Reshoring involves relocating manufacturing or services back to the company's home country to enhance quality control, reduce supply chain risks, and support local economies. Outsourcing transfers these activities to external firms, often in foreign countries, to benefit from lower labor costs and specialized expertise. Explore the key economic impacts and strategic considerations behind reshoring and outsourcing decisions.
Why it is important
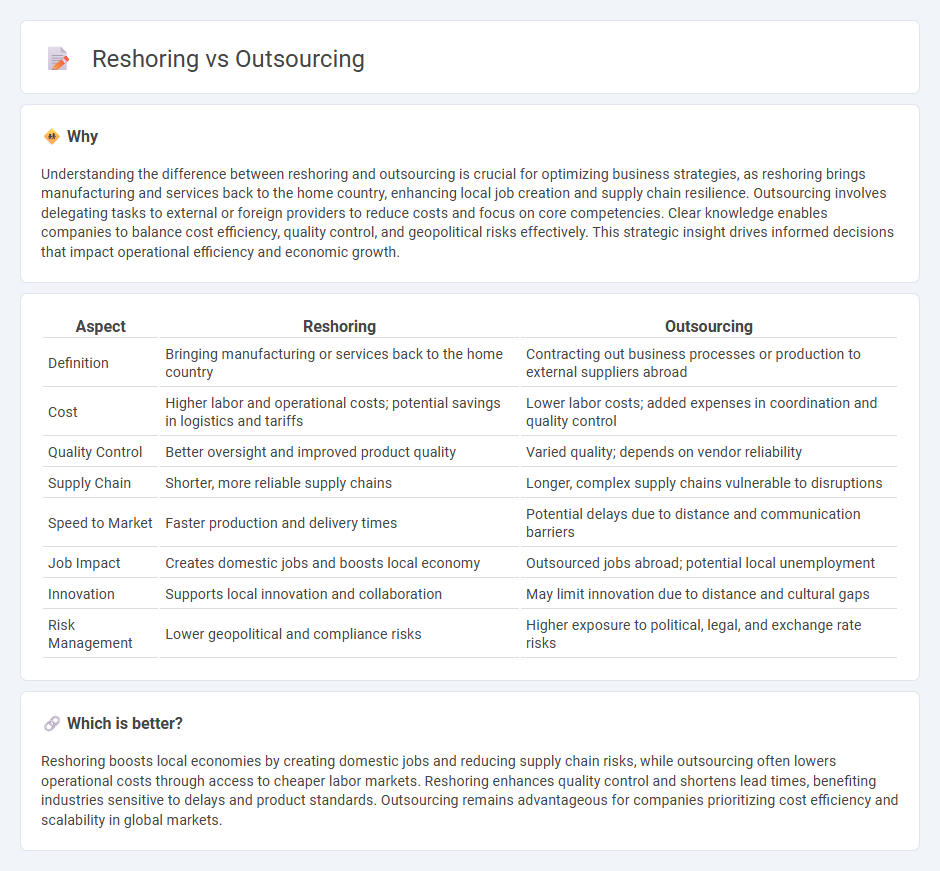
Understanding the difference between reshoring and outsourcing is crucial for optimizing business strategies, as reshoring brings manufacturing and services back to the home country, enhancing local job creation and supply chain resilience. Outsourcing involves delegating tasks to external or foreign providers to reduce costs and focus on core competencies. Clear knowledge enables companies to balance cost efficiency, quality control, and geopolitical risks effectively. This strategic insight drives informed decisions that impact operational efficiency and economic growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reshoring | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bringing manufacturing or services back to the home country | Contracting out business processes or production to external suppliers abroad |
| Cost | Higher labor and operational costs; potential savings in logistics and tariffs | Lower labor costs; added expenses in coordination and quality control |
| Quality Control | Better oversight and improved product quality | Varied quality; depends on vendor reliability |
| Supply Chain | Shorter, more reliable supply chains | Longer, complex supply chains vulnerable to disruptions |
| Speed to Market | Faster production and delivery times | Potential delays due to distance and communication barriers |
| Job Impact | Creates domestic jobs and boosts local economy | Outsourced jobs abroad; potential local unemployment |
| Innovation | Supports local innovation and collaboration | May limit innovation due to distance and cultural gaps |
| Risk Management | Lower geopolitical and compliance risks | Higher exposure to political, legal, and exchange rate risks |
Which is better?
Reshoring boosts local economies by creating domestic jobs and reducing supply chain risks, while outsourcing often lowers operational costs through access to cheaper labor markets. Reshoring enhances quality control and shortens lead times, benefiting industries sensitive to delays and product standards. Outsourcing remains advantageous for companies prioritizing cost efficiency and scalability in global markets.
Connection
Reshoring and outsourcing are interconnected strategies in global supply chain management, with reshoring involving the return of business operations to the home country and outsourcing focusing on delegating tasks to external firms, often abroad. Companies evaluate cost efficiencies, labor market conditions, and geopolitical risks to decide between reshoring and outsourcing, impacting domestic employment rates and national economic growth. Advances in technology, such as automation and digital communication, have reshaped the dynamics between reshoring and outsourcing, influencing decisions to optimize production costs and supply chain resilience.
Key Terms
Labor Costs
Labor costs significantly impact the decision between outsourcing and reshoring, with outsourcing often appealing due to lower wages in countries like India, Vietnam, or the Philippines. Reshoring, however, addresses rising offshore labor costs, quality control, and supply chain agility by bringing jobs back to higher-wage countries such as the U.S., Germany, or Japan. Explore how shifting labor cost trends influence global manufacturing strategies and business competitiveness.
Supply Chain
Outsourcing supply chain activities often reduces operational costs by leveraging global suppliers but can introduce risks such as longer lead times and less control over quality. Reshoring enhances supply chain visibility, reduces transportation expenses, and mitigates disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions or pandemics. Explore the benefits and challenges of outsourcing versus reshoring to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Domestic Production
Domestic production through reshoring enhances supply chain resilience by reducing dependency on foreign suppliers and minimizing transportation costs. Outsourcing offers cost advantages by leveraging global labor markets but may expose companies to geopolitical risks and quality control challenges. Explore more about how reshoring strategies impact competitive advantage and economic growth.
Source and External Links
What Is Outsourcing? (Including Types and Advantages) - This article discusses outsourcing as a business strategy to contract external companies for tasks, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - This resource explains outsourcing as a practice where companies hire third-party providers to handle operations or services, including IT and customer support.
What is Outsourcing? Definition, Advantages, and Examples - This article provides a definition of outsourcing, highlighting its benefits such as cost savings and access to specialized expertise.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com