Slowbalization marks a shift from rapid global integration to more cautious economic interdependence, impacting trade flows and supply chain structures worldwide. Regionalization emphasizes strengthening economic ties within specific geographic areas, fostering localized manufacturing and market resilience. Explore the implications of these trends on global markets and future economic strategies.
Why it is important
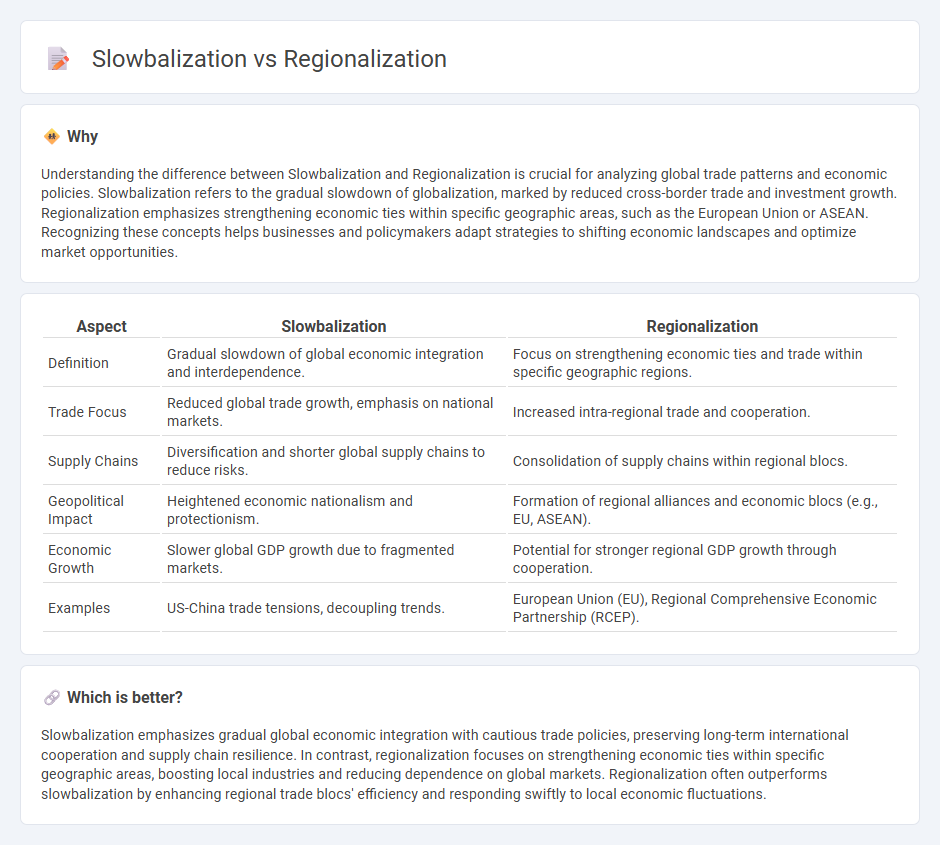
Understanding the difference between Slowbalization and Regionalization is crucial for analyzing global trade patterns and economic policies. Slowbalization refers to the gradual slowdown of globalization, marked by reduced cross-border trade and investment growth. Regionalization emphasizes strengthening economic ties within specific geographic areas, such as the European Union or ASEAN. Recognizing these concepts helps businesses and policymakers adapt strategies to shifting economic landscapes and optimize market opportunities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Slowbalization | Regionalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual slowdown of global economic integration and interdependence. | Focus on strengthening economic ties and trade within specific geographic regions. |
| Trade Focus | Reduced global trade growth, emphasis on national markets. | Increased intra-regional trade and cooperation. |
| Supply Chains | Diversification and shorter global supply chains to reduce risks. | Consolidation of supply chains within regional blocs. |
| Geopolitical Impact | Heightened economic nationalism and protectionism. | Formation of regional alliances and economic blocs (e.g., EU, ASEAN). |
| Economic Growth | Slower global GDP growth due to fragmented markets. | Potential for stronger regional GDP growth through cooperation. |
| Examples | US-China trade tensions, decoupling trends. | European Union (EU), Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). |
Which is better?
Slowbalization emphasizes gradual global economic integration with cautious trade policies, preserving long-term international cooperation and supply chain resilience. In contrast, regionalization focuses on strengthening economic ties within specific geographic areas, boosting local industries and reducing dependence on global markets. Regionalization often outperforms slowbalization by enhancing regional trade blocs' efficiency and responding swiftly to local economic fluctuations.
Connection
Slowbalization and regionalization both reflect shifts in global economic dynamics, emphasizing reduced dependence on extensive global supply chains and increased focus on local and regional markets. Slowbalization leads to deliberate deceleration of globalization processes, encouraging firms and governments to prioritize regional trade agreements, diversified supply chains, and localized production. This trend aligns with regionalization by strengthening economic integration within specific geographic areas, thereby enhancing resilience against global disruptions and fostering sustainable economic growth.
Key Terms
Supply Chains
Regionalization shifts supply chains closer to consumer markets, enhancing resilience by reducing dependency on distant suppliers and minimizing transportation costs. Slowbalization reflects a trend of decelerated global trade growth due to geopolitical tensions, trade barriers, and shifting economic priorities impacting supply chain efficiency worldwide. Explore the implications of these trends on global logistics and business strategies to optimize supply chain resilience.
Trade Blocs
Trade blocs such as the European Union, ASEAN, and the USMCA illustrate regionalization by promoting economic integration and reducing trade barriers among member countries, boosting intra-regional commerce. Slowbalization reflects a shift from globalization towards more localized supply chains and selective trade partnerships amid geopolitical tensions and pandemic-induced disruptions. Discover how these contrasting trends shape global trade dynamics and impact economic policies worldwide.
De-globalization
Regionalization emphasizes strengthening economic ties within specific geographic areas, boosting trade and investment among neighboring countries, while slowbalization reflects a gradual decline in global economic integration post-2008 financial crisis. De-globalization manifests through rising protectionism, reshoring of supply chains, and reduced cross-border capital flows, challenging the rapid globalization era. Explore the implications of these trends on global trade and international relations to understand the future of the world economy.
Source and External Links
Differentiating Region, Regionalization, and Regionalism - Consensus - Regionalization is the process of creating regions through spatial clustering, distinct from regionalism, which refers to broader integration and cooperation among regions.
Benefits of Regionalization - Rural Community Assistance Partnership - Regionalization in public services, such as water systems, involves pooling resources among neighboring entities to improve efficiency, share services, or transfer responsibilities while meeting regulatory requirements.
Regionalisation - Wikipedia - Regionalisation is the tendency to form decentralized regions, observed in various fields like geography, politics, and ecology, and can also refer to dividing a country into smaller administrative units with more local power.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com