Soft saving focuses on gradually setting aside small amounts of money regularly to build financial security, emphasizing low risk and liquidity. Soft investing involves allocating moderate funds into low-volatility assets aimed at steady growth while minimizing potential losses. Explore more about how balancing soft saving and soft investing strategies can enhance your financial stability.
Why it is important
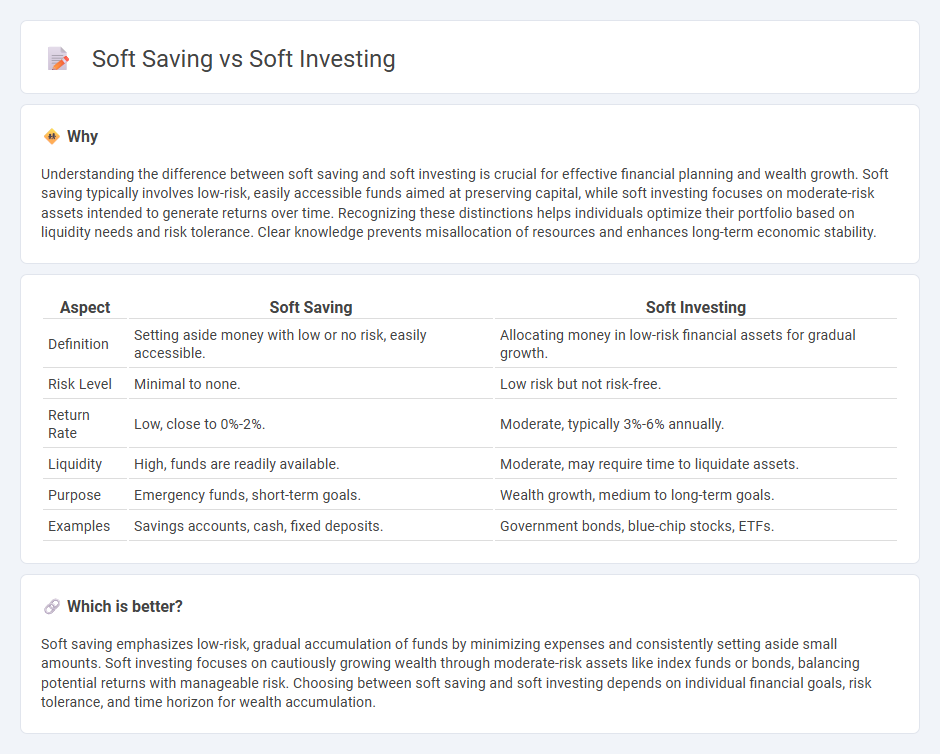
Understanding the difference between soft saving and soft investing is crucial for effective financial planning and wealth growth. Soft saving typically involves low-risk, easily accessible funds aimed at preserving capital, while soft investing focuses on moderate-risk assets intended to generate returns over time. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals optimize their portfolio based on liquidity needs and risk tolerance. Clear knowledge prevents misallocation of resources and enhances long-term economic stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Saving | Soft Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Setting aside money with low or no risk, easily accessible. | Allocating money in low-risk financial assets for gradual growth. |
| Risk Level | Minimal to none. | Low risk but not risk-free. |
| Return Rate | Low, close to 0%-2%. | Moderate, typically 3%-6% annually. |
| Liquidity | High, funds are readily available. | Moderate, may require time to liquidate assets. |
| Purpose | Emergency funds, short-term goals. | Wealth growth, medium to long-term goals. |
| Examples | Savings accounts, cash, fixed deposits. | Government bonds, blue-chip stocks, ETFs. |
Which is better?
Soft saving emphasizes low-risk, gradual accumulation of funds by minimizing expenses and consistently setting aside small amounts. Soft investing focuses on cautiously growing wealth through moderate-risk assets like index funds or bonds, balancing potential returns with manageable risk. Choosing between soft saving and soft investing depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon for wealth accumulation.
Connection
Soft saving focuses on small, consistent contributions to savings accounts or low-risk funds, creating a steady financial cushion. Soft investing complements this approach by channeling manageable amounts into diversified, low-volatility assets like bonds or index funds, balancing growth potential with risk. Together, they form a prudent financial strategy that emphasizes gradual wealth accumulation while maintaining liquidity and minimizing exposure to market fluctuations.
Key Terms
Risk Tolerance
Soft investing involves moderate risk through diversified assets to achieve growth while preserving capital, appealing to individuals with balanced risk tolerance. Soft saving emphasizes low-risk, liquidity-focused strategies such as high-yield savings accounts or certificates of deposit, ideal for conservative risk preferences. Explore in-depth comparisons to align your financial approach with your personal risk tolerance.
Liquidity
Soft investing prioritizes maintaining high liquidity by favoring assets like money market funds and short-term bonds that can be quickly converted to cash without significant loss of value. Soft saving emphasizes accessible cash reserves, typically in savings accounts or certificates of deposit, which offer easy withdrawal but lower returns compared to investment vehicles. Explore more to understand which strategy effectively balances liquidity and growth for your financial goals.
Return on Investment
Soft investing emphasizes moderate-risk assets with steady returns, aiming to balance growth and security, while soft saving prioritizes liquidity and minimal risk, often yielding lower returns. Return on Investment (ROI) in soft investing typically surpasses that of soft saving due to strategic asset allocation in bonds, dividend stocks, or mutual funds. Explore detailed comparisons and strategies to maximize ROI in your financial planning.
Source and External Links
Equity Market-Neutral Investing: More Than One Type of Catalyst - Soft investing in this context refers to "soft-catalyst investing," a strategy that involves more intensive research and creativity than hard-catalyst investing, aiming for less crowded, differentiated investment ideas with effective hedging to reduce unwanted market exposures, though it typically has a lumpier return profile due to less consensus about the catalysts.
Soft dollar - Wikipedia - Soft dollars are a financial industry practice where investment managers use commissions generated from client transactions to obtain brokerage services or research, instead of paying direct hard cash for those services, often governed by regulations like Section 28(e) of the Securities Exchange Act.
Understanding Structured Notes: Soft (Barrier) Protection - In structured notes, soft (barrier) protection refers to a feature that absorbs an underlier's negative returns up to a certain protection level, reducing the potential loss while allowing for upside gains, thus mitigating risk in volatile markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com