De-dollarization involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in global trade and finance, aiming to enhance economic sovereignty and mitigate currency risk. A multicurrency system promotes the use of multiple national currencies for international transactions, fostering diversified economic partnerships and stability against dollar fluctuations. Explore how these strategies impact global markets and reshape international economic dynamics.
Why it is important
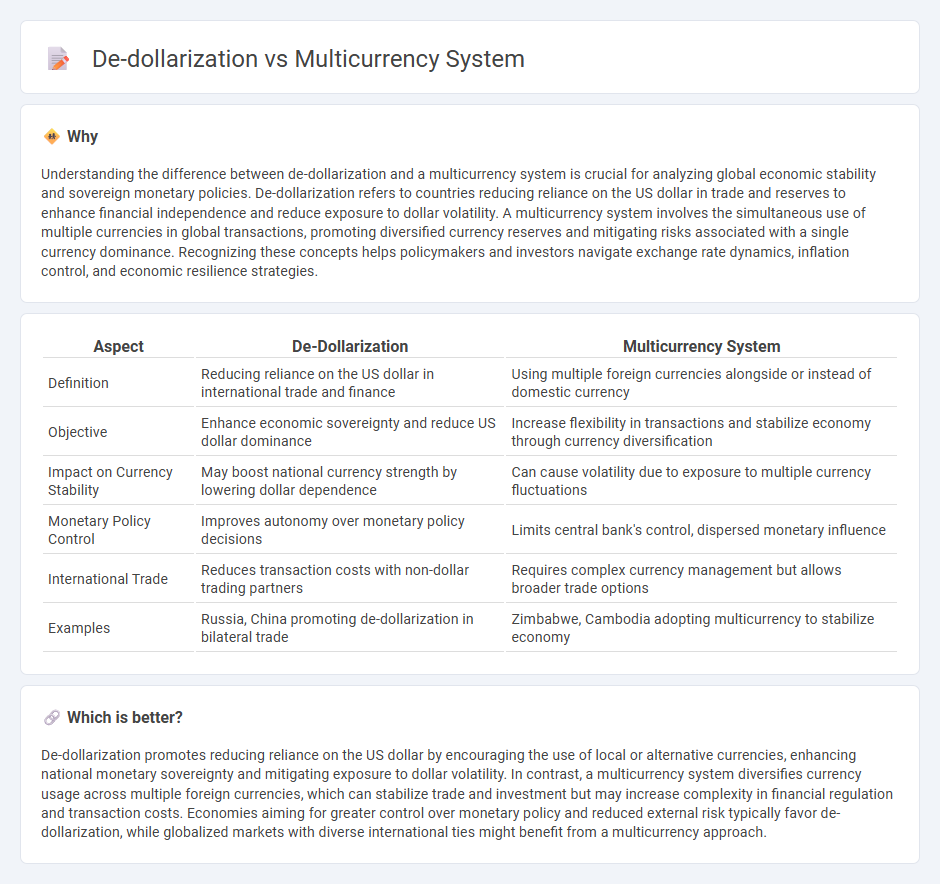
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and a multicurrency system is crucial for analyzing global economic stability and sovereign monetary policies. De-dollarization refers to countries reducing reliance on the US dollar in trade and reserves to enhance financial independence and reduce exposure to dollar volatility. A multicurrency system involves the simultaneous use of multiple currencies in global transactions, promoting diversified currency reserves and mitigating risks associated with a single currency dominance. Recognizing these concepts helps policymakers and investors navigate exchange rate dynamics, inflation control, and economic resilience strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-Dollarization | Multicurrency System |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance | Using multiple foreign currencies alongside or instead of domestic currency |
| Objective | Enhance economic sovereignty and reduce US dollar dominance | Increase flexibility in transactions and stabilize economy through currency diversification |
| Impact on Currency Stability | May boost national currency strength by lowering dollar dependence | Can cause volatility due to exposure to multiple currency fluctuations |
| Monetary Policy Control | Improves autonomy over monetary policy decisions | Limits central bank's control, dispersed monetary influence |
| International Trade | Reduces transaction costs with non-dollar trading partners | Requires complex currency management but allows broader trade options |
| Examples | Russia, China promoting de-dollarization in bilateral trade | Zimbabwe, Cambodia adopting multicurrency to stabilize economy |
Which is better?
De-dollarization promotes reducing reliance on the US dollar by encouraging the use of local or alternative currencies, enhancing national monetary sovereignty and mitigating exposure to dollar volatility. In contrast, a multicurrency system diversifies currency usage across multiple foreign currencies, which can stabilize trade and investment but may increase complexity in financial regulation and transaction costs. Economies aiming for greater control over monetary policy and reduced external risk typically favor de-dollarization, while globalized markets with diverse international ties might benefit from a multicurrency approach.
Connection
De-dollarization drives the adoption of a multicurrency system by reducing dependence on the US dollar for international trade and reserves. Countries implementing de-dollarization diversify their foreign exchange holdings and promote local or alternative currencies to stabilize their economies. This interconnected shift enhances financial sovereignty and mitigates risks associated with dollar fluctuations and sanctions.
Key Terms
Multicurrency System:
A multicurrency system allows countries to use multiple currencies for trade and reserves, reducing reliance on a single dominant currency like the US dollar. This system enhances financial flexibility, supports international trade diversity, and mitigates currency risk in global transactions. Explore deeper insights into how multicurrency systems impact global economic stability and influence strategic financial planning.
Exchange Rate Mechanisms
A multicurrency system involves the use of multiple currencies simultaneously within an economy, influencing exchange rate mechanisms by increasing complexity and requiring more flexible currency conversion frameworks. De-dollarization aims to reduce reliance on the US dollar, promoting the use of alternative currencies which can stabilize exchange rates and enhance monetary sovereignty. Explore further to understand how these strategies impact global financial stability and currency valuation.
Currency Reserves
A multicurrency system diversifies currency reserves by holding multiple foreign currencies, reducing dependency on the US dollar and mitigating exchange rate risks. De-dollarization actively shifts reserves away from the US dollar, promoting national currencies and alternative currencies such as the euro or yuan to enhance financial sovereignty. Explore how these strategies impact global currency reserves and economic stability.
Source and External Links
What is a Multi-Currency System - A multi-currency system is a financial infrastructure that enables businesses to conduct transactions, record financial data, and perform accounting functions in multiple currencies, facilitating international business operations in a single solution and managing foreign currency risk effectively.
How multicurrency ecommerce payments work - Multicurrency payments allow businesses to accept and handle money in different currencies by converting the paid amount at the transaction time, enabling buyers to pay in their local currency while sellers receive the currency they prefer.
Multicurrency management solutions - Multicurrency management involves automated liquidity solutions like multi-currency notional pools that optimize cash flow, reduce foreign exchange costs, and improve cash visibility and control for multinational corporate treasuries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com