Soft landing in the economy refers to a scenario where economic growth slows down just enough to prevent inflation without triggering a recession, achieving stability through careful policy adjustments. Normalization involves returning interest rates and economic policies to long-term averages after periods of unconventional stimulus or crisis intervention to foster sustainable growth. Explore the nuances between these economic strategies and their impact on market stability by learning more.
Why it is important
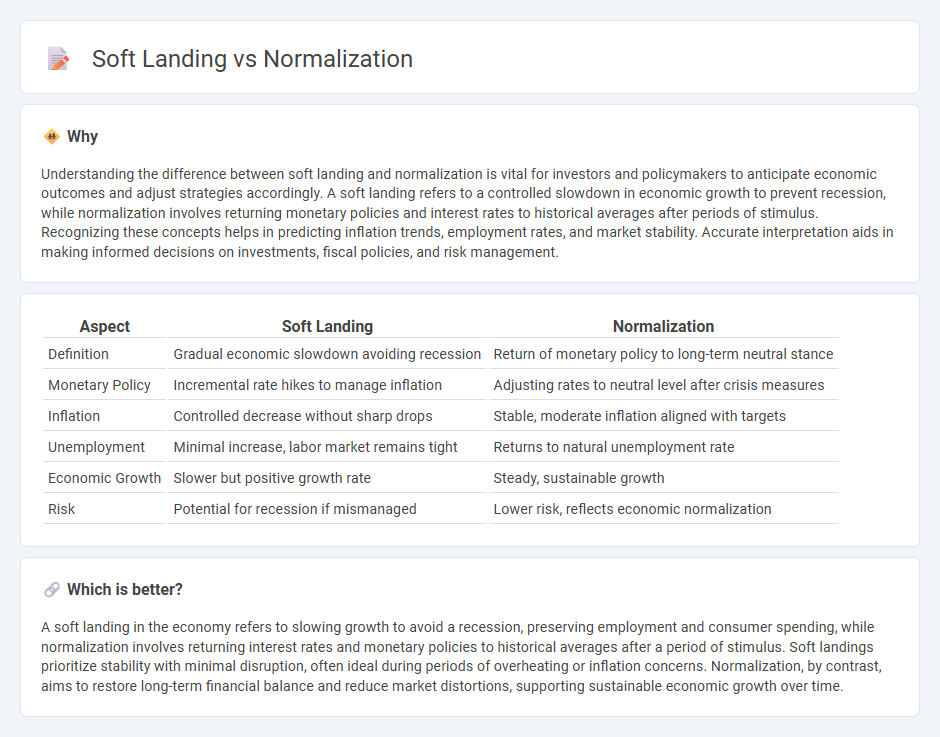
Understanding the difference between soft landing and normalization is vital for investors and policymakers to anticipate economic outcomes and adjust strategies accordingly. A soft landing refers to a controlled slowdown in economic growth to prevent recession, while normalization involves returning monetary policies and interest rates to historical averages after periods of stimulus. Recognizing these concepts helps in predicting inflation trends, employment rates, and market stability. Accurate interpretation aids in making informed decisions on investments, fiscal policies, and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Landing | Normalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual economic slowdown avoiding recession | Return of monetary policy to long-term neutral stance |
| Monetary Policy | Incremental rate hikes to manage inflation | Adjusting rates to neutral level after crisis measures |
| Inflation | Controlled decrease without sharp drops | Stable, moderate inflation aligned with targets |
| Unemployment | Minimal increase, labor market remains tight | Returns to natural unemployment rate |
| Economic Growth | Slower but positive growth rate | Steady, sustainable growth |
| Risk | Potential for recession if mismanaged | Lower risk, reflects economic normalization |
Which is better?
A soft landing in the economy refers to slowing growth to avoid a recession, preserving employment and consumer spending, while normalization involves returning interest rates and monetary policies to historical averages after a period of stimulus. Soft landings prioritize stability with minimal disruption, often ideal during periods of overheating or inflation concerns. Normalization, by contrast, aims to restore long-term financial balance and reduce market distortions, supporting sustainable economic growth over time.
Connection
Soft landing in economic terms refers to a scenario where an economy slows down just enough to curb inflation without triggering a recession, closely tied to the process of monetary policy normalization. Normalization involves central banks adjusting interest rates and reducing balance sheets to more typical levels after periods of accommodative policy, aiming to stabilize growth and inflation. Effective normalization supports a soft landing by preventing overheating while maintaining steady economic expansion.
Key Terms
Interest Rates
Normalization of interest rates involves gradually raising rates to historical averages to stabilize economic growth and inflation, while a soft landing aims to carefully adjust rates to slow the economy without triggering a recession. Central banks use normalization to signal confidence in the economy's health, whereas soft landing strategies prioritize minimizing unemployment and financial market shocks. Explore more about how interest rate policies impact global economic stability and future monetary decisions.
Inflation
Normalization refers to the process where central banks gradually increase interest rates to historic averages to control inflation without triggering recession. Soft landing describes a scenario in which inflation slows down sufficiently, allowing economic growth to continue without a sharp rise in unemployment. Explore the differences in central bank strategies to better understand their impacts on inflation dynamics.
GDP Growth
Normalization refers to central banks gradually returning interest rates to pre-crisis levels to prevent overheating, while soft landing aims to slow GDP growth just enough to avoid inflation without triggering a recession. Achieving a soft landing involves carefully managing monetary policy to sustain steady GDP growth around the economy's potential output, minimizing unemployment spikes and economic shocks. Explore detailed strategies and economic models to understand how policymakers balance these goals and impact GDP growth.
Source and External Links
Normalization (statistics) - Normalization in statistics involves adjusting values measured on different scales to a common scale, often prior to averaging, and can include methods like aligning entire probability distributions or creating normalized values for better comparison between datasets.
Normalization vs. Standardization: Key Differences Explained - Normalization broadly means adjusting data to a common scale with techniques like min-max normalization, log normalization, decimal scaling, and mean normalization to help analyze features on comparable scales.
Numerical data: Normalization | Machine Learning - Normalization transforms features to similar scales to help machine learning models train more effectively by improving convergence speed and prediction accuracy, especially when feature ranges vary widely.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com