entails permanently altering product size, often signaling brand repositioning or cost strategy changes. Accurate knowledge helps in making informed economic decisions and promotes transparency in market pricing strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shrinkflation | Product Downsizing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing product quantity/size while maintaining price | Removing items or reducing components in a product package |
| Purpose | Maintain price perception; manage inflation effects | Cut production costs; simplify product offering |
| Consumer Impact | Less quantity for same price; often unnoticed | Fewer features or items; more noticeable by consumers |
| Common Sectors | Food, beverages, household goods | Electronics, bundled products, retail packages |
| Price Strategy | Price remains constant despite smaller size | Often price reduction accompanies downsizing |
| Example | Chocolate bar reduced from 200g to 180g with same price | Electronics sold without accessories previously included |
Which is better?
Shrinkflation and product downsizing both reduce product quantity while maintaining price, but shrinkflation cleverly preserves packaging size, minimizing consumer perception of change, making it more effective for maintaining sales. Product downsizing involves directly reducing package or product size, which risks consumer awareness and potential dissatisfaction. Economically, shrinkflation better balances cost savings with customer retention due to less visible alterations.
Connection
Shrinkflation and product downsizing are interrelated strategies used by manufacturers to manage rising production costs without increasing retail prices, directly impacting consumer purchasing power. Both practices involve reducing the quantity or size of products--shrinkflation subtly decreases product volume while maintaining packaging size, whereas product downsizing explicitly reduces packaging dimensions. These cost-containment measures contribute to inflationary pressures and affect market competitiveness within the consumer goods economy.
Key Terms
Inflation
Product downsizing involves reducing the size or quantity of a product while maintaining its price, directly impacting consumer purchasing power during inflationary periods. Shrinkflation combines price increases with simultaneous size reductions, subtly eroding value without changing the upfront cost. Explore how these strategies influence inflation dynamics and their effects on consumer behavior in greater detail.
Consumer perception
Consumers often perceive downsizing as a transparent product adjustment, recognizing smaller packaging without significant price deception, while shrinkflation is viewed more negatively due to unchanged prices masking reduced quantities. Research shows increased consumer trust when companies communicate downsizing openly, contrasting with frustration and feelings of deceit linked to shrinkflation practices. Discover insights on how these perceptions influence brand loyalty and purchasing behavior.
Cost-cutting
Product downsizing involves reducing the size or quantity of a product while maintaining its original price, a direct method for cost-cutting that helps companies manage rising production expenses without raising prices. Shrinkflation refers specifically to shrinking product size or quantity subtly to decrease costs, often keeping packaging and pricing nearly identical to avoid consumer backlash. Discover more about how these strategies impact consumer perception and corporate profitability.
Source and External Links
Shrinkflation: How inflation is downsizing some of your favourite foods - Product downsizing, or shrinkflation, is a strategy where companies reduce the quantity of a product while maintaining the same price to offset rising costs, often without consumers noticing; it is legal as long as empty packaging space serves a purpose, but can lead to consumer backlash if changes are not communicated transparently.
What to Accomplish (and Avoid) When Downsizing Packages - Shrinkflation helps companies manage inflation and supply chain issues by decreasing product volume while trying to retain brand value, but risks damaging reputation if perceived as deceptive, so good packaging design and clear communication are essential.
Shrinkflation: Evidence on Product Downsizing and Consumer ... - Research shows that shrinkflation typically reduces product sizes by about 11% while increasing unit prices by 9%, and despite these changes, consumer purchase behavior remains relatively inelastic, signifying limited response to downsizing across a broad range of goods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com