Gigification transforms traditional labor markets by leveraging on-demand freelance work and digital platforms, enhancing flexibility and cost-efficiency for businesses. Outsourcing delegates specific tasks or services to external companies, often reducing operational expenses and focusing on core competencies. Explore the dynamic impacts of gigification and outsourcing on modern economic strategies.
Why it is important
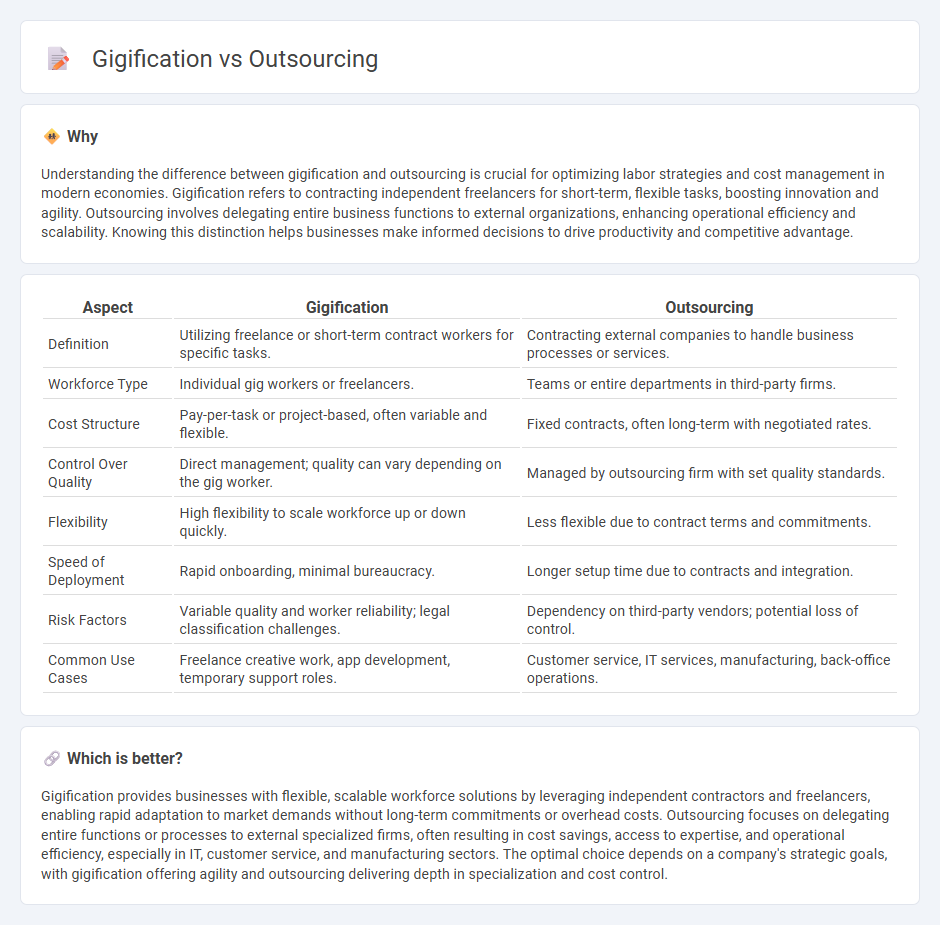
Understanding the difference between gigification and outsourcing is crucial for optimizing labor strategies and cost management in modern economies. Gigification refers to contracting independent freelancers for short-term, flexible tasks, boosting innovation and agility. Outsourcing involves delegating entire business functions to external organizations, enhancing operational efficiency and scalability. Knowing this distinction helps businesses make informed decisions to drive productivity and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gigification | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Utilizing freelance or short-term contract workers for specific tasks. | Contracting external companies to handle business processes or services. |
| Workforce Type | Individual gig workers or freelancers. | Teams or entire departments in third-party firms. |
| Cost Structure | Pay-per-task or project-based, often variable and flexible. | Fixed contracts, often long-term with negotiated rates. |
| Control Over Quality | Direct management; quality can vary depending on the gig worker. | Managed by outsourcing firm with set quality standards. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to scale workforce up or down quickly. | Less flexible due to contract terms and commitments. |
| Speed of Deployment | Rapid onboarding, minimal bureaucracy. | Longer setup time due to contracts and integration. |
| Risk Factors | Variable quality and worker reliability; legal classification challenges. | Dependency on third-party vendors; potential loss of control. |
| Common Use Cases | Freelance creative work, app development, temporary support roles. | Customer service, IT services, manufacturing, back-office operations. |
Which is better?
Gigification provides businesses with flexible, scalable workforce solutions by leveraging independent contractors and freelancers, enabling rapid adaptation to market demands without long-term commitments or overhead costs. Outsourcing focuses on delegating entire functions or processes to external specialized firms, often resulting in cost savings, access to expertise, and operational efficiency, especially in IT, customer service, and manufacturing sectors. The optimal choice depends on a company's strategic goals, with gigification offering agility and outsourcing delivering depth in specialization and cost control.
Connection
Gigification and outsourcing are interconnected through their shared focus on flexibility and cost efficiency in the modern economy. Gigification expands the labor market by enabling companies to hire freelance and contract workers on demand, while outsourcing allocates specific business functions to external service providers, often in different countries. Both practices leverage digital platforms and global talent pools to optimize operational costs and enhance scalability.
Key Terms
Labor Flexibility
Outsourcing offers businesses access to specialized skills and cost savings by delegating tasks to external providers, while gigification leverages independent contractors for short-term, flexible project work. Labor flexibility in outsourcing is structured around long-term partnerships, whereas gigification emphasizes on-demand scalability with minimal commitment. Explore the advantages and challenges of each approach to optimize workforce strategies effectively.
Cost Efficiency
Outsourcing enables companies to reduce operational costs by delegating tasks to specialized providers in lower-cost regions, optimizing resource allocation and improving profitability. Gigification, characterized by leveraging gig economy workers for short-term, flexible projects, offers cost savings through reduced employee benefits and increased scalability. Explore the detailed cost efficiency impacts of outsourcing and gigification to determine the best strategy for your business.
Employment Security
Employment security declines as gigification increases, with workers facing unstable contracts and limited benefits compared to traditional outsourcing models. Outsourcing often maintains formal employment relationships, providing more predictable income and social protections. Explore how these trends impact workforce stability and long-term career prospects.
Source and External Links
What is Outsourcing? Definition, Advantages, and Examples - Outsourcing is a business practice where a company contracts a third-party service provider to perform specific tasks or services, allowing cost savings, access to expertise, and focus on core activities while sometimes creating communication challenges and economic impacts.
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - TechTarget - Outsourcing involves hiring a third party to perform tasks or services, ranging from IT and customer support to manufacturing and HR, emphasizing relationship management and clear contractual terms.
What Is Outsourcing? (Including Types and Advantages) | Indeed.com - Outsourcing refers to hiring external companies or contractors to handle business functions for cost reduction and efficiency, including types like onshore, offshore, nearshore, and onsite outsourcing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com