Neobank stacking integrates multiple digital banking services within a single platform, offering seamless user experiences and personalized financial products. Banking-as-a-service (BaaS) enables third-party providers to build and launch banking solutions by accessing licensed banking infrastructure through APIs. Explore the differences and benefits of these innovative banking models to understand their impact on the economy.
Why it is important
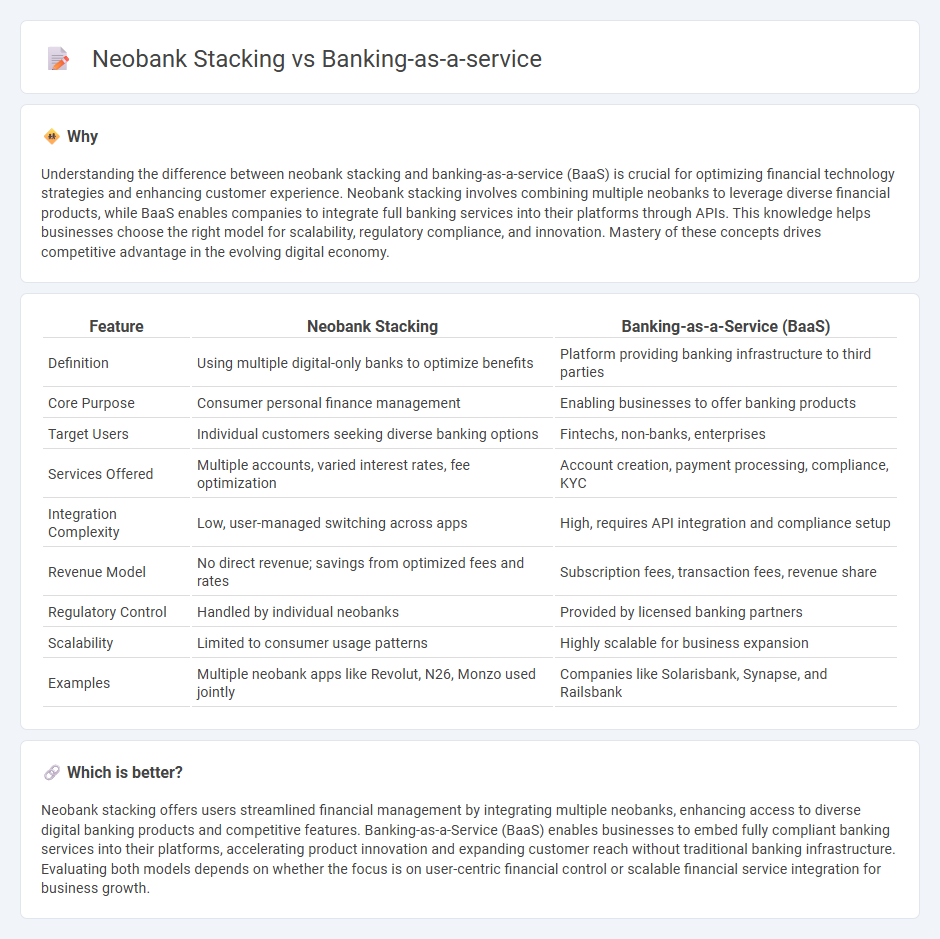
Understanding the difference between neobank stacking and banking-as-a-service (BaaS) is crucial for optimizing financial technology strategies and enhancing customer experience. Neobank stacking involves combining multiple neobanks to leverage diverse financial products, while BaaS enables companies to integrate full banking services into their platforms through APIs. This knowledge helps businesses choose the right model for scalability, regulatory compliance, and innovation. Mastery of these concepts drives competitive advantage in the evolving digital economy.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neobank Stacking | Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using multiple digital-only banks to optimize benefits | Platform providing banking infrastructure to third parties |
| Core Purpose | Consumer personal finance management | Enabling businesses to offer banking products |
| Target Users | Individual customers seeking diverse banking options | Fintechs, non-banks, enterprises |
| Services Offered | Multiple accounts, varied interest rates, fee optimization | Account creation, payment processing, compliance, KYC |
| Integration Complexity | Low, user-managed switching across apps | High, requires API integration and compliance setup |
| Revenue Model | No direct revenue; savings from optimized fees and rates | Subscription fees, transaction fees, revenue share |
| Regulatory Control | Handled by individual neobanks | Provided by licensed banking partners |
| Scalability | Limited to consumer usage patterns | Highly scalable for business expansion |
| Examples | Multiple neobank apps like Revolut, N26, Monzo used jointly | Companies like Solarisbank, Synapse, and Railsbank |
Which is better?
Neobank stacking offers users streamlined financial management by integrating multiple neobanks, enhancing access to diverse digital banking products and competitive features. Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) enables businesses to embed fully compliant banking services into their platforms, accelerating product innovation and expanding customer reach without traditional banking infrastructure. Evaluating both models depends on whether the focus is on user-centric financial control or scalable financial service integration for business growth.
Connection
Neobank stacking leverages banking-as-a-service (BaaS) platforms to integrate multiple neobank services onto a single digital interface, enhancing customer access to diverse financial products. BaaS enables neobanks to offer customized banking solutions by providing API-driven infrastructure that supports seamless third-party service integration. This synergy drives innovation, reduces operational costs, and accelerates the deployment of comprehensive digital banking ecosystems.
Key Terms
API Integration
API integration in banking-as-a-service (BaaS) platforms empowers businesses to embed comprehensive financial services directly into their applications, enabling seamless access to banking functionalities. Neobank stacking leverages multiple specialized neobanks through APIs to offer a diversified suite of financial products, enhancing user experience by combining strengths from various providers. Explore the nuances of API integration in BaaS versus neobank stacking to optimize your fintech strategy.
Regulatory Compliance
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms provide regulated banking infrastructure to third parties, ensuring adherence to strict regulatory standards such as KYC, AML, and GDPR compliance. Neobank stacking relies on integrating multiple specialized fintech services, which may pose complex regulatory challenges due to fragmented compliance responsibilities. Explore the compliance nuances between BaaS and neobank stacking to optimize regulatory adherence in fintech innovation.
White-Label Solutions
White-label solutions in banking-as-a-service (BaaS) enable fintech companies to offer fully branded financial products by leveraging established banking infrastructure, reducing time-to-market and compliance burdens. Neobank stacking often combines multiple neobanks' services to provide diversified features but typically relies on existing user interfaces without full backend integration. Explore how white-label BaaS can transform your financial service offerings with seamless customization and scalability.
Source and External Links
Banking As a Service (BaaS) Explained & Industry Outlook - Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms enable third parties to develop new banking products by opening banks' APIs, allowing fintechs or digital banks to offer white-label banking and create new revenue streams through subscription or per-service fees.
Banking as a Service (BaaS): What It Is + Examples - BaaS allows non-bank businesses to offer tailored financial products by integrating licensed banks' infrastructure via APIs, enabling fintechs and enterprises to provide embedded financial services such as digital wallets and lending solutions under their own brand.
A Primer on Banking-as-a-Service - BaaS helps licensed banks and fintechs deliver banking products to customers through third-party platforms, lowering customer acquisition costs, monetizing existing infrastructure, and reducing IT spending by outsourcing core banking infrastructure through APIs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com